Léman Express
| Léman Express |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
The Léman Express , or LEX for short , is the S-Bahn on Lake Geneva ( Lac Léman in French ) in the greater Geneva area . The opening of the entire network with the Cornavin – Eaux-Vives – Annemasse (CEVA) railway as the centerpiece took place on December 15, 2019. The bi-national route network in Switzerland and France is Europe's largest cross-border S-Bahn.
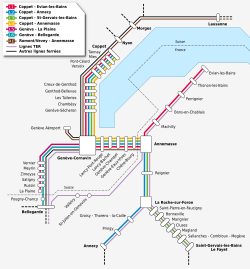
Lines and mesh
The network is 230 kilometers long and serves 45 train stations.
| line | Line route | length | Hold | Travel time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Coppet - Annemasse - Evian | 70 km | 22nd | 83 min |
| L2 | Coppet - Annemasse - Annecy | 70 km | 22nd | 100 min |
| L3 | Coppet - Annemasse - Saint-Gervais-les-Bains | 80 km | 26th | 112 min |
| L4 | Coppet - Annemasse | 30 km | 17th | 46 min |
| L5 | Geneva - La Plaine | km | 7th | 17 min |
| L6 | Geneva - Bellegarde | 40 km | 8th | 35 min |
In addition to the six lines of the Léman Express, the following lines also exist:
-
 Annemasse - Genève - Lausanne - St-Maurice
Annemasse - Genève - Lausanne - St-Maurice
TER Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
- TERGenève - Bellegarde (Ain) - Lyon-Part-Dieu
- TERGenève - Bellegarde (Ain) - Grenoble (- Valence )
- TER Annecy - La Roche-sur-Foron , (Railway d'Aix-les-Bains-Le Revard à Annemasse)
- TER Saint-Gervais-les-Bains - La Roche-sur-Foron ↔ Annemasse , ( La Roche-sur-Foron – Saint-Gervais line )
- TER Évian-les-Bains - Annemasse - Bellegarde , ( Léaz – Saint-Gingolph line and Lyon – Genève line )
In addition, the following SBB long-distance trains run between Geneva and Lausanne:
-
 1 Genève-Aéroport - Bern - Zurich HB - St. Gallen
1 Genève-Aéroport - Bern - Zurich HB - St. Gallen
-
 5 Genève-Aéroport / Lausanne - Biel / Bienne - Zurich HB (- St. Gallen )
5 Genève-Aéroport / Lausanne - Biel / Bienne - Zurich HB (- St. Gallen ) -
 15th Genève-Aéroport - Lausanne - Bern - Zofingen - Lucerne
15th Genève-Aéroport - Lausanne - Bern - Zofingen - Lucerne
-
 90 Genève-Aéroport - Lausanne - Brig
90 Genève-Aéroport - Lausanne - Brig
-
 Genève - Brig - Milano Centrale (- Venezia SL )
Genève - Brig - Milano Centrale (- Venezia SL )
On the new CEVA route, the RER-only stations will have a uniform 225-meter-long platform. This means that FLIRT compositions can run in triple traction, offering around 600 seats per train. Platforms of 320 meters will be built for the RegioExpress trains, sufficient for six-part KISS double-decker units in double traction with over 1000 seats.
history
background
The greater Geneva area has been suffering from the steadily growing cross-border commuter traffic for years. 84 percent of the 550,000 daily cross-border journeys in 2015 were made by car due to a lack of efficient public transport.
With the new Léman Express S-Bahn , Geneva’s transport system should become more efficient. The Geneva government expects a 12 to 14 percent reduction in car traffic after the opening of the Léman Express.
Pioneer Rhône Express Régional

The forerunners of the Léman Express go back to 1994. The line from Geneva to La Plaine , which has crossed the border to Bellegarde-sur-Valserine in France since September 3, 2001 , has been referred to as RER since 1994, which is interpreted here as Rhône Express Régional to differentiate itself from the Réseau Express Régional in Paris .
