Fevipiprant: Difference between revisions
consistent citation formatting |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Chemical compound}} |
|||
{{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} |
|||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
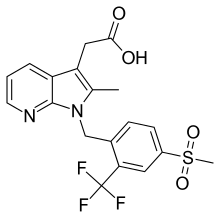
| IUPAC_name = {2-methyl-1-[4-(methylsulfonyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-1''H''-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl}acetic acid |
| IUPAC_name = {2-methyl-1-[4-(methylsulfonyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-1''H''-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl}acetic acid |
||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
||
| bioavailability = Unaffected by food<ref name="pmid27310331">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, |
| bioavailability = Unaffected by food<ref name="pmid27310331">{{cite journal | vauthors = Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, Sandham D, Dubois G, Elbast W, Goldsmith P, Weiss M | title = Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Novel CRTh2 Receptor Antagonist: Results From 2 Randomized, Phase 1, Placebo-Controlled Studies in Healthy Volunteers | journal = Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development | volume = 5 | issue = 4 | pages = 306–313 | date = July 2016 | pmid = 27310331 | pmc = 5071756 | doi = 10.1002/cpdd.244 }}</ref> |
||
| metabolism = Hepatic [[glucuronidation]] |
| metabolism = Hepatic [[glucuronidation]] |
||
| elimination_half-life = ~20 hours |
| elimination_half-life = ~20 hours |
||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
<!--Chemical data--> |
<!--Chemical data--> |
||
| C=19 | H=17 | F=3 | N=2 | O=4 | S=1 |
| C=19 | H=17 | F=3 | N=2 | O=4 | S=1 |
||
| molecular_weight = 426.41 g/mol |
|||
| smiles = CC1=C(C2=C(N1CC3=C(C=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)C)C(F)(F)F)N=CC=C2)CC(=O)O |
| smiles = CC1=C(C2=C(N1CC3=C(C=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)C)C(F)(F)F)N=CC=C2)CC(=O)O |
||
| StdInChI=1S/C19H17F3N2O4S/c1-11-15(9-17(25)26)14-4-3-7-23-18(14)24(11)10-12-5-6-13(29(2,27)28)8-16(12)19(20,21)22/h3-8H,9-10H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26) |
| StdInChI=1S/C19H17F3N2O4S/c1-11-15(9-17(25)26)14-4-3-7-23-18(14)24(11)10-12-5-6-13(29(2,27)28)8-16(12)19(20,21)22/h3-8H,9-10H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Fevipiprant''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]; code name '''QAW039''') is a [[pharmaceutical drug|drug]] being developed by [[Novartis]] |
'''Fevipiprant''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]; code name '''QAW039''') is a [[pharmaceutical drug|drug]] of the [[piprant]] class that was being developed by [[Novartis]]. It is a selective, orally available [[receptor antagonist|antagonist]] of the [[prostaglandin DP2 receptor|prostaglandin D<sub>2</sub> receptor 2]] (DP<sub>2</sub> or CRTh2).<ref name="pmid27310331"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sykes DA, Bradley ME, Riddy DM, Willard E, Reilly J, Miah A, Bauer C, Watson SJ, Sandham DA, Dubois G, Charlton SJ | title = Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy | journal = Molecular Pharmacology | volume = 89 | issue = 5 | pages = 593–605 | date = May 2016 | pmid = 26916831 | doi = 10.1124/mol.115.101832 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid27354118">{{cite journal | vauthors = Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, Osuntokun W, Goldsmith P, Weiss M, Beier J | title = The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma | journal = Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics | volume = 39 | pages = 54–63 | date = August 2016 | pmid = 27354118 | doi = 10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005 }}</ref> |
||
Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy. ''Mol Pharmacol''. 2016 May;89(5):593-605. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.101832 PMID 26916831</ref><ref name="pmid27354118">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, etal | title=The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma | journal=Pulm Pharmacol Ther | year= 2016 | volume= 39 | issue= | pages= 54–63 | pmid=27354118 | doi=10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005}} </ref> |
|||
By 2016 it had advanced to [[phases of clinical research|phase III]]<ref>{{ClinicalTrialsGov|NCT02555683|A 52-week, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of QAW039 when Added to Existing Asthma Therapy in Patients with Uncontrolled Severe Asthma|date = 4 May 2020}}</ref> [[clinical trial]]s for the treatment of [[asthma]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gonem S, Berair R, Singapuri A, Hartley R, Laurencin MF, Bacher G, Holzhauer B, Bourne M, Mistry V, Pavord ID, Mansur AH, Wardlaw AJ, Siddiqui SH, Kay RA, Brightling CE | title = Fevipiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 antagonist, in patients with persistent eosinophilic asthma: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial | journal = The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine | volume = 4 | issue = 9 | pages = 699–707 | date = September 2016 | pmid = 27503237 | doi = 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30179-5 | hdl-access = free | hdl = 2381/38430 }}</ref> However, in 2019 Novartis announced that it was removing fevipiprant from its development program, given that the medicine has failed in two clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The firm said that it had hoped fevipiprant would be a billion-dollar-selling asthma drug.<ref>{{Cite news |date=2019-12-16 |title=Novartis drops asthma drug fevipiprant after trial failures |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-novartis-asthma-idUSKBN1YK0DR |access-date=2023-05-09}}</ref> |
