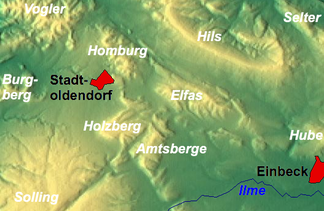
Homburgwald
| Homburgwald | |
|---|---|
|
Homburgwald (Homburg) near Stadtoldendorf |
|
| Highest peak | unnamed hill ( 406.1 m above sea level ) |
| location | Holzminden district , Lower Saxony |
| part of | (Northern) Solling foreland |
| Classification according to | Handbook of the natural spatial structure of Germany (sheet 99 Göttingen) |
| Coordinates | 51 ° 54 ' N , 9 ° 39' E |
| rock | Gypsum , anhydrite , limestone , sandstone , siltstone , mudstone |
| Age of the rock | Zechstein , red sandstone |
The Homburgwald (also called Homburg or Homburger Berge ) is one to 406.1 m above sea level. NN high low mountain range of the Weser Uplands in the district of Holzminden in Lower Saxony ( Germany ). In the natural division of Germany (Göttingen sheet), the Homburgwald is referred to as Stadtoldendorfer Wald and is part of the (northern) Solling foreland .
Geographical location
The Homburgwald is located on the eastern flank of the central part of the elongated Weserbergland between the low mountain ranges and ridges of Hils in the northeast, Elfas in the southeast, Amtsberge in the south-southeast, Holzberg in the south, Solling in the south, Burgberg in the southwest and Vogler in the northwest. It lies between Eschershausen in the north and Stadtoldendorf in the south; A section of the federal highway 64 , which connects Eschershausen with Einbeck , runs past it to the west, north and east .
mountains
The mountains and elevations in the Homburgwald include - with an altitude in meters above sea level (NN); if not otherwise stated usually according to:
|
|
Flowing waters
The rivers in and around the Homburgwald include:
- Lenne (passes the Homburgwald in the east, northeast and north; tributary of the Weser)
-
Forstbach (arises directly south of the Homburgwald; tributary of the Weser)
- Rauchbach (rises in the south of the Homburgwald; source stream of the Forstbach)
- Fahrenbach (rises on the western flank of the Homburgwald; tributary of the Forstbach)
Worth seeing
The sights as well as natural and cultural monuments in the Homburgwald include:
On the Great Homburg (approx. 403 m above sea level ) are the ruins of the Homburg , from whose castle tower you can enjoy the view. You can also look into the distance from the Kellberg Tower (20 m high) on the Kellberg (343.1 m) east of Stadtoldendorf. To the west of the Homburgwald on the southern edge of the Odfeld is the Amelungsborn monastery .
Natural monuments are the Seven Brothers beech and the Tentrus oak located at a crossroads. There is a local story about the latter that a man named Tentrus was found frozen there in ancient times. He was tired on a corridor between Eschershausen and Stadtoldendorf and went to sleep there on a winter night. As early as the middle of the twentieth century, only a dead tree stump was left of the original oak, but it was still evidence of the former size of this tree.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ^ Jürgen Hövermann: Geographical land survey: The natural space units on sheet 99 Göttingen. Federal Institute for Regional Studies, Bad Godesberg 1963. → Online map (PDF, 4 MB)