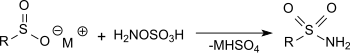Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 3 NO 4 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to beige crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 113.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.2 g cm −3 (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
210 ° C (with decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility | ||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Hydroxylamine- O -sulfonic acid (HOSA) is formed during the sulfonation of hydroxylamine and is a versatile reagent for introducing amino groups , converting aldehydes to nitriles , alicyclic ketones to lactams and for the formation of a wide variety of nitrogen-containing heterocycles . The acid is present as a zwitterion because of the presence of the basic amino group and the acidic sulfo group .
presentation
According to a laboratory specification , hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid can be obtained by adding hydroxylamine sulfate to 30 percent fuming sulfuric acid (oleum) at room temperature and then precipitating the resulting hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid with diethyl ether . The yields are 98-99% with purities at 92-98%.
On an industrial scale, hydroxylamine sulfate can initially be produced in situ from nitromethane and 100 percent sulfur trioxide in a one-pot reaction , which is reacted with sulfur trioxide to form hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid.
In the sulfonation of hydroxylamine sulfate with chlorosulfonic acid in bulk, HOSA is obtained in 95 to 97 percent yield and 96 to 99 percent purity. The sulfonation of hydroxylamine sulfate with 27 percent oleum provides HOSA in an industrial process with recycling of the excess oleum in approx. 90 percent yield and, after washing with glacial acetic acid, in 99.9 percent purity.
A reaction variant of the reaction of hydroxylamine sulfate with fuming sulfuric acid at 110 ° C for 6 hours and delayed cooling to room temperature over 8 hours produces HOSA with larger and thus more easily filterable crystals with yields of approx. 80% and purities over 98%.
properties
Hydroxylamine- O -sulfonic acid is a white to beige-colored hygroscopic solid with a pungent odor that dissolves very well in water, but not in non-polar solvents such as e.g. B. diethyl ether or chloroform dissolves. The substance rapidly decomposes in an aqueous medium above room temperature to form caustic and corrosive solutions. Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid is hygroscopic, sensitive to heat and must be stored in a cool place and with exclusion of moisture.
use
Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid reacts in the basic as a nucleophile and in the neutral and acidic as an electrophile
Amination reactions
Hydroxylamine- O -sulfonic acid reacts with primary and secondary amines to form mono- and disubstituted hydrazines , for example with piperidine in a buffered aqueous solution to form N- aminopiperidine in 96 percent yield ,
with tertiary amines to form trisubstituted hydrazinium salts and with pyridine to form the 1-aminopyridinium salt,
which is obtained after recrystallization in 63 to 72 percent yield as almost white crystals.
From 1-Aminopyridiniumsalzen are by acylation of the photochemically active 1-N-Iminopyridiniumylide accessible.
The photochemical rearrangement of the 1- N -iminipyridinium ylides obtained leads to 1 H -1,2-diazepines in high yields .
N-amination of 1 H -benzotriazole with hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid gives a mixture of 1-aminobenzotriazole (38%) and 2-aminobenzotriazole (11%) in addition to unreacted 1 H -benzotriazole. From 1-aminotriazole, oxidation with lead (IV) acetate produces dehydrobenzene in almost quantitative yield, which in non-polar solvents such as e.g. B. dichloromethane , rapidly dimerized to biphenylene at 20 ° C in 82 percent yield .
Electron- poor heterocycles , such as. B. tetrazole , can be N-aminated with hydroxylamine O -sulfonic acid, while still electron-poor compounds such. B. 5-Nitrotetrazole only react with stronger aminating agents such as O -Tosylhydroxylamin or O -Mesitylenesulfonylhydroxylamin to form amino compounds that have been investigated as explosives.
In the N-amination of the unsubstituted tetrazole, a mixture of 1-amino- and 2-aminotetrazole is obtained.
Sulfur compounds, such as thioethers , can also be converted with hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid to form the sulfinimines isosteric (but significantly more unstable) with sulfoxides
or phosphorus compounds , such as triphenylphosphine, are aminated to phosphinimines via the intermediate aminotriphenylphosphonium hydrogen sulfate.
The reaction of hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid with metal salts of sulfinic acids in sodium acetate solution produces primary sulfonamides in very good yields.
