Kigoma (region)
| Kigoma | |
|---|---|
| Basic data | |
| Country | Tanzania |
| Capital | Kigoma |
| surface | 45,075 km² |
| Residents | 2,127,930 (2012) |
| density | 47 inhabitants per km² |
| ISO 3166-2 | TZ-08 |
Coordinates: 4 ° 44 ′ S , 30 ° 10 ′ E
Kigoma is the westernmost of the 31 regions of Tanzania with the capital Kigoma . The region is bordered by the Kagera Province to the north, the Shinyanga region to the northeast, the Tabora region to the east, the Katavi and Rukwa regions to the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west and Burundi to the northwest .
geography
The region is 45,075 square kilometers (of which 8552 square kilometers are water) and has around 2.1 million inhabitants (as of 2012). Kigoma is east of Lake Tanganyika . The land rises steeply to 1750 meters from its shore, which is 800 meters above sea level. There is a hilly plateau that rises gently to the north and east. The land is drained by three major rivers, the Malagarasi , the Luiche and the Ruchugi . The valleys lie at around 1000 meters above sea level until the rivers flow into marshy deltas in Lake Tanganyika.
According to the altitude, the region can be divided into four zones:
- Lakeshore: The narrow strip on the lake shore is at an altitude of 800 to 1000 meters above sea level. It is cut by numerous brooks that flow into the lake. Every year 600 to 1000 millimeters of rain fall.
- Miombo forest: This zone, named after the Miombo tree, lies at an altitude of 1000 to 1200 meters with also 600 to 1000 millimeters of precipitation annually.
- Middle zone: It connects to the forest zone at an altitude of 1200 to 1500 meters, has annual rainfall of 850 to 1100 millimeters and is a swampy area.
- Highlands: The highlands are between 1500 and 1750 meters above sea level and rain falls between 1000 and 1600 millimeters per year. The area is divided into two parts. In the north it connects to the Middle Zone and is densely populated, in the south the Mahale Mountains rise up from the highlands to an altitude of 2373 meters and the area has been declared a Mahale Mountains National Park .
The climate in the region is tropical, Aw according to the effective climate classification . It has a distinct rainy season from late October to May with a short dry period of two to three weeks in January or February. A longer dry season follows from late May to early October. The average daytime temperature is between 25 degrees Celsius in December and 28 degrees Celsius in September. The temperature decreases with altitude.
|
Climate table Kigoma (city)
Source: climate-data.org
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
history
In the pre-colonial period, the region was a source of ivory and slaves. Tabora and Ujiji were assembly points before they were transported to the coast. On October 27, 1871, Henry Mortin Stanley met David Livingston in Ujiji on the shores of Lake Tanganyika . During the colonial period, the country belonged to the western region with the capital Tabora. During the German rule from 1884 to 1919 the government building and the train station were built. In 1964, the Kigoma region was founded, it consisted of the three districts of Kasulu, Kibondo and Kigoma.
Administrative division
The Kigoma region is divided into six districts and eight constituencies (councils):
| District | Residents
1988 |
Residents
2002 |
Residents
2012 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kibondo | 175,585 | 210.308 | 261,331 |
| Kasulu | 319.711 | 437.053 | 634.038 |
| Kigoma | 361.474 | 348,884 | 427.024 |
| Uvinza | n / A | 284,644 | 383,640 |
| Buhigwe | n / A | 189,689 | 254,342 |
| Kakonko | n / A | 203,469 | 167,555 |
population
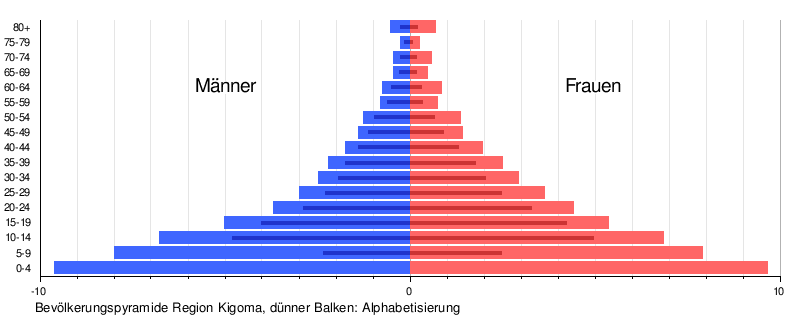
In 2012, almost fifty percent of the population were under 15 years old and only five percent were older than 60. The literacy rate was 71 percent for men and 65 percent for women (as of 2012).
