Distigmin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Distigmine bromide | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Distigmin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 32 Br 2 N 4 O 4 (dibromide) | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White crystalline powder (dibromide) |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 576.33 g · mol -1 (dibromide) | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
solid (dibromide) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
~ 150 ° C (dibromide, decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
5.0–5.5 (dibromide, aqueous solution) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
28.82 mg ml −1 ( in 0.1 mol l −1 HClO 4 ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Distigmin (also: Hexamarium Bromid , Distigmin- Bromid ) is the generic name for an indirect parasympathomimetic with a long duration of action. It has a similar profile of action to neostigmine and pyridostigmine and is used as a drug for neurogenic bladder emptying disorders with relaxation of the bladder muscle , hypotonic chronic constipation , Hirschsprung's disease , peripheral paralysis of the striated muscles or myasthenia gravis .
The active ingredient used is distigmine bromide ; it was patented by the Austrian nitrogen works in 1957 and went on sale in 1959.
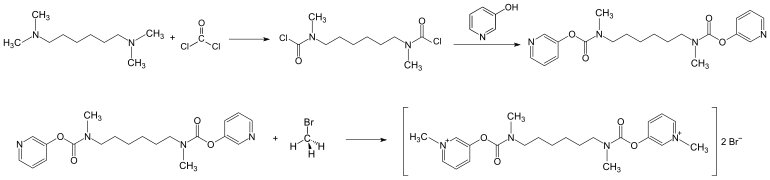
Extraction
The literature describes the synthesis starting from N , N , N ', N ' -tetramethylhexamethylenediamine with phosgene and 3-hydroxypyridine . Distigmine bromide is formed by alkylation with methyl bromide .
pharmacology
In medical use, the name distigmin refers to the dibromide salt . It is sometimes referred to synonymously as distigmine bromide .
Pharmacodynamics
Distigmine bromide reacts to form a carbamic acid ester with the esteric center of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase and makes it inoperable. The increased acetylcholine concentration at the motor endplate causes the ureter , gall bladder , bladder muscle and bronchial muscles to contract. In the eye, there is contraction of the ciliary body , constriction of the pupils , decrease in intraocular pressure, and disturbances of accommodation . In addition, a decrease in heart rate, increased sweat secretion and an increase in peristalsis and secretion in the digestive tract were observed. In low doses, fasciculations of the skeletal muscles occur, in high doses, symptoms of paralysis due to depolarization are possible.
Pharmacokinetics
Like neostigmine, distigmine is a quaternary ammonium compound with a strong acetylcholinesterase bond which, after hydrolysis , is excreted renally with a delay. It is hardly soluble in fat, does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier and does not significantly affect ganglionic transmission in the autonomic nervous system. The average absorption time is 10 hours and the oral bioavailability is 4.65%. The plasma half-life is 65 hours, and acetylcholinesterase is reversibly inhibited for about 38 to 40 hours. Repeated ingestion shows no accumulation of the effect on acetylcholinesterase inhibition.
After intravenous administration, 4% of the substance was found in the faeces, 85% was excreted renally .
Contraindications
In Parkinson's disease , myotonia , thyrotoxicosis , uveitis , bronchial asthma , cardiac arrhythmias, constrictions and spasmodic conditions of the intestine, the biliary or urinary tract and in the circulatory system, it may not be used. Distigmine is also contraindicated in the event of mechanical blockage of the intestine or the lower urinary tract .
Interactions
Antiarrhythmics , glucocorticoids and dipyridamole reduce the effect. Anticholinergics , tricyclic or tetracyclic antidepressants , neuroleptics , lithium and antihistamines antagonize the muscarinic effect, the nicotinic effect is rarely influenced. Depolarizing muscle relaxants can be prolonged. With simultaneous use with other direct or indirect parasympathomimetics , a myasthenic crisis is possible. Distigmine bromide antagonizes the effect of curare- like relaxants. With or shortly after beta blockers, increased hypotension and long-lasting bradycardia may occur.
Side effects
Often, side effects point to an overdose. Muscarin-like side effects outweigh effects on the muscles and can be balanced with atropine or similar substances. A slowed pulse is observed very often, which in rare cases can become life-threatening and arrhythmic. In individual cases, atrial fibrillation and cardiac arrest also occur . These side effects are particularly important in postoperative treatment. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and sweating are also very common, and the flow of saliva is often increased. Bowel and muscle cramps, urinary incontinence, involuntary muscle twitching and difficulty swallowing occur occasionally, in extreme cases paralysis. Rarely, drowsiness, speech disorders, irregular menstruation, rashes, and seizures may occur. Constriction of the airways rarely causes shortness of breath with increased mucus formation. Distigmin can impair eyesight due to pupillary constriction, accommodation disorders and increased tear flow.
Trade names
- Monopreparations
- Ubretid (D, A, CH, NL, UK)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on distigmine bromide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 1, 2016.
- ↑ Entry on distigmine bromide on page 117 (PDF). In: Römpp Lexikon Chemie, 10th edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 2, 2016.
- ^ A b c d e Kleemann , Engel, Kutscher, Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances, 4th edition, Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9 . Page 685
- ↑ a b c d e f The Japanese Pharmacopoeia, Edition 14 / I: Official Monographs , Yakuji Nippo. Ltd., Tokyo (2001), ISBN 978-4-8408-0672-5 , page 599 (PDF).
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of distigmine bromide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), retrieved on March 8, 2016, is reproduced from a self-classification by distributors .
- ↑ entry to Distigmine bromide in ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on 2 March 2016th
- ↑ a b Technical information on Ubretid in the Swiss Medicines Compendium. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- ↑ Patent application US2789981 : Bis-carbamic acid ester compounds, and a process of making same. Registered on September 19, 1955 , published on April 23, 1957 , applicant: Österr. Nitrogen works, inventor: Otto Schmid.
- ↑ AGES Pharmaceutical Specialty Register , accessed on March 2, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d Patient information on Ubretid in the AGES medicinal specialties register. Retrieved March 1, 2016.
- ↑ Vree TB, Waitzinger J, Hammermaier A, Radhofer-Welte S .: Absolute bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, renal and biliary clearance of distigmine after a single oral dose in comparison to iv administration of 14C-distigmine-bromide in healthy volunteers . In: Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. . 37, Aug 1999, pp. 393-403. PMID 3485122 .
- ↑ Derek G. Waller, Andrew G. Renwick, Keith Hillier: Medical Pharmacology and Therapeutics , Saunders Ltd .; 3rd edition (2009), ISBN 978-0-7020-2991-2 .