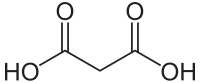
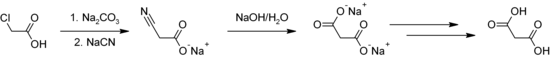Malonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Malonic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 4 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 104.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.60 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
132-135 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
Decomposition from 140 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.1 Pa (18.5 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Malonic acid (propanedioic acid ) is a dicarboxylic acid which is crystalline at room temperature and whose esters and salts are called malonates (e.g. diethyl malonate = diethyl malonate ).
History and occurrence
Malonic acid was discovered in 1858 during the oxidation of malic acid . The name is derived from the Latin malum = apple (plant genus). Malonic acid is found in sugar beet juice. Malonic acid is a cell toxin that inhibits the citrate cycle ( Krebs cycle ) by inhibiting succinate dehydrogenase .
Presentation and extraction
Malonic acid is produced, among other things, by reacting chloroacetic acid with sodium cyanide (NaCN) ( Kolbe nitrile synthesis ) and subsequent hydrolysis of the cyanoacetic acid formed.
properties
Malonic acid forms colorless and odorless crystals that have a melting point of 136 ° C and easily dissolve in water. The compound occurs in three polymorphic crystal forms. A γ form only exists at low temperatures and changes to the β form at −225.9 ° C. The phase transition from the β form to the α form takes place at 79 ° C. The forms α and β or β and γ are enantiotropic to one another. The solid decomposes above the melting point with elimination of carbon dioxide to form acetic acid . This decarboxylation takes place from 70 ° C in aqueous solution . In higher boiling solvents, such as ethylene glycol , trimethylene glycol , 1,3-butanediol and 2,3-butanediol , the reaction proceeds in excess of 100 ° C as a first-order reaction .
If malonic acid is heated with strongly dehydrating agents, e.g. B. with phosphorus pentoxide , intramolecular dehydration results in poor yields of carbon suboxide , also called malonic anhydride.
Malonic acid is a CH-acidic compound, i. This means that the electron-withdrawing effect of the two carboxy groups can easily split off a proton at the central carbon.
use
Malonic acid derivatives are the building blocks of the Knoevenagel condensation or malonic ester synthesis and are used, for example, to produce barbituric acid and its derivatives . In particular, William Henry Perkin, Jr. succeeded. for the first time a cyclopropanation by reaction of the CH-acidic malonic acid diethyl ester with 1,2-dibromoethane and two equivalents of sodium ethoxide. When mixtures of cyclic imines and malonic acid are heated , β- aminocarboxylic acids are formed . 10 to 100 tons are imported into Europe every year.
Malonate: Risk of confusion with malate and maleate
Malonate must not be confused with the acid anion of malic acid , the malate ion, or the anion of maleic acid , the maleate .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on MALONIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on July 2, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on malonic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 13, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on malonic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b chem.wisc.edu: pKa Data , Compiled by R. Williams (PDF, 78 kB).
- ↑ Malonic acid data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 10, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Nathan Weiner: Malonic acid in: Organic Syntheses . 18, 1938, p. 50, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.018.0050 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 376 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Fukai, M .; Matsuo, T .; Suga, H .: Thermodynamic properties of phase transitions in malonic acid and its deuterated analog in Thermochim. Acta 183 (1991) 215-243, doi : 10.1016 / 0040-6031 (91) 80461-Q .
- ^ Clark, LW: The Kinetics of the Decarboxylation of Malonic Acid and Other Acids in Neutral Solvents in J. Phys. Chem. 71 (1967) 2597-2601, doi : 10.1021 / j100867a031 .
- ↑ Jürgen Martens, Jürgen Kintscher and Wolfgang Arnold: Synthesis and stereochemistry of new 2-substituted 4-thiazolidinyl acetic acids, in: Tetrahedron , 1991 , 47 , pp. 7029-7036, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 96157-5 .
- ↑ Malonic acid - Substance Information - ECHA. Retrieved May 10, 2018 (UK English).
- ^ William B. Jensen: The Origin of the Names Malic, Maleic, and Malonic Acid , in: J. Chem. Educ. , 2007 , 84 , p. 924, doi : 10.1021 / ed084p924 .