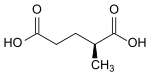
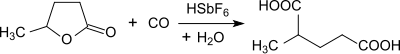2-methylglutaric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| ( R ) -2-methylglutaric acid (left) or ( S ) -2-methylglutaric acid (right) | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | 2-methylglutaric acid | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 10 O 4 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
white to slightly reddish-yellow crystal powder |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 146.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
2-methylglutaric acid ( 2-methylpentanedioic acid ) is a water-soluble α, ω- dicarboxylic acid , which is derived from glutaric acid and has a methyl group in the 2-position . The chiral dicarboxylic acid obtained as a racemate during the synthesis is easily accessible from γ-valerolactone , a platform chemical made from renewable raw materials .
Manufacturing
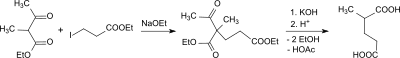
The first synthesis of 2-methylglutaric acid was reported as early as 1878. The reaction of 2-methyl-3-oxo-butanoic acid ethyl ester (ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate) with 3-iodopropionic acid ethyl ester produces the corresponding β-keto ester, which after acid cleavage with concentrated potassium hydroxide solution and subsequent acidification with dilute sulfuric acid in acetic acid and 2-methylglutaric acid passes over.
The synthesis of 2-methylglutaric acid from levulinic acid - the precursor of γ-valerolactone - was described in 1886. The addition of hydrocyanic acid to levulinic acid leads to the corresponding cyanohydrin 4-hydroxy-4-cyanovaleric acid. The cyano group is hydrolyzed to the carboxy group with dilute sulfuric acid and dehydrated to 2-methyl-pent-2-enoic acid, which is then hydrogenated to 2-methylpentanoic acid.
Also in 1886, the reaction of γ-valerolactone with hydrogen cyanide to cyanovaleric acid and further to 2-methylglutaric acid was described.
In a synthesis route also published in 1896, analogous to the Wislicenus synthesis of 1878, instead of the methyl-substituted acetoacetic ester, the dimethyl ester of methylmalonic acid with dimethyl 3-iodopropionate is converted into a triester in a malonic ester synthesis with sodium methoxide and then hydrolyzed with sulfuric acid to form 2-methylglutaric acid.
A variant of this synthesis route is the Michael addition of diethyl malonate to ethyl methacrylate in the presence of sodium ethoxide . The triester obtained is hydrolyzed with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
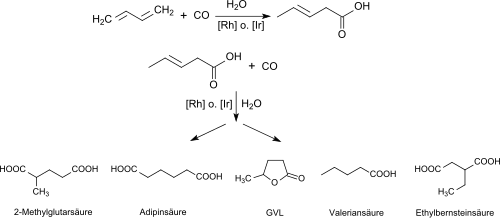
The hydrocarboxylation of 1,3-butadiene carried out on an industrial scale with carbon monoxide in the presence of rhodium catalysts and hydrogen iodide as a promoter leads to 3-pentenoic acid in the first step and, in a further reaction with CO in the presence of rhodium complexes, methyl iodide as promoter, dichloromethane and small amounts of water or in the presence of iridium complexes, hydrogen iodide, acetic acid and water (in addition to unreacted 3-pentenoic acid and the isomeric 2- and 4-pentenoic acid) to a mixture of adipic acid , γ-valerolactone, valeric acid , 2-ethylsuccinic acid, dimethylsuccinic acid and about 17% 2-methylglutaric acid.
This reaction has been intensively investigated as a route to adipic acid as a dicarboxylic acid building block for nylon 6,6 , but has not caught on because the yield of the target product is too low for commercial use.
From the technical mixture of the hydrocarboxylation, 2-methylglutaric acid z. B. isolate by vacuum distillation in the form of its cyclic anhydride (2-methylglutaric anhydride).
Analogous to the hydrocarboxylation of butadiene with CO, hydrocyanation with hydrogen cyanide on a palladium contact produces a mixture containing 2-methylglutaronitrile via the intermediate product 3-pentenenitrile , which mixture can be hydrolyzed to 2-methylglutaric acid.
A product mixture of similar composition is obtained from the reaction of γ-valerolactone with carbon monoxide in acetic acid solution with hydrogen bromide as a promoter.
Under standard reaction conditions (30 ° C, atmospheric pressure) for one hour, γ-valerolactone reacts with carbon monoxide in the presence of the (extremely toxic and caustic) superacid fluoro-antimonic acid HSbF 6 (in the molar ratio HF / SbF 5 1: 2.3) in almost quantitative yield to 2-methylglutaric acid.
properties
2-methylglutaric acid is an odorless, white, water-soluble solid that crystallizes in intergrown prisms. In the early literature, the acid was also described as being very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether . The chiral dicarboxylic acid is the product of chemical synthesis as a racemate.
Applications
Diester
Diesters of 2-methylglutaric acid, such as. B. dimethyl-2-methylglutarate are used as non-volatile and non-flammable, biodegradable solvents in detergents for industrial applications, such as. B. marketed in dry cleaning, but also in the household and in cosmetics.
