Nickel arsenide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||
| __ Ni 3+ __ As 3− | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Nickel arsenide | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | NiAs | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 133.62 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| density |
7.57 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
968 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Nickel arsenide NiAs is a compound of the elements nickel and arsenic and exists as a red metallic solid. NiAs is the prototype of an AB structure with hexagonal close packing of spheres .
Occurrence
Nickel arsenide occurs as a mineral nickel line (also nickelite or red nickel pebbles ), but in which there are also fluctuating proportions of iron , sulfur and antimony .
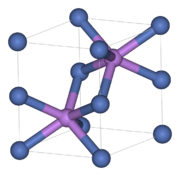
Nickel arsenide structure
The NiAs structure with its hexagonal close packing of spheres (layer sequence ABAB) of the " anions " represents the most common AB structure type after the cubic NaCl structure , which many chalcogenides , arsenides , antimonides and bismuthides of the transition metals adopt. The bond between nickel and arsenic has only a small ionic content and already has a strong metallic character. NiAs crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system in the space group P 6 3 / mmc (space group no. 194) . The unit cell has the lattice parameters a = b = 361.8 pm , c = 503.4 pm, α = β = 90 ° and γ = 120 °. The nickel “ cations ” are located in the octahedral gaps of the hexagonal closest packing formed by six arsenic “anions”, while the arsenic atoms are surrounded by six nickel atoms, which in turn form a trigonal prism. This results in a coordination number of 6 for both types of atoms (coordination = 6: 6). The relationship between the NiAs structure and the hexagonal cadmium iodide structure is that if the cations are omitted in every second octahedral layer, an AB2 layer structure of the CdI 2 type is created.
The following inorganic compounds or minerals crystallize in the NiAs structure:
- Monochalcogenides of the transition metals of the 4th period :
- Numerous pnictogenides (compounds with anions of the 5th main group):
- Phosphides : VP
- Arsenides : TiAs, MnAs, CoAs, NiAs
- Antimonides : TiSb, VSb, CrSb, MnSb, FeSb, CoSb, NiSb , IrSb, PdSb, PtSb
- Bismutides : MnBi, NiBi, RhBi, InBi, PtBi
- Other minerals: langistite (Co, Ni) As, pyrrhotite Fe 1-x S, stumpflite Pt (Sb, Bi), sudburyite (Pd, Ni) Sb
Properties, use and safety information
Nickel arsenide is used as a catalyst in the removal of metal contaminants from hydrocarbons . Due to its acute toxicity, all contact, e.g. B. the skin and eyes, with nickel arsenide can be avoided. The release of even more toxic nickel compounds in the event of fire or through acids is particularly dangerous. In contrast to many other nickel compounds, nickel arsenide does not seem to have a carcinogenic effect in some animal experiments, but it has been shown to be carcinogenic for humans. Despite the insolubility of nickel arsenide in water, the compound poses a great danger to aquatic organisms.
Individual evidence
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1716.
- ↑ a b c Safety data sheet ( Memento of the original dated September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Entry for CAS no. 27016-75-7 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ Entry on nickel arsenide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .
- NN Greenwood, A. Earnshaw: Chemistry of the Elements. 1., corr. Edition. VCH, Weinheim / Basel / Cambridge / New York 1990, ISBN 3-527-26169-9 .
Web links
- Interactive crystal structure page (English, largely self-explanatory)
- Using as a catalyst NiAs (Engl.)
- Information about the carcinogenic potential (Engl.)