Methyl isothiocyanate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
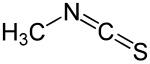
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Methyl isothiocyanate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 3 NS | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 73.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.07 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
30-34 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
117-118 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
59 hPa (40 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
79.4 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Methyl isothiocyanate ( MITC ), also called methyl mustard oil , is an organic compound that is derived from isothiocyanates , the salts or esters of isothiocyanic acid . It is isomeric to methyl thiocyanate .
Occurrence
MITC is a component of mustard oils and occurs in small amounts in capers , for example .
properties
Like other isothiocyanates, MITC smells like horseradish . It is a strong irritant to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract, and can cause pneumonia and kidney damage . MITC already melts at 35 ° C. The substance is sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and other organic solvents . It is unstable, reactive and sensitive to light and oxygen . Methyl isothiocyanate has a corrosive effect on metals such as zinc , iron and others . In alkaline media there is rapid hydrolysis , in acidic or neutral media it is slow.
use
Methyl isothiocyanate is a pesticide and is preferably used to combat free-living nematodes , root knuckle nebulas and carbohydrates , as well as against root rot and grubs and the like. It is used as a soil disinfectant and acts as a fungicide , nematicide and also as a herbicide .
Many commercial crop protection products do not contain methyl isothiocyanate itself, but rather compounds which only decompose to methyl isothiocyanate when applied. For example, contains Basamid ® of the company BASF the active ingredient dazomet (thiadiazine). In a moist environment it breaks down into formaldehyde , carbon disulfide and methyl isothiocyanate. Most dithiocarbamates , such as B. Metam-sodium break down into methyl isothiocyanate.
safety instructions
Methyl isothiocyanate is considered to be highly hazardous to water (class 3) and is not biodegradable, but degrades in moist soil within several weeks. It is highly toxic to fish. The concentration in drinking water should not exceed 0.1 µg · l −1 , in running waters not 0.5 µg · l −1 . The detection limit is 0.05 µg · l −1 .
The UN number of methyl isothiocyanate is 2477 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on methyl isothiocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c data sheet methyl isothiocyanate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Müfit Bahadir, Harun Parlar and Michael Spiteller: Springer Umweltlexikon , ISBN 3-540-63561-0
- ↑ Entry on methyl isothiocyanate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-22.
- ↑ Method for the determination of methyl isothiocyanate (patent.de)
- ↑ Entry on methyl isothiocyanate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 15, 2014.
- ↑ State Office for the Environment and Nature, North Rhine-Westphalia: Immediate report methyl isothiocyanate in the Rhine (PDF; 86 kB).




