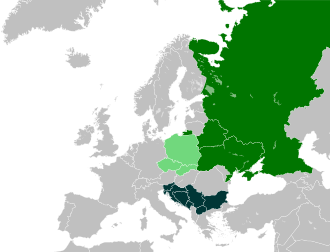
West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are, along with the South and East Slavic languages, one of the three branches of the Slavic languages , which in turn belong to the Indo-European language family . They are spoken by around 56 million people in eastern Central Europe , especially in Poland , the Czech Republic , Slovakia and Lusatia .
The West Slavic language family includes:
- Czech group
- Sorbian group
- Czech-Slovak group
- Czech
- Knaan †
- Slovak
- partly: Batschka Russian
The characteristics of the West Slavic languages compared to the East and South Slavic are:
-
Original Slavic * tj and * dj are represented as c and (d) z, respectively;
see. Polish świeca , Czech svíce , Slovak svieca , Kashubian- Świeca , upper and Lower swěca <Proto-Slavic * světja 'light candle'
or polish Miedza , Czech meze , Slovak medza , Sorbian mjeza , Lower mjaza <Proto-Slavic * Medja 'Rain'. - Ur-Slavic * or, * ol, * er, * el between consonants are represented in the Czech-Slovak group as ra, la, rě, lě and in the other West Slavic languages as ro, lo, re, le (so-called liquid ametathesis );
see. Polish, Upper Sorbian mróz , Lower Sorbian mroz with Czech mráz , Slovak mráz < Ur- Slavic * morzъ 'Frost'
or Polish mleko , Czech mléko , Slovak mlieko < Ur- Slavic * melko 'milk'. In Sorbian there is mostly a change e> o in these groups, therefore Upper Sorbian mlóko (orthographic mloko ), Lower Sorbian mloko .