Reduction reactions
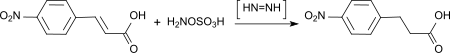
From HOSA or HOSA-hydroxylamine sulphate mixtures, diimine is formed in the alkaline in situ , which selectively hydrogenates conjugated multiple bonds.
Reactions with carbonyl compounds
At room temperature and below, hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid reacts with ketones and aldehydes as a nucleophile to form the corresponding oxime- O- sulfonic acids or their salts. At temperatures above room temperature, the oxime- O- sulfonic acids of aldehydes react with elimination of sulfuric acid in high yields to form nitriles .
Under similar conditions, aliphatic ketones give oximes in very high yields, while aryl alkyl ketones react to amides under Beckmann rearrangement .
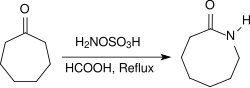
Under acidic conditions, e.g. B. in the presence of concentrated formic acid , alicyclic ketones react when heated under reflux for several hours in high yields to form lactams .
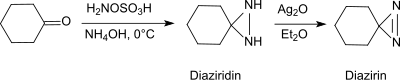
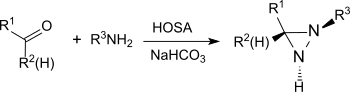
Under basic conditions, HOSA reacts with aldehydes and ketones, such as B. cyclohexanone , in the presence of primary amines with the formation of diaziridines , which can easily be oxidized to the more stable diazirines .
The reaction also gives substituted diaziridines from simple aldehydes and ketones in high chemical yields and diastereoselectivities .
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid on the carbonyl group of the salicylaldehyde and subsequent cyclization produces 1,2-benzisoxazole in 95 percent yield.
1,2-Benzisoxazole is a structural element in the antipsychotics risperidone and paliperidone , as well as the anticonvulsant zonisamide .
In a one-pot reaction, N- aryl [3,4- d ] pyrazolopyrimidines are accessible in good yields, starting from the easily obtainable 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carboxaldehyde, which can be used as purine analogs in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
More reactions
The chemiluminescence of the luminol / cobalt (II) chloride system is drastically increased by adding hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 20, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid for synthesis (PDF) from Merck , accessed on September 3, 2015.
- ↑ a b E. Erdik, J. Saczewski: Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid . In: e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . 2013, doi : 10.1002 / 047084289X.rh058.pub2 .
- ↑ a b R.G. Wallace: Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid - a versatile synthetic reagent . In: Aldrichimica Acta . tape 13 , no. 1 , 1980, p. 3-11 ( sigmaaldrich.com ).
- ^ Holleman-Wiberg, Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry, 101st edition, de Gruyter Verlag 1995 ISBN 3-11-012641-9
- ↑ a b H.J. Matsuguma, LF- Audrieth: Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid . In: Inorganic Syntheses . tape 5 , 1957, pp. 122-125 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470132364.ch32 .
- ↑ Patent US3281209 : Process for the preparation of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. Applied on May 28, 1964 , published October 25, 1966 , Applicant: Commercial Solvents Corp., Inventor: HL Wehrmeister, HI Yalowitz.
- ^ MW Rathke, AA Millard: Boranes in functionalization of olefins to amines: 3-pinanamines . In: Org. Synth. tape 58 , 1978, p. 32 , doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.058.0032 .
- ↑ Patent US4737354 : Preparation of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. Registered on January 29, 1987 , published on April 12, 1988 , applicant: BASF AG, inventor: H. Fuchs, F.-J. Weiss, E. Thomas, J. Ritz.
- ↑ Patent US8038975 : Process for preparing crystalline hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. Registered on January 21, 2008 , published on October 18, 2011 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: L. Wittenbecher, R. Goth.
- ↑ Ender Erdik, Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic Acid, http://reag.paperplane.io/00001523.htm
- ↑ E. Labarthe, AJ Bougrine, V. Pasquet, H. Delalu: A New Strategy for the Preparation of N-aminopiperidines Using Hydroxylamine- O -Sulfonic Acid: Synthesis, Kinetic modeling, Phase Equilibria, Extraction and Processes . In: Adv. Chem. Engineer. Sci. tape 3 , 2013, p. 157-163 , doi : 10.4236 / aces.2013.32019 .
