Ebnat (Aalen)
|
Ebnat
City of Aalen
|
|
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 48 ° 48 ′ 0 ″ N , 10 ° 11 ′ 0 ″ E | |
| Height : | 613 (610-620) m |
| Area : | 21.09 km² |
| Residents : | 3342 (Jun. 1, 2016) |
| Population density : | 158 inhabitants / km² |
| Incorporation : | July 1, 1972 |
| Postal code : | 73432 |
| Area code : | 07367 |
|
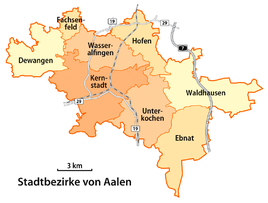
Map of the districts of Aalen, Ebnat in the southeast
|
|
|
Ebnat from the air
|
|
Ebnat is a district of the large district town of Aalen in the Ostalbkreis in Baden-Württemberg , Germany . With over 3,300 inhabitants, Ebnat is the largest town in the front Härtsfeld .
geography
location
Ebnat lies on the plateau of the eastern Swabian Alb , the Härtsfeld . In addition to the main town of Ebnat, the Ebnat district includes the hamlets Affalterwang and Niesitz , as well as the Diepertsbuch homestead .
Neighboring places
The Ebnat district is bordered to the west by the Unterkochen district and the city of Oberkochen , to the north by the Waldhausen district , to the east by the Neresheim district of Elchingen and to the south by the Heidenheim district of Großkuchen with the hamlet of Nietheim .
history
Earliest settlement
Burial mounds from the Hallstatt period (approx. 800 to 480 BC) indicate that the Ebnat area was already settled by the Celts .
From the Middle Ages
The first documentary mention of the place Ebnat, which means something like level , can be found in a document Pope Bonifatius VIII. From the year 1298. In this document also the place Siegenweiler , which is now lost, is mentioned. The historical development before that is largely unknown, but it can be assumed that the place existed before 1298. Until 1258 Ebnat belonged to the Counts of Dillingen . After the family died out in 1258, the place came to the Neresheim monastery . The Counts of Oettingen , who maintained a customs office in Ebnat, also claimed the place through the bailiff's rights at the monastery. The trade lasted until 1764, when the monastery became imperial . In 1803 the place fell first to the House of Thurn und Taxis , in 1806 to Bavaria and in 1810 came to Württemberg, where he belonged to the Oberamt Neresheim . When it was dissolved in 1938, Ebnat came to the Aalen district .
On July 1, 1972, Ebnat was incorporated into the city of Aalen.
Holzhauerbund
The Ebnater Holzhauerbund can look back on a long history. Every year the members of the Holzhauerbund meet in January for the edition of St. Vincent on or around St. Vincent's Day . The statutes are read out and each member pays the contribution of 20 cents. The Holzhauerbund was originally a rudimentary protection for those working in the forest. Accidents in the forest and their families were supported from the association's assets.
Members of the Holzhauerbund are foresters and private forest owners, but also anyone interested in village tradition.
politics
Local council
The local council of the Ebnat district currently has 14 members whose term of office is five years. The last election took place in the Baden-Württemberg municipal elections on May 26, 2019. This resulted in the following composition (the changes in parliamentary groups refer to the penultimate election in 2014):
| fraction | Number of seats | change |
|---|---|---|
| CDU | 7 seats | +1 |
| FW Ebnat | 4 seats | ± 0 |
| SPD | 1 seats | -1 |
| GREEN | 2 seats | +2 |
Mayor
The mayor of the Ebnat district is Manfred Traub (CDU).
coat of arms
Ebnat's coat of arms shows a golden abbot's staff, which testifies to the village's long association with Neresheim monastery. There are also two so-called “Gnadenhäuschen”, small, simply furnished huts for poor people. These mostly only one-story houses were often to be found in Ebnat.
Economy and Infrastructure
Ebnat has several stops for regional bus transport to Aalen and Neresheim, a connection to the A 7 motorway and some retail stores that are organized in the HGV Ebnat .
There are two kindergartens and a primary school with a teaching pool.
Ebnat has an industrial area with medium-sized companies in the metal, plastics and construction industries.
traffic
Ebnat is located directly on the A 7 and had its own station for the Härtsfeldbahn , which was closed in 1972. The traffic on the motorway slip road to the A 7 separates the northern part of Ebnat at peak times.
Local partnership
There is a Jumelage to the Swiss Ebnat-Kappel .
Buildings
The baroque parish church of the Immaculate Conception , the parish barn that goes with it, and the old parsonage are listed.
The Maria Eich pilgrimage chapel is located in the “Scheiterhau” forest area, four hundred meters from a hikers' car park on the southwestern outskirts of Ebnat . The present building, erected in 1925, goes back to a place of prayer built into an oak in 1686.
literature
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population development 2016 , from: aalen-ebnat.de, accessed on July 12, 2016.
- ^ Karlheinz Bauer: Aalen . Theiss, Stuttgart 1983, ISBN 3-8062-0321-0 , p. 64 ff .
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 445 .
- ↑ Election result AA_OR Ebnat 2019 , aalen.de, accessed on August 10, 2019
- ^ General monument database (ADAB) of the State Office for Monument Preservation Baden-Württemberg .