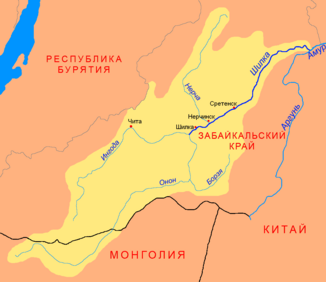
Nercha
|
Nercha Нерча |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 20030100412118100012629 | |
| location | Transbaikalia Region ( Russia ) | |
| River system | Amur | |
| Drain over | Shilka → Amur → Tatar Sound | |
| confluence | from south. and Nördl. Nercha in the Jablonowy Mountains 54 ° 35 ′ 39 ″ N , 117 ° 50 ′ 41 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 990 m | |
| muzzle |
Schilka coordinates: 51 ° 55 '1 " N , 116 ° 38' 28" E 51 ° 55 '1 " N , 116 ° 38' 28" E |
|
| Mouth height | 465 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 525 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0.91 ‰ | |
| length | 580 km | |
| Catchment area | 27,500 km² | |
| Drain |
MQ |
90 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Nerchugan | |
| Right tributaries | Akima , Uldurga | |
| Small towns | Nerchinsk | |
|
Nercha (Нерча) in the catchment area of the Shilka |
||
The Nertscha ( Russian Нерча ) is a 580 kilometer long left tributary of the Shilka in Transbaikalia ( Russia , Asia ).
course
The Nertscha arises at an altitude of about 990 m in the mountain range Oljokminski Stanowik in the northeastern part of the Jablonowy Mountains , which here represents the watershed to the Oljokma and thus the river system of the Lena , from the north Nertscha (Severnaya Nertscha) and southern Nertscha ( Yuzhnaya Nercha). Both arise at a height of about 1300 m on the western flank of the Gora Tschernyschowa mountain ( 1672 m )
The Nertscha initially turns in a south-westerly direction and flows mostly meandering in a wide valley through the low mountain ranges north of the Shilka , southeast of the main ridge of the Tscherski Mountains (not to be confused with the Tscherski Mountains of the same name in northeast Siberia). Later it turns in a more south-southeast direction, whereby the valley narrows in sections. Finally the river flows into the Amur source river Schilka at a height of 465 m .
The most important tributaries are the Nertschugan from the left and the Akima and Uldurga from the right. In its entire course, the Nercha flows through the Transbaikalia region .
Hydrography
The catchment area of the Nertscha covers 27,500 km². In the vicinity of the mouth, the river is over 200 meters wide and only a meter deep; the flow velocity is 0.5 m / s.
The nertscha freezes from October to the end of April / beginning of May, whereby it freezes to the bottom from January to April. It is flooded from May to October. The water flow near the mouth is an annual average of 90 m³ / s.
Infrastructure and economy
The Nertscha is not navigable, but was previously used for logging.
The area through which the Nertscha flows in the upper reaches is only sparsely populated; there are only a few places on the river from the middle reaches. About seven kilometers above the estuary lies the small town of Nerchinsk named after the river , one of the oldest in Transbaikalia. At the Nertscha estuary is the urban-type settlement Priiskowy , where the Priiskowaja station of the Trans-Siberian Railway is located (route km 6490 from Moscow ; from here a freight connection line leads a few kilometers beyond Nerchinsk along the Nercha). The Transsib crosses the river a few hundred meters above its confluence with the Schilka.
The area on the lower reaches is also relatively well developed by roads; Regional roads lead from Nerchinsk to Sretensk , Balei and Aginskoye . The Chita - Chernyshevsk section of the M58 Amur to Khabarovsk , part of the Trans-Siberian road connection, which has been under construction for a long time , crosses the river near the village of Snamenka , about 30 kilometers northwest of Nerchinsk.
The Nertschatal was an important gold mining area until the second half of the 20th century , but this importance has since been lost in favor of other areas of Russia.