Innbach
| Innbach | ||
| Data | ||
| location | Upper Austria | |
| River system | Danube | |
| Drain over | Danube → Black Sea | |
| source | in Kohlgrube 48 ° 7 ′ 17 " N , 13 ° 40 ′ 37" E |
|
| Source height | approx. 600 m above sea level A. | |
| muzzle | at Wilhering in the Danube Coordinates: 48 ° 19 ′ 16 ″ N , 14 ° 9 ′ 39 ″ E 48 ° 19 ′ 16 ″ N , 14 ° 9 ′ 39 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | approx. 250 m above sea level A. | |
| Height difference | approx. 350 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 6.6 ‰ | |
| length | 53 km | |
| Catchment area | 385.6 km² (without Aschach) | |
| Discharge at the Pichl gauge near Wels A Eo : 66.8 km² Location: 37.38 km above the mouth |
NNQ (06.04.2002) MNQ 1971–2008 MQ 1971–2008 Mq 1971–2008 MHQ 1971–2008 HHQ (31.01.1982) |
2 l / s 390 l / s 830 l / s 12.4 l / (s km²) 16.5 m³ / s 41.8 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Weinbach, Wilder Innbach, Trattnach , Polsenz , Aschach | |
| Residents in the catchment area | 26,800 (excluding Trattnach and Aschach) | |
|
Wiesmühle in Fraham |
||
|
The Innbach flows into the Danube |
||
The Innbach is a river in Upper Austria with a length of about 53 km. It rises on the edge of the Hausruck and flows into the Danube at Wilhering . Its catchment area is 386 km².
course
The Innbach rises at a height of around 600 m in the village of Kohlgrube in the municipality of Wolfsegg am Hausruck . It is mainly fed by pit water from former lignite mines. It runs largely in a northeasterly direction. After Gaspoltshofen , the Innbach passes through the communities of Meggenhofen , Kematen am Innbach , Pichl bei Wels and Wallern an der Trattnach , where the Trattnach flows into it. Shortly after Eferding , it joins the Aschach and a few kilometers later flows into the Danube below the Ottensheim-Wilhering power station on the Danube. In the past, the Innbach flowed into a tributary of the Danube near Trattwörth ( Fraham municipality ) , the confluence was relocated as part of the Aschach and Ottensheim-Wilhering power plant construction . Innbach and Aschach now flow for the last few kilometers in an artificially created channel with straight lines parallel to the Danube.
In the first 1.5 km after the source, the Innbach falls by around 100 meters in altitude, which corresponds to a gradient of 6.7%. The gradient then gradually flattens out and is only 1.7 ‰ in the lower reaches.
Tributaries
The most important feeder is the Trattnach, which at its confluence with 196.4 km² drains a much larger catchment area than the Innbach with 117.7 km². Shortly before it flows into the Danube, the Innbach takes in the Aschach, which flowed directly into the Danube until the Aschach power station was built.
Water flow
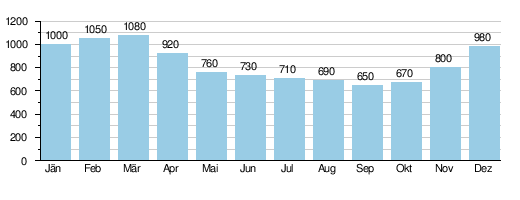
The mean discharge at the Pichl gauge near Wels is 0.83 m³ / s, which corresponds to a discharge rate of only 12.4 l / s · km². The Innbach has an extremely balanced flow regime , the maximum in March is only 1.7 times higher than the minimum in September.
Average monthly runoff of the Innbach (in l / s) at the Pichl gauge near Wels,
survey period 1971–2008, source:
use
Due to its abundant water flow, there were a large number of mills on the Innbach.
environment
Above Gaspoltshofen, the Innbach is relatively natural and richly structured, from there to the confluence of the Trattnach it is heavily regulated and straightened in places. Below, in the Eferdinger Basin , it flows again relatively naturally with meander stretches and remnants of the original alluvial forest .
The catchment area of the Innbach is used intensively for agriculture: 51% of the catchment area is arable land. As a result, and through wastewater that is only partially cleaned in sewage treatment plants, the Innbach is heavily polluted with nutrients. In the upper reaches (as of 2007) it has mostly quality class II, from the merging with the Trattnach quality class II to III.
fauna
The Innbach is populated by a variety of fish, including: brown trout , brook trout , Koppe , minnow , grayling , gudgeon , rainbow trout , chub , barbel , roach , rudd , Schneider , perch , nose , hazel , arbor , carp , bream , burbot , Pike , pikeperch and even catfish .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Office of the Upper Austrian Provincial Government (ed.): Trattnach and Innbach, investigations on water quality. Status 1992 - 1994. Water Protection Report 11/1995, Linz 1995 ( PDF; 269 MB )
- ↑ a b c Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (Ed.): Hydrographisches Jahrbuch von Österreich 2008. 116th volume. Vienna 2010, p. OG 162, PDF (10.9 MB) on bmlrt.gv.at (yearbook 2008)
- ↑ Office of the Upper Austrian Provincial Government (ed.): Pollinger Ache and Enknach and summary of the results of the Inn and Hausruck districts and their comparison with the central area, investigations on water quality. Status 1992-1995 . (Water Protection Report 12/1995, Linz 1995 ; 177 MB PDF )
- ^ Office of Upper Austria. State government: water quality maps


