Fevipiprant: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
Added additional, referenced information from just-released Reuters News article (Dec 15-16/2019). Basel-based Novartis has decided to give up on Fevipiprant, given how this drug has now failed two more important clinicial trials (this time for moderate-to-severe-asthma patients). This organohalogen drug is thus being jettisoned from this company's development program. |
m Journal cites:, templated 1 journal cites |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
||
| bioavailability = Unaffected by food<ref name="pmid27310331">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, etal | title=Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Novel CRTh2 Receptor Antagonist: Results From 2 Randomized, Phase 1, Placebo-Controlled Studies in Healthy Volunteers | journal=Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev | year= 2016 | volume= 5 | issue= 4 | pages= 306–13 | pmid=27310331 | doi=10.1002/cpdd.244 | pmc=5071756}} |
| bioavailability = Unaffected by food<ref name="pmid27310331">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, etal | title=Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Novel CRTh2 Receptor Antagonist: Results From 2 Randomized, Phase 1, Placebo-Controlled Studies in Healthy Volunteers | journal=Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev | year= 2016 | volume= 5 | issue= 4 | pages= 306–13 | pmid=27310331 | doi=10.1002/cpdd.244 | pmc=5071756}}</ref> |
||
| metabolism = Hepatic [[glucuronidation]] |
| metabolism = Hepatic [[glucuronidation]] |
||
| elimination_half-life = ~20 hours |
| elimination_half-life = ~20 hours |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Fevipiprant''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]; code name '''QAW039''') is a [[pharmaceutical drug|drug]] being developed by [[Novartis]] which acts as a selective, orally available [[receptor antagonist|antagonist]] of the [[prostaglandin DP2 receptor|prostaglandin D<sub>2</sub> receptor 2]] (DP<sub>2</sub> or CRTh2).<ref name="pmid27310331"/><ref>Sykes DA, Bradley ME, Riddy DM, Willard E, Reilly J, Miah A, Bauer C, Watson SJ, Sandham DA, Dubois G, Charlton SJ. |
'''Fevipiprant''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]; code name '''QAW039''') is a [[pharmaceutical drug|drug]] being developed by [[Novartis]] which acts as a selective, orally available [[receptor antagonist|antagonist]] of the [[prostaglandin DP2 receptor|prostaglandin D<sub>2</sub> receptor 2]] (DP<sub>2</sub> or CRTh2).<ref name="pmid27310331"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sykes DA, Bradley ME, Riddy DM, Willard E, Reilly J, Miah A, Bauer C, Watson SJ, Sandham DA, Dubois G, Charlton SJ | date = May 2016 | title = Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy | url = | journal = Mol Pharmacol | volume = 89 | issue = 5| pages = 593–605 | doi = 10.1124/mol.115.101832 | pmid = 26916831 }}</ref><ref name="pmid27354118">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, etal | title=The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma | journal=Pulm Pharmacol Ther | year= 2016 | volume= 39 | issue= | pages= 54–63 | pmid=27354118 | doi=10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005}}</ref> |
||
Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy. ''Mol Pharmacol''. 2016 May;89(5):593-605. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.101832 {{PMID|26916831}}</ref><ref name="pmid27354118">{{cite journal|vauthors=Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, etal | title=The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma | journal=Pulm Pharmacol Ther | year= 2016 | volume= 39 | issue= | pages= 54–63 | pmid=27354118 | doi=10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005}} </ref> |
|||
{{As of|2016}}, it is in [[phases of clinical research|phase III]]<ref>https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02555683</ref> [[clinical trial]]s for the treatment of [[asthma]].<ref>{{cite journal|vauthors=Gonem S, Berair R, Singapuri A, Hartley R, Laurencin M, Bacher G, etal | title=Fevipiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 antagonist, in patients with persistent eosinophilic asthma: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial | journal=Lancet Respir Med | year=2016 | volume= 4| issue= 9| pages= 699–707| pmid= 27503237| doi=10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30179-5| hdl=2381/38430 }}</ref> |