- ↑ R. Gösl, A. Meuwsen: 1-aminopyridinium iodide . In: Org. Synth. tape 43 , 1963, pp. 1 , doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.043.0001 .
- ^ J. Streith: The Photochemistry of N-Iminopyridinium Ylides in Retrospect. From a Simple Concept to Some Applications . In: CHIMIA . tape 45 , no. 3 , 1991, pp. 65-76 .
- ↑ J. Streith: The photochemistry of aromatic-N-ylides. Rearrangement and fragmentation patterns . In: Pure & Appl. Chem. Band 49 , no. 3 , 1977, pp. 305-315 , doi : 10.1351 / pac197749030305 .
- ↑ Campbell CD, Rees CW: Reactive intermediates. Part I. Synthesis and oxidation of 1- and 2-aminobenzotriazole . In: J. Chem. Soc. C . 1969, p. 742-747 , doi : 10.1039 / J39690000742 .
- ↑ TM Klapötke, DG Piercey, J. Stierstorfer: Amination of energetic anions: high-performing energetic materials . In: Dalton Trans. Band 41 , 2012, p. 9451-9459 , doi : 10.1039 / C2DT30684K .
- ↑ R. Appel, W. Büchner, E. Guth: On the knowledge of the imine, I. About phosphinimines and sulfinimines . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 618 , no. 1 , 1958, p. 53-58 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19586180107 .
- ↑ SL Graham, TH Scholz: The reaction of sulfinic acid salts with hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid. A useful synthesis of primary sulfonamides . In: Synthesis . tape 1986 (2) , 1986, pp. 1031-1032 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1986-31862 .
- ↑ W. Dürckheimer: A simple method for generating diimine in situ . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 721 , 1969, p. 240-243 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19697210133 .
- ↑ J. Streith, C. Fizet: Nucleophilic versus electrophilic properties of the nitrogen atom in derivatives O-sulfonyl hydroxylamines . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 18 , no. 37 , 1977, pp. 3297-3300 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (01) 83223-8 .
- ↑ C. Fizet, J. Streith: Hydroxylamine-o-sulfonic acid: A convenient reagent for the oxidative conversion of aldehydes into nitriles . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 15 , no. 36 , 1974, p. 3187-3188 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (01) 91857-X .
- ↑ GA Olah, AP Fung: Hexahydro-2- (1H) -azocinone . In: Org. Synth. tape 63 , 1985, pp. 188 , doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.063.0188 .
- ↑ E. Schmitz, R. Ohme: 3,3-Pentamethylene diaciridine . In: Org. Synth. tape 45 , 1965, p. 83 , doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.045.0083 .
- ↑ AW Beebe, EF Dohmeier, G. Moura-Letts: Diastereoselective synthesis of substituted diaziridines from simple ketones and aldehydes . In: Chem. Commun. tape 51 , 2015, p. 13511-13514 , doi : 10.1039 / C5CC04813C .
- ^ DS Kemp, RB Woodward: The N-ethylbenzisoxazolium cation — I: Preparation and reactions with nucleophilic species . In: Tetrahedron . tape 21 , no. 11 , 1965, pp. 3019-3035 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 96921-2 .
- ^ LE Evans, MD Cheeseman, K. Jones: N-N Bond-Forming Cyclization for the One-Pot Synthesis of N-Aryl [3,4-d] pyrazolopyrimidines . In: Org. Lett. tape 14 , no. 13 , 2012, p. 3546-3549 , doi : 10.1021 / ol301561a .
- ↑ C. Morrill, S. Babu, NG Almstead, Y.-C. Moon: Synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted pyrazolo [3,4-d] pyrimidines from 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carboxaldehyde: insights into selectivity and reactivity . In: Synthesis . tape 45 , 2013, p. 1791-1806 , doi : 10.1055 / s-0033-1338862 .
- ↑ M. Saqib, W. Gao, J. Lai, L. Qi, S. Majeed, MRHS Gilani, G. Xu: Hydroxylamine- O- sulfonic acid as an efficient coreactant for luminol chemiluminescence for selective and sensitive detection . In: Chem. Commun. tape 51 , 2015, p. 6536-6539 , doi : 10.1039 / C5CC01090J .