Ethacridine lactate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
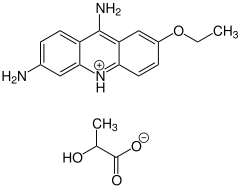
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Ethacridine lactate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3,9-diamine-7-ethoxyacridinium ( RS ) lactate ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow, odorless, crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 343.38 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
235 ° C (discoloration from 200) [( RS ) -lactate monohydrate] |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
easy in water (145–150 g · l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Ethacridine lactate is an antiseptic from the series of acridines , the antibacterial effect of which has been known since 1913. It is the salt of the base ethacridine with lactic acid and is used as a racemate . Typical of ethacridine lactate is its yellow color and the property of coloring objects and skin yellow.
application areas
Ethacridine lactate is mainly used to treat infected wounds and pyoderma such as abscesses , boils or impetigo contagiosa . Implants with ethacridine lactate are used in dentistry for wound care. It is also used as a bladder and vaginal rinse solution.
In ointments, the substance is usually used in 0.2 percent concentration. For rinses or moist bandages, 0.05 to 0.1 percent solutions are common.
In addition, ethacridine lactate is used for diarrhea (preparations: Metifex ® , Tannacomp ® ).
unwanted effects
Ethacridine lactate, like other substances of the hydroxy quinoline type, often triggers contact allergies .
The use against diarrhea is described as "problematic", since a clinical picture was observed in connection with long-term, high-dose administration of clioquinol (which was also used against diarrhea), which has become known as SMON ( Subacute Myelo-Optico-Neuropathy ). Nerve damage, bladder, rectal and visual disturbances occurred. It is suspected that the same side effects could occur with ethacridine.
Extraction and presentation
Ethacridine lactate can be obtained from 2-chloro-4-nitrotoluene through a multi-stage reaction with potassium permanganate , 4-phenetidine , phosphorus pentachloride and ammonia .
Chemical properties
Ethacridine lactate forms water-soluble crystals of a light yellow color. At a pH of 7.3 and a temperature of 37 ° C, it is completely dissociated. The antibacterial effect of the acridine derivatives increases with the degree of dissociation . Ethacridine lactate is sensitive to light and should be stored protected from light. By heating a solution of ethacridine lactate, better solubility can be achieved.
pharmacology
It is believed that acridines, like ethacridine lactate, act on the RNA-containing cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria. The binding to the bacterial DNA or RNA prevents the protein biosynthesis of the bacteria. Ethacridine lactate has an antibacterial effect, especially against staphylococci , streptococci and coli bacteria. It also has an effect on fungi, protozoa such as amoebas , coccidia , trichomonads and anaplasmas . So far there is no information on the development of resistance to ethacridine lactate.
Pharmacokinetics
Orally administered ethacridine lactate is less than 0.1 percent absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The enzyme acridine dehydrogenase contained in the liver and kidneys of humans oxidizes acridine derivatives such as ethacridine lactate to acridone derivatives. These are excreted renally . However, most of the dose is excreted in the faeces . The extent to which ethacridine lactate is absorbed through the skin and wound surfaces has not yet been investigated. However, aminoacridines are known to penetrate tissues quickly. After intravenous administration, ethacridine lactate is rapidly distributed to all organs. But the blood-brain barrier is not crossed.
toxicity
No cases of poisoning have become known. The LD 50 in animal experiments is between 1.8 and 5.36 grams per kilogram of body weight, depending on the species. It is not known whether ethacridine lactate has a tumorigenic potential as there are no long-term studies on animals. In addition, ethacridine lactate has not yet been adequately tested for mutagenicity . As already shown for other acridine derivatives, in vitro studies on prokaryotes gave clear indications of a mutagenic potential. There are also no studies on teratogenicity to date, nor are there any experiences with human safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding . For this reason, ethacridine lactate should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, also because it is not known whether the substance is excreted in breast milk .
Others
Fresh ethacridine lactate stains can be removed with an alcoholic solvent such as isopropanol . Another option is to clean the soiled laundry in a warm 3% acetic acid solution . In the case of severe "Rivanol stains", the cleaning effect can be increased by adding 15 ml of 3 percent hydrogen peroxide solution per liter.
Trade names
Metifex (D), NeoChinosol (D), Rivanol (A, D), as well as a generic (CH)
Tannacomp (D), Tyrothricin (CH)
See also
literature
- Ernst Mutschler u. a .: drug effects . 8th edition. Scientific publishing company. Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8047-1763-2
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on ethacridine lactate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; P. 3716, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ Entry on ethacridine lactate in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b c d e Technical information on Rivanol ® ointment from Dermapharm.
- ↑ P. Altmeyer, M. Bacharach-Buhles: Springer Enzyklopädie Dermatologie, Allergologie, Umweltmedizin , p. 1775, 1st edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin, 2002, ISBN 3-540-41361-8 .
- ↑ Ernst Mutschler u. a .: drug effects . 9th edition. Scientific publishing company. Stuttgart 2001. pp. 792, 663; ISBN 3-8047-1763-2 .
- ↑ T. Takasu: [SMON - a model of the iatrogenic disease]. In: Rinsh? shinkeigaku = Clinical neurology. Volume 43, Number 11, November 2003, pp. 866-869, PMID 15152488 . (Review).
- ↑ Franz v. Bruchhausen, Gerd Dannhardt, Siegfried Ebel, August W. Frahm, Eberhard Hackenthal, Ulrike Holzgrabe: Hagers Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice Volume 8: Substances EO . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-57994-3 , pp. 100 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ F. von Bruchhausen: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice: Drugs AK , p. 101, 5th edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-540-61618-7 .
- ↑ Technical information on Rivanol ® 1 g and Rivanol ® 0.1 g from Dermapharm.
- ↑ Red List (August 2009).
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland (August 2009).