{{As of|2016}}, it is in [[phases of clinical research|phase III]]<ref>https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02555683</ref> [[clinical trial]]s for the treatment of [[asthma]].<ref>{{cite journal|vauthors=Gonem S, Berair R, Singapuri A, Hartley R, Laurencin M, Bacher G, etal | title=Fevipiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 antagonist, in patients with persistent eosinophilic asthma: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial | journal=Lancet Respir Med | year=2016 | volume= 4| issue= 9| pages= 699–707| pmid= 27503237| doi=10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30179-5| hdl=2381/38430 }}</ref> |
||
On Monday, December 16, 2019, Switzerland-based Novartis officially announced that it was jettisoning fevipiprant from its development program, given that the medicine has failed in two additional clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The firm said that it had hoped fevipiprant would be a billion-dollar-selling asthma drug. |
On Monday, December 16, 2019, Switzerland-based Novartis officially announced that it was jettisoning fevipiprant from its development program, given that the medicine has failed in two additional clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The firm said that it had hoped fevipiprant would be a billion-dollar-selling asthma drug.<ref>Novartis drops asthma drug fevipiprant after trial failures. Reuters News. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-novartis-asthma/novartis-drops-asthma-drug-fevipiprant-after-trial-failures-idUSKBN1YK0DR - Accessed Sunday, December 15, 2019, from North America.</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 54: | Line 53: | ||
[[Category:Carboxylic acids]] |
[[Category:Carboxylic acids]] |
||
[[Category:Trifluoromethyl compounds]] |
[[Category:Trifluoromethyl compounds]] |
||
{{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} |
{{respiratory-system-drug-stub}} |
||
Revision as of 11:27, 15 April 2020
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unaffected by food[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | ~20 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (≤30%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.911 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
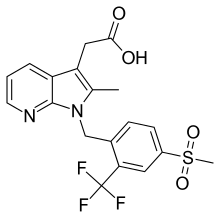
| Formula | C19H17F3N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 426.41 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fevipiprant (INN; code name QAW039) is a drug being developed by Novartis which acts as a selective, orally available antagonist of the prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTh2).[1][2][3]
As of 2016[update], it is in phase III[4] clinical trials for the treatment of asthma.[5]
On Monday, December 16, 2019, Switzerland-based Novartis officially announced that it was jettisoning fevipiprant from its development program, given that the medicine has failed in two additional clinical trials in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The firm said that it had hoped fevipiprant would be a billion-dollar-selling asthma drug.[6]
See also
References
- ^ a b Erpenbeck VJ, Vets E, Gheyle L, Osuntokun W, Larbig M, Neelakantham S, et al. (2016). "Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Novel CRTh2 Receptor Antagonist: Results From 2 Randomized, Phase 1, Placebo-Controlled Studies in Healthy Volunteers". Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 5 (4): 306–13. doi:10.1002/cpdd.244. PMC 5071756. PMID 27310331.
- ^ Sykes DA, Bradley ME, Riddy DM, Willard E, Reilly J, Miah A, Bauer C, Watson SJ, Sandham DA, Dubois G, Charlton SJ (May 2016). "Fevipiprant (QAW039), a Slowly Dissociating CRTh2 Antagonist with the Potential for Improved Clinical Efficacy". Mol Pharmacol. 89 (5): 593–605. doi:10.1124/mol.115.101832. PMID 26916831.
- ^ Erpenbeck VJ, Popov TA, Miller D, Weinstein SF, Spector S, Magnusson B, et al. (2016). "The oral CRTh2 antagonist QAW039 (fevipiprant): A phase II study in uncontrolled allergic asthma". Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 39: 54–63. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2016.06.005. PMID 27354118.
- ^ https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02555683
- ^ Gonem S, Berair R, Singapuri A, Hartley R, Laurencin M, Bacher G, et al. (2016). "Fevipiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 antagonist, in patients with persistent eosinophilic asthma: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial". Lancet Respir Med. 4 (9): 699–707. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30179-5. hdl:2381/38430. PMID 27503237.
- ^ Novartis drops asthma drug fevipiprant after trial failures. Reuters News. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-novartis-asthma/novartis-drops-asthma-drug-fevipiprant-after-trial-failures-idUSKBN1YK0DR - Accessed Sunday, December 15, 2019, from North America.
