Acebutolol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of two stereoisomers - simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Acebutolol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 28 N 2 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Blockade of β receptors with poor β 1 selectivity and intrinsic activity present |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 336.43 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
119-123 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Acebutolol is an organic chemical compound that is one of the aromatics and amides . The substance is used as a drug belonging to the group of beta blockers .
Presentation and extraction
Acebutolol is made in five steps. The synthesis is based on 4-aminophenol , which is converted in the first step with butyric anhydride to form the acid amide 4-butyramidophenol and in the second step with acetyl chloride to form O- acetyl-4-butyramidophenol. After isomerization ( Fries rearrangement ) of the phenyl acetate structure to the 2-hydroxyacetophenone structure at 140 ° C. in the presence of aluminum chloride , an etherification with epichlorohydrin takes place . The target compound results from the ring opening of the epoxy function with isopropylamine . The synthesis sequence gives the racemate .
Clinical information
Acebutolol belongs to the group of medium-acting beta blockers, with a half-life of 4 to 12 hours and a duration of action of up to 24 hours. The bioavailability of acebutolol is 60% and it has a low selectivity for β 1 -adrenoceptors over other β-adrenoceptors . It is excreted by the kidneys and should therefore not be given to patients with renal insufficiency.
Intrinsic sympathetic activity
The specialty of acebutolol and some other beta blockers ( oxprenolol and pindolol ) is their intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA).
Other Information
Stereochemistry
Acebutolol has a chiral center, the racemate is used medicinally . The two enantiomers of a chiral drug almost always show a different pharmacology and pharmacokinetics, which was previously often ignored due to ignorance of stereochemical relationships. The active stereoisomer ( eutomer ) is ( S ) -form of acebutolol.
| Acebutolol enantiomers | |
|---|---|
 CAS No .: 68107-81-3 |
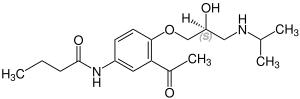 CAS No .: 68107-82-4 |
literature
- T. Karow / R. Lang-Roth General and Special Pharmacology and Toxicology 2003 pp. 62 - 66.
- G. Herold Internal Medicine 2004.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on acebutolol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Acebutolol hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 22, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on acebutolol in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m A. Kleemann , J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications , 4th edition (2000), Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart , ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9
- ↑ Patent GB 1247384 (May & Baker, 1967).
- ↑ Verma, KK; Tyagi, P .: in Anal. Chem. 56 (1984) 2157.
- ↑ EJ Ariëns (1984): Stereochemistry, a basis for sophisticated nonsense in pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology . In: Eur J Clin Pharmacol . 26 (2); 663-668; PMID 6092093 .
- ↑ Joni Agustiana, Azlina Harun Kamaruddina, Subhash Bhatiaa: Single enantiomeric blockers — The existing technologies , Process Biochemistry 45 ( 2010 ) 1587-1604.
Trade names
Prent (D)
Acebutolol in combination with Mefrusid : Sali-Prent (D), Acebutolol in combination with Nifedipine : Tredalat (D)