Facilities and services
|
 |
Economy and Infrastructure
Of those over ten years of age, 67 percent were employed, eleven percent worked in the household (cooking, hygiene, care), sixteen percent in training, 2.5 percent unemployed and 3.5 percent unable to work. Of the employees, 76 percent worked in agriculture (as of 2012).
AgricultureOf the 227,000 families involved in agriculture, 93 percent grew corn, 79 percent cassava, 39 percent bananas, and 17 percent rice. More than a third of these households also kept pets. The largest numbers of farm animals were poultry and goats (as of 2012). |
 |
Infrastructure
- Road: The region has a road network of 1781 kilometers in length. Of these, 468 kilometers are main roads and 592 kilometers are regional roads that are maintained by the state. The responsible district is responsible for the 713 kilometers of secondary roads. The most important road connections are three national roads: to the northeast to Lake Victoria , to the east via Tabora and Dodoma to Dar es Salaam and to the southeast via Mpanda to Lake Malawi .
- Railway: The Tanganyika Railway connects Kigoma via Dodoma with the port of Dar es Salaam . The line is designed as a 1000 millimeter narrow-gauge railway and is 1254 kilometers long. It was built in colonial times and completed in 1914.
- Shipping: In Kigoma there is a port on Lake Tanganyika that offers connections to Bujumbura (Burundi), Kalemie (Democratic Republic of the Congo) and Mpulungu (Zambia).
Nature reserves, sights
- Gombe Stream National Park : This area was designated as a nature reserve in 1943 and declared a national park in 1968. It is located sixteen kilometers north of the city of Kigoma and is 56 square kilometers in size. He became known because Jane Goodall carried out research with chimpanzees here.
- Mahale Mountains National Park : The 1613 square kilometer montane rainforest lies on the shores of Lake Tanganyika. Due to the lush vegetation there are no roads, only forest paths. The park contains 73 species of mammals, nine species of primate, including a chimpanzee population.
- Moyowosi Game Reserve: This game reserve is a 6,000 square kilometer hunting area that was established in 1981. It is known for its abundance of buffalo, giraffes, antelopes, hippos and crocodiles.
- Lake Tanganyika: With a length of 660 kilometers, the lake is the longest and, with a depth of 1,436 meters, the second deepest lake on earth. It marks the southern end of the western Great African Rift Valley . The lake is also known for its large variety of brightly colored cichlids .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Kigoma Region, History. The United Republic of Tanzania, accessed November 3, 2019 (Swahili).
- ↑ a b Kigoma Region, Socio-Economic Profile. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, December 1998, pp. 2–5 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Climate Data, Kigoma. Retrieved November 3, 2019 .
- ↑ 50 years of the declaration of independence in Tanzania. (PDF) pp. 4–6 , accessed on November 3, 2019 (Swahili).
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 16 Kigoma Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, p. 16 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ↑ Home | Districts | KIGOMA REGION. Retrieved December 16, 2019 .
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 16 Kigoma Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, pp. 19, 63 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Kigoma Region, Socio-Economic Profile. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, December 1998, pp. 150–151 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 16 Kigoma Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, p. 69 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Kigoma Region, Water. The United Republic of Tanzania, accessed November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 16 Kigoma Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, pp. 94–95 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 16 Kigoma Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, pp. 128–130 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Kigoma Region, Socio-Economic Profile. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, December 1998, p. 112 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Trunk Roads Network. (PDF) Retrieved November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Modal Choice between Rail and Road Transportation, Evidence from Tanzania. (PDF) World Bank Group, August 2017, pp. 7–8 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Kigoma Region, Socio-Economic Profile. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, December 1998, pp. 121–122 , accessed on November 3, 2019 .
- ^ Gombe Stream National Park. Retrieved November 4, 2019 .
- ^ Mahale Mountains National Park. Retrieved November 4, 2019 .
- ↑ Moyowosi Game Reserve. Retrieved November 4, 2019 .
- ↑ Lake Tanganyika. Encyclopaedia Britannica, accessed November 4, 2019 .
- ↑ Lake Tanganyika Cichlids. Retrieved November 4, 2019 .







