Local government in Sabah
The local government in Sabah is the lowest level of government in Sabah , Malaysia . It ranks third in the Malaysian government system, after the federal and state governments. Local governments have the authority to collect property taxes, pass local laws and regulations, and issue licenses and permits for any type of business in their area. In addition, however, it is also obliged to provide basic supply facilities, to regulate waste collection and waste disposal and to guarantee city and regional planning .
The municipal constitution in Sabah is based on the Local Government Ordinance 1961 . This ordinance also regulates the responsibilities and functions of the municipal bodies . A state ministry, the Ministry of Local Government and Housing , first established after the state elections in 1963, regulates the activities of local authorities in the state of Sabah.
Basis of local administration
Sabah is divided into administrative districts. The administrative districts are composed of cities and specified areas. These administrative districts, generally referred to as LAA ( local authority area ), are classified according to the status of the administrative district of
- the "Dewan Bandaraya" or "City Hall" ,
- the "Majilis Perbandaran" or "Municipal Council" ,
- the "Majilis Daerah" or "District Council"
ruled.
This structure is based on the Local Government Ordinance 1961 . This ordinance authorizes the Yang di-Pertua Negeri by decree, among other things, to give the districts certain powers and to determine the names and boundaries of the districts. The structure of the administrative districts was first established in 1961 with this ordinance and then changed if necessary by decree (Administrative Divisions Proclamation) .
| District | Name of the local executive | put into effect | Council members | underlying decree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beaufort | Beaufort District Council | January 1, 1962 | 20th | Beaufort District Council Instrument |
| Beluran | Beluran District Council | July 1, 1968 | 11 | Labuk / Sugut District Council Instrument 1968 |
| Keningau | Keningau District Council | January 1, 1962 | 20th | Keningau District Council Instrument |
| Kota Belud | Kota Belud District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Kota Belud District Council Instrument |
| Kinabatangan | Kinabatangan District Council | July 1, 1968 | 11 | Kinabatangan District Council Instrument |
| Kota Kinabalu | Kota Kinabalu Municipal Council | 1st January 1979 | 20th | Kota Kinabalu Municipal Council Instrument 1978 |
| Kota Marudu | Kota Marudu District Council | January 1, 1983 | 18th | Kota Marudu District Council Instrument |
| Kuala Penyu | Kuala Penyu District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Kuala Penyu District Council Instrument |
| Kudat | Kudat Town Board | January 1, 1983 | 20th | Kudat Town Board Instrument 1982 |
| Kunak | Kunak District Council | June 1, 1994 | 18th | Kunak District Council Instrument 1994 |
| Lahad Datu | Lahad Datu District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Lahad Datu District Council Instrument |
| Papar | Papar District Council | January 1, 1962 | 20th | Papar District Council Instrument |
| Penampang | Penampang District Council | January 1, 1962 | 20th | Penampang District Council Instrument |
| Nabawan | Nabawan District Council | January 1, 1964 | 11 | Pensiangan District Council Instrument 1964 |
| Pitas | Pitas District Council | June 8, 2010 | 18th | Pitas District Council Instrument 2009 |
| Putatan | Putatan District Council | June 8, 2010 | 18th | Putatan District Council Instrument 2010 |
| Ranau | Ranau District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Ranau District Council Instrument |
| Sandakan | Sandakan Municipal Council | January 1, 1982 | 20th | Sandakan Municipal Council Instrument |
| Semporna | Semporna District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Semporna District Council Instrument |
| Sipitang | Sipitang District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Sipitang District Council Instrument |
| Tambunan | Tambunan District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Tambunan District Council Instrument |
| Tawau | Tawau Municipal Council | January 1, 1982 | 24 | Tawau Municipal Council Instrument |
| Tenom | Tenom District Council | January 1, 1962 | 18th | Tenom District Council Instrument |
| Tongod | Tongod District Council | |||
| Tuaran | Tuaran District Council | January 1, 1962 | 20th | Tuaran District Council Instrument 1961 |
Division into districts
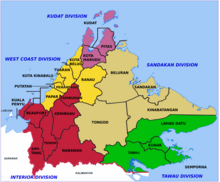
Sabah is initially divided into five administrative areas - Interior Division , West Coast Division , Kudat Division , Sandakan Division and Kudat Division . Districts are assigned to these administrative areas.
A district officer is responsible for managing a district . An Assistant District Officer is assigned to him . The administrative seat of the district is the District Office (Pejabat Daerah) .
Usually the districts are named after the largest city within the respective area or after the seat of the administration; for example, the city of Tawau is the largest city in the Tawau district and at the same time namesake of the Tawau Division .
Districts can be further divided into sub-districts (daerah kecil, lit. "small district") . These do not represent a separate administrative level, but are to be understood as an “extended arm” of the district office , which perform certain administrative tasks in the municipalities. Subdistrict status is an important step in a borough's path to full district status.