|||
A 2021 analysis sponsored by Novartis of the two phase III trials of fevipiprant concluded that "The ZEAL studies did not demonstrate significant improvement in lung function or other clinical outcomes. These results suggest that DP2 receptor inhibition with fevipiprant is not effective in the studied patient population".<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Castro M, Kerwin E, Miller D, Pedinoff A, Sher L, Cardenas P, Knorr B, Lawrence D, Ossa D, Wang W, Maspero JF | title = Efficacy and safety of fevipiprant in patients with uncontrolled asthma: Two replicate, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (ZEAL-1 and ZEAL-2) | journal = EClinicalMedicine | volume = 35 | pages = 100847 | date = May 2021 | pmid = 33997741 | pmc = 8099656 | doi = 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100847 }}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Prostaglandin DP2 receptor]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Grapiprant]] |
|||
* [[Setipiprant]] |
* [[Setipiprant]] |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
[[Category:Antiasthmatic drugs]] |
[[Category:Antiasthmatic drugs]] |
||
[[Category:Receptor antagonists]] |
[[Category:Receptor antagonists]] |
||
[[Category:Benzosulfones]] |
|||
[[Category:Carboxylic acids]] |
|||
[[Category:Trifluoromethyl compounds]] |
|||
[[Category:Abandoned drugs]] |
|||
{{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} |
{{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} |
||
Latest revision as of 06:10, 29 April 2024
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unaffected by food[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | ~20 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (≤30%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.911 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H17F3N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 426.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fevipiprant (INN; code name QAW039) is a drug of the piprant class that was being developed by Novartis. It is a selective, orally available antagonist of the prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTh2).[1][2][3]
By 2016 it had advanced to phase III[4] clinical trials for the treatment of asthma.[5] However, in 2019 Novartis announced that it was removing fevipiprant from its development program, given that the medicine has failed in two clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The firm said that it had hoped fevipiprant would be a billion-dollar-selling asthma drug.[6]
A 2021 analysis sponsored by Novartis of the two phase III trials of fevipiprant concluded that "The ZEAL studies did not demonstrate significant improvement in lung function or other clinical outcomes. These results suggest that DP2 receptor inhibition with fevipiprant is not effective in the studied patient population".[7]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, et al. (July 2016). "Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Novel CRTh2 Receptor Antagonist: Results From 2 Randomized, Phase 1, Placebo-Controlled Studies in Healthy Volunteers". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development. 5 (4): 306–313. doi:10.1002/cpdd.244. PMC 5071756. PMID 27310331.
- ^ Sykes DA, Bradley ME, Riddy DM, Willard E, Reilly J, Miah A, et al. (May 2016). "Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy". Molecular Pharmacology. 89 (5): 593–605. doi:10.1124/mol.115.101832. PMID 26916831.
- ^ Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, et al. (August 2016). "The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma". Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 39: 54–63. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005. PMID 27354118.
- ^ Clinical trial number NCT02555683 for "A 52-week, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of QAW039 when Added to Existing Asthma Therapy in Patients with Uncontrolled Severe Asthma" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ^ Gonem S, Berair R, Singapuri A, Hartley R, Laurencin MF, Bacher G, et al. (September 2016). "Fevipiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 antagonist, in patients with persistent eosinophilic asthma: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial". The Lancet. Respiratory Medicine. 4 (9): 699–707. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30179-5. hdl:2381/38430. PMID 27503237.
- ^ "Novartis drops asthma drug fevipiprant after trial failures". Reuters. 2019-12-16. Retrieved 2023-05-09.
- ^ Castro M, Kerwin E, Miller D, Pedinoff A, Sher L, Cardenas P, et al. (May 2021). "Efficacy and safety of fevipiprant in patients with uncontrolled asthma: Two replicate, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (ZEAL-1 and ZEAL-2)". EClinicalMedicine. 35: 100847. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100847. PMC 8099656. PMID 33997741.
