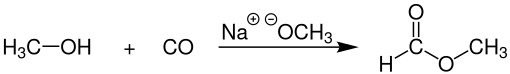Formic acid methyl ester
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Formic acid methyl ester | |||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 4 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pleasant odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 60.05 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.97 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−100 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
32 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1,344 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG : 120 mg m −3 or 50 ml m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−386.1 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Formic acid methyl ester (according to IUPAC nomenclature: methyl methanoate , also known as methyl formate ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of carboxylic acid esters .
Extraction and presentation
Industrial synthesis
Methyl formate is produced on an industrial scale by carbonylating methanol with carbon monoxide at temperatures of 70-100 ° C. and pressures of 50-65 bar. Metal alcoholates such as sodium or potassium methoxide are usually used as catalysts . The complete reaction takes place in a cascade of bubble column reactors , in which the liquid methanol is guided in cocurrent against the carbon monoxide gas . The work-up is carried out by distillation using a rectification column .
Laboratory scale
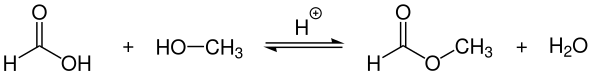
Smaller amounts can be synthesized in the laboratory by the acid-catalyzed esterification of formic acid with methanol , but only with limited yield.
In more recent work, methyl formate is obtained by oxidative coupling of methanol to nanoporous gold as a catalyst at low temperatures and with high selectivity .
properties
Physical Properties
Methyl formate has a density of 0.97 g cm −3 at 20 ° C, a relative gas density of 2.07 (density ratio to dry air at the same temperature and pressure) and a relative density of the steam-air mixture of 1, 66 (density ratio to dry air at 20 ° C and normal pressure ). At 20 ° C it has a vapor pressure of 638 hPa (950 hPa at 30 ° C and 1400 hPa at 40 ° C).
Chemical properties
Formic acid methyl ester is an extremely flammable liquid from the group of carboxylic acid esters . The ester dissolves well in water at 300 g / l at 20 ° C., whereby it is hydrolyzed. In addition, a solution of 200 g · l −1 at a temperature of 20 ° C has a pH value of 4 - 5.
use
Methyl formate is used as a solvent for fats , oils , fatty acids , cellulose esters and acrylic resins . It is also an intermediate in organic syntheses (e.g. formamide and dimethylformamide ) and is a precursor in the production of formic acid . Furthermore, methyl formate is used as a binder in the foundry industry (beta-set process) and is used as a blowing agent for various polymers . It is also used as a refrigerant ( R611 ) and as a pesticide for tobacco and dried fruits as well as for combating grain beetles .
Diphosgene can also be produced from methyl formate by chlorinating it under UV light :
safety instructions
Methyl formate is an extremely flammable, highly volatile liquid. The vapors form explosive mixtures with air. The main routes of absorption of methyl formate and its vapors are via the respiratory tract and the skin . The main acute modes of action are irritation of the eyes and respiratory tract ; at high concentrations, lung damage is possible. Methyl formate has a lower explosion limit of approx. 5.0% by volume (120 g / cm 3 ) and an upper explosion limit of approx. 23.0% by volume (570 g / cm 3 ). The ignition temperature is 450 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2 and explosion group IIA. The limit gap width was determined to be 0.94 mm. With a flash point of −27 ° C, methyl formate is very easily flammable.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Entry on methyl formate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 29, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on methyl formate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on 29 December 2018 .
- ^ Wilhelm Riemenschneider, Hermann M. Bolt: Esters, Organic. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley ‐ VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA., April 30, 2005, p. 247, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a09_565.pub2 .
- ↑ Entry on methyl formats in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 29, 2018. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-22.
- ^ Daniel Schneider, Klaus-Dieter Mohl, Martin Schäfer, Jürgen Paschold, Joaquim Henrique Teles, Stefan Rittinger: Process for the production of methyl formate by reacting methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system that contains alkali metal formate and alkali alcoholate. In: Google Patents. BASF SE, January 18, 2017, accessed April 2, 2019 .
- ^ Portal for Organic Chemistry: Gold Catalysis
- ↑ A. Wittstock, V. Zielasek, J. Biener, CM Friend, M. Bäumer: Nanoporous Gold Catalysts for Selective Gas-phase Oxidative Coupling of methanol at Low Temperature , Science, 327 (2010) No. 5963, pp. 319-322; doi : 10.1126 / science.1183591 .
- ↑ Pure methyl formate. In: BASF product search. BASF SE, 2014, accessed on December 29, 2018 (German, English).
- ↑ Formic acid methyl ester. In: Chemical Dictionary. May 10, 2000, accessed December 29, 2018 .