Salicylaldehyde
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Salicylaldehyde | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 6 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish liquid with a bitter almond odor and a burning taste |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 122.13 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.17 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−7 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
197 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.77 h Pa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
6.79 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5734 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Salicylaldehyde is a naturally occurring chemical compound in some plants and insects that is widely used today as a fragrance and in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. It is derived from both benzaldehyde and phenol . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached aldehyde (-CHO) and hydroxyl group (-OH) as substituents . Salicylaldehyde belongs to the group of hydroxybenzaldehydes .
history
Around 1838 the Swiss pharmacist and pharmacist Johann Pagenstecher succeeded in extracting salicylaldehyde from the flowers of meadowsweet .
Occurrence
Insects ( leaf beetles ) produce this compound in special glands to combat predators from the salicin of their host plants. It still occurs in the marsh sparrow or meadowsweet ( Filipendula ulmaria , formerly: Spiraea ulmaria ).
Extraction and presentation
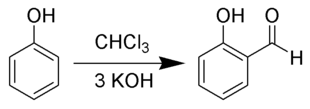
In the past, salicylaldehyde was obtained by the Reimer-Tiemann reaction (1876, early carbene chemistry). In this case, be chloroform , potassium hydroxide and phenol used as starting materials. Phase transfer catalysis is now used as an improvement .
properties
Salicylaldehyde has with respect to the phenol (9.99) a significantly lower pK s value of 6.79; the electron-withdrawing aldehyde group ( −M effect ) increases the acidity; the phenolic OH bond is increasingly polarized.
use
Salicylaldehyde is used as an intermediate in the dye and drug industry and in a 10% alcoholic solution to detect ketones (e.g. acetone in urine ) and fusel oils in alcohol . It is also used to manufacture Schiff bases , e.g. B. the complexing agent N , N '-Bis (salicylidene) ethylenediamine (abbreviation: salen ), whose cobalt (II) complex ( salcomin ) can reversibly bind oxygen, is used. It is also used as a fragrance in perfumes .
Oxidation with hydrogen peroxide results in catechol ( Dakin reaction ).
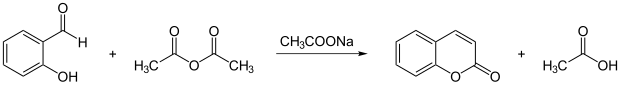
Coumarin is produced from salicylaldehyde and acetic anhydride using Perkin's synthesis .
literature
- Edwin A. Robinson: The reaction of dichloromethylene with water and with phenoxide ions (Reimer-Tiemann reaction) , in: J. Chem. Soc. , 1961 , pp. 1663-1671; doi : 10.1039 / JR9610001663 .
- Karl Winterfeld : Internship in organic-preparative pharmaceutical chemistry . 6th edition, Steinkopff.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on salicylaldehyde. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 2, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on salicylaldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet salicylaldehyde (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 22, 2011.
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ P. Rademacher: Organic Chemistry IV. (PDF; 203 kB)
- ↑ HD Dakin : Catechol In: Organic Syntheses . 3, 1923, p. 28, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.003.0028 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 159 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Erich Koepp, Fritz Vögtle: Perkin synthesis with cesium acetate . In: Synthesis . tape 1987 , no. January 2 , 1987, doi : 10.1055 / s-1987-27880 .