In 2012 there were 11 sub-districts in Sabah:
| Banggi | Kemabong | Matunggong | Membakut |
| Menumbok | Pagalungan | Paitan | Sook |
| Tamparuli | Telupid | Tungku |
State of administrative districts
There are three different types of administrative districts in Sabah. The lowest level of an administrative district is the district administered by a district council . Certain criteria are set for upgrading:
| Dewan Bandaraya (City Hall) |
Majilis Perbandaran (Municipal Council) |
Majilis Daerah (District Council) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| population | from 500,000 inhabitants | from 150,000 inhabitants | fewer than 150,000 inhabitants |
| Tax income | sustainable secured income of at least 100 million ringgit | sustainable secured income of at least 20 million ringgit | less than 20 million ringgits |
| Applicable to | Kota Kinabalu | Sandakan, Tawau | Beaufort, Keningau, Kinabatangan / Tongod, Kota Belud, Kota Marudu / Pitas, Kuala Penyu, Kunak, Lahad Datu, Nabawan, Papar, Penampang / Putatan, Ranau, Semporna, Sipitang, Tambunan, Tenom, Tuaran, Kudat |
The criteria for the status of an administrative district set by the Local Government Department of the State of Malaysia comprise a whole catalog of requirements. For example, Kota Kinabalu had to prove, among other things, for its status as a City Hall :
- sustainable urban development,
- the presence of an industrial center, a financial and commercial center and hotels geared towards tourism and business,
- a fully developed infrastructure including local public transport,
- a public perception of the city on a national and international level,
- a full range of educational institutions such as university, college, museum and public library,
- an international center for sporting and cultural activities and
- the organization of national and international congresses.
Others
Differences from other states
In contrast to other states in Malaysia, there is no administrative level of the mukim in Sabah . In the context of the municipal administration in Sabah, mukim are a collection of different settlements and villages, which, however, are again subject to the district offices as a whole .
Dependency relationships
In contrast to the situation in Germany, where the municipal councils always represent the citizens of the municipality, even in their different forms (communal people's representation), the members of the "City Hall" , the "Municipal Council" and the "District Council" are not democratic People elected, but are installed in their office by the Minister of State for Local Government and Housing (Ministry of Local Government and Housing) . The effectiveness of local laws and ordinances is also only established through ratification by the Minister of State.
Common abbreviations
The following abbreviations are often found in the administrative literature for Sabah:
| Abbr. | Meaning in Malay | official English expression | German translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAA | Local Authority Area | municipal administrative area | |
| DB | Dewan Bandaraya | City Hall | City Hall, City Council |
| MP | Majilis Perbandaran | Municipal Council | Municipal council |
| MD | Majilis Daerah | District Council | District council |
| LB | Lembaga Bandaran | Town Board |
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Full text of the Local Government Ordinance 1961 , last amended on May 2, 1996 in the version of July 2010; Accessed February 20, 2012
- ↑ Local Government Ordinance, No. 3
- ^ Administrative Divisions Proclamation 2009
- ↑ Beaufort District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ↑ Labuk / Sugut District Council Instrument 1968 of May 27, 1968
- ↑ Keningau District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ↑ Kota Belud District Council Instrument 1961, December 16, 1961
- ↑ Kinabatangan District Council Instrument 1961, May 27, 1968
- ^ Kota Kinabalu Municipal Council Instrument dated December 30, 1978
- ↑ Kota Marudu District Council Instrument 1983 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. dated January 27, 1983
- ^ Kuala Penyu District Council Instrument 1961, December 16, 1961
- ^ Kudat Town Board Instrument 1982, May 23, 1994
- ↑ Kunak District Council Instrument 1994 of May 23, 1994
- ^ Lahad Datu District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Papar District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Penampang District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Pensiangan District Council Instrument 1964, January 14, 1964
- ↑ Pitas District Council Instrument 2009 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. dated December 23, 2009
- ↑ Putatan District Council Instrument 2010 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. dated June 8, 2010
- ^ Ranau District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Sandakan Municipal Council Instrument, January 27, 1983
- ↑ Semporna District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Sipitang District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Tambunan District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Tawau Municipal Council Instrument of March 8, 1983
- ^ Tenom District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ^ Tuaran District Council Instrument 1961 of December 16, 1961
- ↑ Chapter 63 of the Interpretation Ordinance , amended by the Administrative Divisions Ordinance of November 1, 1954, last amended on January 1, 1979.
- ↑ Ministry for Rural Development: Senarai Pejabat Daerah Kecil ( Memento of the original from March 15, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ; Accessed July 9, 2012
- ↑ 60th State Council Meeting for Local Government (MNTK) ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , June 3, 2008, accessed February 20, 2012
- ↑ Local Government Department: Criteria Status for Local Authority ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Department of Statistics, Malaysia: Population Distribution by Local Authority Areas and Mukims, 2010 , p. 440
Remarks
- ↑ The initially obvious translations into German ("City Hall" = City Council, "Municipal Council" = Municipal Council and "District Council" = District Administrator) are deliberately not used, as they suggest that the responsibilities and structures of Sabah's local government are similar to those in Germany would be comparable. Since this is in no way the case, the terms used in the English and Malay languages have been retained as technical terms.
- ↑ By decree of December 2nd, 2004 it was ordered, among other things, that in future the word "Labuk / Sugut" should be replaced by the word "Beluran".
- ↑ By decree of December 2, 2004 it was ordered, among other things, that in future the word "Pensiangan" should be replaced by the word "Nabawan".
- ↑ around EUR 250 million
- ↑ balanced housekeeping is a requirement
- ↑ about 5 million EUR