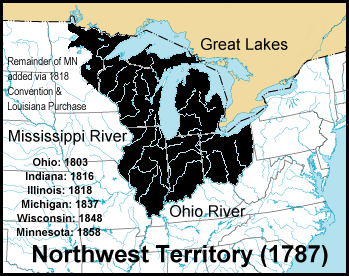
Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory , also territory north of the Ohio River , was an existing historical territory of the United States from 1787 to 1803, originally about 630,000 km² in size (for comparison: Germany has 357,000 km²), which was north of the Ohio and west of Pennsylvania .
At the time the Northwest Territory was established, the US western border was on the Mississippi .
The Northwest Territory was established by law on July 14, 1787 by the Continental Congress with the Northwest Ordinance (Northwest Ordinance) and confirmed on August 7, 1789 by the Congress of the United States with small changes. The regulation governed the administration and prepared for admission to the Union. The 13 states on the east coast, especially Massachusetts , Connecticut and Virginia , which had previously made overlapping claims west of the Appalachians , handed over sovereignty over an area northwest of the Ohio to the federal government. Among other things, the law stipulated that federal states should be formed from the territory as soon as certain requirements, especially the population, were met, and ordered the establishment of public school systems. In addition, slavery was banned in the area forever.
The states of Ohio , Indiana , Illinois , Michigan and Wisconsin as well as the part of Minnesota east of the Mississippi later emerged from the Northwest Territory .
history
In the 17th century, Europeans entered the area for the first time with French fur traders. The first records exist of the French explorer Jean Nicolet when he came to the Northwest Territory in 1634. The French set up widely spaced trading posts to control the vast area. After the French and Indian War lost , France had to cede the territory to Great Britain in the Treaty of Paris in 1763 .
During this time, the area was relatively densely populated by Indian tribes who bitterly resisted the white expansion. Therefore, the British issued a proclamation in 1763 in which European colonization west of the Appalachians was forbidden in order to appease the Indians. This proclamation caused great unrest among the white population and was one of the initiating factors of the American Revolutionary War . At the end of that war, Great Britain ceded the area north of the Ohio River and west of the Appalachians to the United States with the Treaty of Paris in 1783 . Despite the formal surrender, however, British troops remained in the area. In the Jay Treaty of 1795 it was agreed that British subjects were to leave the area, but this was never fully enforced. It was only after the war of 1812 that the Americans achieved complete sovereignty over the territory.
Several states (Virginia, Massachusetts, New York, and Connecticut) had ownership claims in the territory. Other states, like Maryland , refused to ratify the constitutional articles as long as the other states were allowed to keep their western territories. They feared that these states would grow too fast and that the balance of power within the Union would be disturbed. In order to enable ratification, the states named transferred their property claims to the federal government: New York 1780, Virginia 1784, Massachusetts and Connecticut 1784. With this, almost the entire northwestern territory became the property of the federal government. Only Virginia and Connecticut retained some land to distribute to war veterans as compensation: the Virginia Military District (17,000 km²) and the Connecticut Western Reserve (12,000 km²).
With the Land Ordinance of 1785 a standardized system was created with which the area could be measured and divided into salable plots. Ohio was an exception, which was subdivided according to different methods and thus represents a patchwork of the property division. The rest of the territory was divided into square administrative districts called townships and sections (one mile by one mile), which facilitated land sales and development.
There were initially major problems with the Indians and the British outposts, which hindered American expansion until they were defeated by American General Anthony Wayne in the Battle of Fallen Timbers in 1794 and the Treaty of Greenville sealed the peace in 1795. The Jay Treaty of 1794 temporarily improved relations with British traders in the region, as there were more British and French than Americans in the Northwest Territory by the 1780s. Renewed conflicts between the two groups sparked the war of 1812. In the Treaty of Ghent in 1814, Great Britain irrevocably ceded its claims to the Northwest Territory to the United States.
When the territory was founded, around 45,000 Indians and 2,000 fur traders lived there, mostly British and French. On April 7, 1788, the first American settlement under the new legal status was created near Marietta . Arthur St. Clair became the territory's first governor and formed a government in Marietta on July 15, 1788. On July 4, 1800, the Indiana Territory was created from the larger, western portion of the Northwest Territory; the remaining area was recognized as the US state of Ohio on March 1, 1803 , which ended the 16-year existence of the Northwest Territory.
Legislation and Government

Initially, a modified form of martial law prevailed in the territory . The governor was also the commander-in-chief of the army and embodied both the legislative and executive branches , with the Supreme Court assisting him in legislation . Once the population had grown sufficiently, county governments were established to take on local administrative and judicial functions. The first government got Washington County in 1788, with headquarters in Marietta , followed by Hamilton County in 1790, with headquarters in Cincinnati .
In 1798 the number of new citizens reached 5,000; this allowed territorial legislation and a government, as laid down in the Northwest Ordinance, to be formed. The legislature consisted of the House of Representatives and the Council of Representatives. The first house had 22 representatives, two from each county. The house then nominated ten citizens as members of the council. These proposals were submitted to the US Congress , which nominated five of them for the council assembly. The legislative body was thus formed, with the governor retaining a right of veto .
The land surveying system developed by Thomas Jefferson was first used in the Northwest Territory in 1785. The quadratic division of the country became the hallmark of the Midwest , through which sections, parishes , counties and states could be systematically planned.
In 1798 the territory was able to send a non-voting delegate to the US Congress for the first time, who was elected by the council assembly. The delegates were:
- William Henry Harrison (1799-1800)
- William McMillan (1800-1801)
- Paul Fearing (1801-1803)
Web links
- Original text from the Northwest Ordinance on Our Documents