Tripropylamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tripropylamine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 21 N | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an amine-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 143.27 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.75 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−93 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
156 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
4.3 h Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4181 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Tripropylamine (according to IUPAC nomenclature: N, N -dipropylpropan-1-amine , also tri- n -propylamine ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of tertiary aliphatic amines .
Extraction and presentation
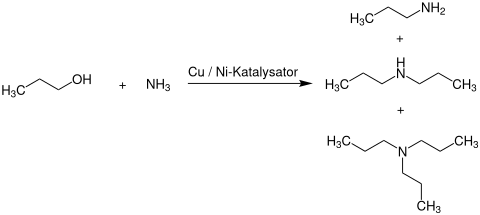
The large-scale production of tripropylamine takes place in a two-stage process. First, n- propanol is reacted with ammonia in the gas phase over a copper- or nickel-containing heterogeneous catalyst at temperatures from 130 to 250 ° C. and pressures generally from 1 to 220 bar to give a product mixture of mono- , di- and tripropylamine.
In the next step, this is separated by multi-stage distillation and the tri- n- propylamine that has already formed is removed. The remaining di- n -propylamine is then in a second reactor at a with aluminum and zirconium (IV) oxide -supported copper or nickel catalyst , at temperatures of 200 to 260 ° C and pressures of 60 to 150 bar to Tri - n -propylamine and ammonia implemented. Unreacted n -propanol, ammonia, and monopropylamine is recycled to the first reaction stage.
The reactors used are mostly tube bundle reactors with a circulating gas stream and a fixed bed , in which molten salts keep the reaction at an almost constant temperature .
properties
Physical Properties
Tripropylamine has a relative gas density of 4.94 (density ratio to dry air at the same temperature and pressure ) and a relative density of the vapor-air mixture of 1.01 (density ratio to dry air at 20 ° C and normal pressure ). In addition, tripropylamine has a vapor pressure of 4.30 hPa at 20 ° C.
Chemical properties
Tripropylamine is a flammable colorless liquid belonging to the group of aliphatic tertiary amines . It is very sparingly soluble in water (0.75 g · l −1 at 25 ° C) and more easily than water. TPA is difficult or very difficult to volatilize . When heated, it decomposes to toxic nitrosamines and can react dangerously with strong oxidizing agents , acids , hydrogen peroxide , oxidizing substances, chlorinated hydrocarbons , nitriles , oxides , peroxides and phenols . At 20 ° C., an aqueous solution of 2.6 g / l has a pH value of 11.4.
use
Tripropylamine (TPA) is an important chemical intermediate in the manufacture of dyes , catalysts and corrosion inhibitors . It is also used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries . Furthermore, TPA has proven itself in the production of quats that are used as phase transfer catalysts .
safety instructions
Tripropylamine is mainly absorbed through the airways and skin . Ingestion can cause severe irritation to the skin and mucous membranes . No information is known about reproductive toxicity , mutagenicity or carcinogenicity . The ignition temperature is 180 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T4. With a flash point of 35 ° C, tripropylamine is considered to be relatively easily flammable. In addition, TPA has a lower explosion limit of 0.7 vol% at 42 g / cm 3 and an upper explosion limit of 5.6 vol% at 335 g / m 3 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry on tripropylamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 22, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5 , pp. 562 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Kevin Huyghe, Steven Brughmans, Falk Simon, Johann-Peter Melder, Peter Raatz: Process for the production of tri-n-propylamine (TPA). In: Google Patents. BASF SE, June 30, 2010, accessed on January 23, 2019 (German, English, French).