Tricyclodecane dimethanol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Mixture of isomers | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tricyclodecane dimethanol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 20 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, viscous liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 196.29 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.136 g cm −3 at 20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
18 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
334.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
<1 h Pa at 20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (11 g · l at 20 ° C) and miscible with polar organic solvents |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.520 (50 ° C, 589 nm) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Tricyclodecanedimethanol is the isomer mixture of primary diols with the basic structure of a tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene formed in the hydroformylation of dicyclopentadiene and subsequent hydrogenation . Due to its interesting fluid dynamic and optical properties, TCD-DM is suitable as a diol component in polyesters and polyurethanes and as a molecular building block for (meth) acrylate monomers.
Occurrence and representation
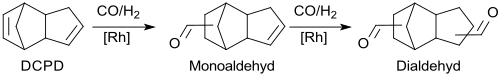
As a non-conjugated diene , dicyclopentadiene DCPD can be hydroformylated to monoaldehyde and further to dialdehyde in stages using the oxo synthesis developed by Otto Roelen using carbon monoxide and hydrogen under homogeneous catalysis with rhodium in aromatic solvents.
Intermediate rhodium hydridocarbonyls interact with the isolated double bonds in the rigid dicyclopentadiene framework from the top and bottom of the ring system and carbon monoxide is inserted into the rhodium-alkyl bond formed. Hydrogen then displaces the acyl complex formed with regeneration of the rhodium hydridocarbonyl and formation of TCD-dicarbaldehyde.
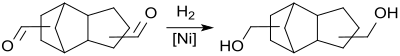
The direct hydrogenation without separation of the homogeneously dissolved rhodium catalyst and without prior isolation of the thermally labile dialdehyde takes place over heterogeneous nickel fixed bed catalysts, the addition of small amounts of water leading to significantly higher yields (approx. 80%, based on DCPD).
The product is separated off and purified by vacuum distillation.
Isomerism
The tricyclic diol tricyclodecanedimethanol is - like its precursor tricyclodecanedicarbaldehyde - a mixture of a total of 32 possible isomers that result from the regio- and stereochemically unselective hydroformylation of dicyclopentadiene, which in turn is a mixture of exo- and endo-isomers. Eight (4 × 2) stereoisomers can each be assigned to the four regioselective isomers (I - IV) - the attack occurs from above the main molecular level (blue arrows) and / or from below (green arrows).
properties
The compound is a colorless liquid with a mild odor that dissolves somewhat in water and does well in polar organic solvents such as organic solvents. B. alcohols, dissolves.
Prolonged storage at temperatures around the pour point of 18 ° C creates cloudiness due to crystallizing isomers. Thanks to the rigid and compact molecular structure of the bridged cycloaliphatic TCD diol isomers, the derivatives formed from them have a number of special mechanical and optical properties.
The refractive index of TCD-DM is very high for a non-aromatic and halogen-free liquid and the viscosity at room temperature is a considerable 14 · 10 6 mPa · s. It is therefore advisable to process TCD-Diol at elevated temperatures or in solution.
Applications
Tricyclodecanedimethanol is used because of its mechanical, e.g. B. adhesion, and optical properties, e.g. B. UV resistance, as an adhesion promoter in high quality clear coats , z. B. proposed for automotive refinishing.
As a diol component, TCD-Diol gives (unsaturated) homo- and copolymeric polyesters , polyurethanes and polycarbonates advantageous properties, such as e.g. B. improved aging resistance, reduced tendency to yellowing, higher heat resistance, low tendency to shrink, increased flexibility with high breaking strength. Polyurethanes with TCD-DM show, because of their lower glass transition temperatures, greater flexibility in the cold and significantly lower permeability for water vapor.
Due to its relatively low viscosity, the diester with acrylic acid is also a suitable monomer for 3D printing , which can be polymerized by UV or electron irradiation.
The resulting polyacrylates are used as dental plastics because of their high crosslinking speed, great hardness, low tendency to shrink and good adhesion properties. The high refractive index makes the TCD diol diacrylate for optical, e.g. B. for eyeglass lenses, and for optoelectronic applications, e.g. B. interesting for optical fibers and coatings.
literature
- Boy Cornils : hydroformylation (oxo synthesis). In: J. Falbe, U. Hasserodt: catalysts, tensides and mineral oil additives , Georg Thieme Verlag, 1978, ISBN 3-13-552601-1 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on tricyclo [5.2.1.0 (2,6)] decanedimethanol, mixture of isomers in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on May 4, 2020 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ a b c d H. Lange, M. Popp, M. Redetzky: Three times faster at the gel point . In: Adhaes Kleb Dicht . tape 60 , no. 6 , 2016, p. 26-31 , doi : 10.1007 / s35145-016-0029-8 .
- ↑ a b c Safety Data Sheet: TCD Alcohol DM. Oxea, July 4, 2018, accessed on May 4, 2020 .
- ↑ Patent DE849548 : Process for the production of oxygen-containing compounds. Published on September 20, 1938 , applicant: Chemische Verwertungsgesellschaft Oberhausen mbH, inventor: O. Roelen.
- ↑ Patent DE1618384 : Process for the preparation of tricyclodecane-dimethylols by hydroformylation of dicyclopentadiene over rhodium-containing catalysts and subsequent hydrogenation to give the corresponding diols. Registered on March 10, 1967 , published on September 16, 1971 , applicant: Ruhrchemie AG, inventor: J. Falbe.
- ↑ Patent EP1604966B1 : Process for the preparation of tricyclo- [5.2.1.0 2,6] -decanedimethylol. Registered on May 31, 2005 , published on January 16, 2013 , applicant: OXEA GmbH, inventor: W. Dukat, E. Storm, K. Schmid.
- ↑ Patent EP1323795A1 : Radiation curable compositions for pigmented liquid inks. Filed December 20, 2001 , published July 2, 2003 , Applicant: UCB SA, Inventors: F. Bergiers, I. Bhattacharya, L. Lindekens, S. van den Branden.
- ↑ Patent EP1163303B1 : The use of tricyclodecane dimethanol for the production of multi-layer coatings . Registered on February 21, 2000 , published on June 16, 2004 , applicant: BASF Coatings AG, inventor: H. Baumgart, H.-P. Rink, U. Roeckrath, T. Farwick.
- ↑ Patent WO9638486A1 : High index / high Abbe number composition. Filed May 24, 1996 , published December 5, 1996 , applicant: Sola International Holdings Ltd., inventor: HK Toh, IR Bateman, DR Diggins, BG Cieslinski.