When the Geneva – La Plaine line was converted from the direct current system to 25 kV with 50 Hz alternating voltage in 2014 , the SBB decommissioned the Bem 550 direct current multiple units and scrapped them in 2015. Today, Stadler FLIRT two-frequency trains of the RABe 522 class operate between Geneva and La Plaine .
Construction of the centerpiece
The main problem was the eight-kilometer network gap between the Genève-La Praille and Eaux-Vives stations . This gap closure was planned at the beginning of the 20th century. Planning was only resumed in early 2000. Most of the new line had to be built underground, as it runs through built-up areas. The costs for the expansion and new construction amount to 1.567 billion francs in Switzerland and 235 million euros in France.
The new route will cut the travel time from Genève-Cornavin to Annemasse from 33 minutes to 17 minutes.
So that the trains of the Léman Express can run every quarter of an hour, two additional crossing stations had to be built in Chambésy and Mies on the single-track S-Bahn track on the Geneva – Coppet line . These extensions and the new Lancy-Pont-Rouge station went into operation on June 11, 2018 and enabled the quarter-hourly service during rush hour.
In search of a new name for the future S-Bahn network, a public Internet consultation was carried out between June 1 and June 15, 2015. The population could choose from four suggested names. The choices were: CEVA Express , Léman Express , Lémanis and Réflex . Of the nearly 7,900 votes cast, the name Léman Express was chosen with almost 41 percent of the vote.
opening
Since December 9, 2018, the lines previously known as Regio have been operated as Léman Express . Lines L1 to L4, which are to serve the new Geneva-Cornavin-Eaux Vives-Annemasse line, ended in Lancy-Pont Rouge in the south of Geneva until they were commissioned.
On December 12, 2019, the Léman Express was officially inaugurated in the presence of Federal Councilor Simonetta Sommaruga , Vaudois State Councilor Nuria Gorrite and Geneva State Councilor Serge Dal Busco. The French Transport Minister Elisabeth Borne had to cancel at short notice to attend the opening ceremony because of the strike over the planned pension reform in France.
Regular operations began on December 15th. Commissioning is massively affected by a general strike against the planned pension reform of the French government on the French side in the first month of operation. Many trains turned prematurely in Chêne-Bourg, only every second drove to Annemasse where they had to switch to replacement buses. In mid-January, operations began in French. Nevertheless, 25,000 passengers used the trains per day in the first month of operation, and up to 50,000 passengers are expected every day.
The full commissioning of the Léman Express as the backbone of public transport in the greater Geneva area is fundamentally changing what is on offer in the region. Around 50 urban and regional bus and tram lines are connected to the S-Bahn stations. In the canton of Geneva, over 80 percent of the population and around 86 percent of the jobs are less than one and a half kilometers from the nearest train station.
future
So that the Léman Express service can be expanded further, the various sub-projects of Léman 2030 between Lausanne and Geneva must first be implemented, including the planned two-lane underground station under Geneva-Cornavin station.
vehicles
The Léman Express fleet will consist of 23 FLIRT trains (RABe 522) from the Swiss manufacturer Stadler Rail and 17 Régiolis trains (Z 31500) from the French manufacturer Alstom . All 40 units are dual-frequency capable and approved both in Switzerland and France, so that transfer-free journeys between Coppet and Evian-Les Bains, Annecy, St-Gervais and Annemasse can be offered. The Léman Express fleet will have a uniform design. The trains are low-floor, air-conditioned, offer large storage areas in the first and sockets in both car classes as well as enough space for prams, bicycles and wheelchairs and a toilet suitable for the disabled.
On the Swiss side, the FLIRT multiple units were gradually put into service in 2018. The first Régiolis units were tested in the first half of 2018. They were delivered by summer 2019 with a view to the full commissioning of the system in December 2019.
SBB is financing the 23 FLIRTs with CHF 236 million. On the French side, it is the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region that finances the 17 Régiolis with up to 210 million euros.
organization
Lémanis SA is responsible for the planning and operation of the cross-border regional rail service Léman Express . Lémanis SA is also the point of contact for the authorities involved in the cantons of Geneva and Vaud , the Federal Office of Transport and the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region .
Lémanis SA, a public limited company under Swiss law , is a subsidiary of SBB and SNCF (via SNCF Mobilités) based in Geneva. The company is 60% owned by SBB and 40% by SNCF. It is not legally a railway company. For legal reasons, it has a sister company in France based in Chambéry. Lémanis SA, founded on March 15, 2017, goes back to the cooperation agreement signed between SBB and SNCF on March 9, 2017 in Paris.
On February 1, 2018, the federal government, the cantons of Geneva and Vaud and the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region signed a letter of intent for the Léman Express. This states that the four partners want to set up a single supervisory organization by 2023 at the latest, which will operate a single company. According to the letter of intent, the Lémanis should become a complete railway company as soon as possible.
View of the unions
The letter of intent offers the operator the option of “a possible tender for the Léman Express rail services on the entire territory of Switzerland and France involved at the end of the ten-year concession, with an exit clause after six years that the operator is granted on the Swiss network”. In the period 2025–2029, the network could therefore be tendered across Europe. The European Union is currently preparing for the liberalization of long-distance transport (2020) and regional transport (2026). The Swiss Transport Staff Union ( SEV) fears that these conditions will put great pressure on working conditions. The CGT Bahn , SUD Rail and the SEV have asked Lémanis for information about future working conditions.
Employment Law
For the staff the central question arises: which company will operate the network and which working conditions will apply? The first step will be the respective house rules. The operating company Lémanis is run jointly by SNCF (40%) and SBB (60%), but the train drivers only work in their own country, although they both have driving permits. This necessitates a change of engine driver in Annemasse.
See also
- S-Bahn in Switzerland
- Track 2000
- Swiss railway projects: Region Western Switzerland
- Border between France and Switzerland
Web links
- Official website of the Léman Express
- Official SBB website for the Vaud S-Bahn
- The S-Bahn systems of Switzerland (p. 24) (PDF file; 5.6 MB) ( page no longer available )
swell
- ↑ Le réseau ferroviaire transfrontalier s'appelle Léman Express In: Journal de Bâle et Genève of June 19, 2015
- ^ "Léman Express" - project of the century to relieve the streets of Geneva On: SRF from October 4, 2019
- ↑ Swiss Railway Review 11/2001: In the “Tram” across the French border
- ↑ Jean-Philippe Coppex, The history of the Rhône Express Régional RER, bilingual German / French, in: Tram Nr. 94, 2008, ISSN 1422-5344
- ↑ Timetable field 151 of the official Swiss timetable
- ↑ A waiting period of 107 years In: InfoForum 1/2017
- ↑ SNCF: Leman Express, le 1er RER transfrontalier franco-suisse
- ^ Une nouvelle gare à Lancy - Pont-Rouge: le premier pas d'une nouvelle mobilité pour Genève. December 8, 2017, accessed December 16, 2019 (French).
- ↑ Le Léman Express va se déployer peu à peu. In: 20minutes.ch. Retrieved May 16, 2018 (French).
- ↑ Le réseau ferroviaire transfrontalier s'appelle Léman Express In: Journal de Bâle et Genève of June 19, 2015
- ↑ Bernard Wuthrich: Le Léman Express, un record de complexité , article in Le Temps of December 12, 2019. Retrieved on December 13, 2019.
- ^ Opening of the Léman Express , DETEC notification dated December 12, 2019.
- ↑ Le Léman Express, marche ou grève. In: Le Temps. December 15, 2019, accessed February 1, 2020 (French).
- ↑ Le Léman Express dépasse les attentes. In: Le Temps . January 20, 2020, accessed on February 1, 2020 (French).
- ^ "Léman Express" - project of the century to relieve the streets of Geneva On: Swiss radio and television from October 4, 2019
- ↑ SBB: Léman 2030
- ^ Swiss Confederation: Underground extension of the Geneva-Cornavin train station - framework agreement signed
- ↑ Translation from: Lemanexpress.ch
- ↑ Léman Express on SBB.ch
- ↑ Top meeting SBB-SNCF in Paris: cooperation across borders. In: bahnonline.ch. March 9, 2017, accessed May 7, 2018 .
- ^ SEV: Léman Express, a Trojan horse? from July 10, 2018