Ester amides
From the diester of 2-methylglutaric acid - in industrial implementation preferably from the diesters of the dicarboxylic acid mixture obtained in the hydrocarboxylation of butadiene with CO - can be in high chemical selectivity at temperatures between 20 and 50 ° C in the presence of sodium methoxide in methanol with dimethylamine in 96% yield produce an ester amide mixture which is used as a solvent, e.g. B. for formulations of pesticides, has interesting properties. The patent application also describes the alternative synthesis of the ester amide mixture formed from 2-methylglutaric acid via its cyclic 2-methylglutaric anhydride, which is first reacted with methanol to form the monomethyl ester, the carboxylic acid function of which is converted with thionyl chloride into a carboxylic acid chloride , which then reacts with dimethylamine to form the ester amide . The order can also be reversed and the cyclic anhydride first reacted with dimethylamine.
polyester
2-Methylglutaric acid can also be used as a dicarboxylic acid component in addition to adipic acid for the production of aliphatic polyesters , which are characterized by the lack of formation of interfering cyclic oligomers and are suitable for the production of biodegradable fibers, films and objects.
Polyamides
Hexamethylenediamine polycondenses with 2-methylglutaric acid at 210 ° C in the presence of sodium hypophosphite as a heat stabilizer to give polyamides.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet 2-Methylglutaric acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 30, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-Methylglutaric acid from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 30, 2015 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on 2-Methylglutaric acid at TCI Europe, accessed on December 30, 2015.
- ↑ a b c K. Auwers: Studies in the group of succinic acids and glutaric acids, IV. About α-methylglutaric acid . In: Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 292 , no. 1 , 1896, p. 132-159 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18962920108 .
- ↑ Entry on 2-Methylglutaric acid in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed on January 28, 2016.
- ↑ a b c Johannes Wislicenus , L. Limpach: Synthesis of glutaric acid and α-methylglutaric acid with the aid of acetoacetic ester . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 192 , no. 1-2 , 1878, pp. 128-135 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18781920109 ( PDF ).
- ↑ K. Yan, Y. Yang, J. Chai, Y. Lu: Catalytic reactions of gamma-valerolactone: A platform to fuels and value-added chemicals . In: Appl. Catal. B: Environmental . tape 179 , 2015, p. 292-305 , doi : 10.1016 / j.apcatb.2015.04.030 .
- ↑ a b N. Yoneda, A. Suzuki, Y. Takahashi: Carboxylation of γ-butyrolactones with carbon monoxide using HF-SbF 5 super acid . In: Chem. Lett. 1981, p. 767-768 , doi : 10.1246 / cl / 1981.767 .
- ↑ K. Krekeler: About the Penthiophengruppe . In: Ber. German chem. Ges. Band 19 , no. 2 , 1886, p. 3266–3274 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.188601902359 ( PDF ).
- ↑ J. Block, K. Krekeler, B. Tollens: About the acids γ-methylhydroxyglutaric acid and methylglutolactonic acid formed from levulinic acid after addition of hydrocyanic acid . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 238 , no. 3 , 1887, p. 287-301 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18872380304 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Wilhelm Wislicenus : On the action of potassium cyan on lactones, II. Valerolactone and potassium cyan . In: Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 233 , no. 1 , 1886, p. 101-116 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18862330107 ( PDF ).
- ↑ K. Machiy, I. Ichimoto, K. Tonari, M. Kirihata, H. Ueda: An Efficient Synthetic Method for (±) -Malyngolide and Its Optical Resolution . In: Agric. Biol. Chem. Volume 49 , no. 6 , 1985, pp. 1767–1773 , doi : 10.1080 / 00021369.1985.10866953 .
- ↑ Patent US4622423 : Hydrocarboxylation of butadiene to 3-pentenoic acid. Applied November 9, 1984 , published November 11, 1986 , applicant: EI Du Pont de Nemours and Company, inventor: PM Burke.
- ↑ Patent US4788333 : Hydrocarboxylation of unsaturated carboxylic acids to linear dicarboxylic acids. Applied January 7, 1985 , published November 29, 1988 , applicant: EI Du Pont de Nemours and Company, inventor: PM Burke.
- ↑ Patent US5227522 : Preparation of adipic acid by hydrocarboxylation of pentenic acids. Applied April 24, 1992 , published July 13, 1993 , Applicant: Rhone-Poulenc Chimie, Inventor: P. Denis, J.-M. Grosselin, F. Metz.
- ↑ Patent US5587056 : Separation of aliphatic diacids from adipic acid admixtures thereof. Applied June 14, 1995 , published December 24, 1996 , Applicant: Rhone-Poulenc Chimie, Inventors: P. Denis, C. Patois, R. Perron.
- ↑ Patent US33496215 : Hydrocyanation of olefins using selected nickel phosphite catalysts. Filed on November 23, 1965 , published on February 17, 1970 , Applicant: you EI DuPont de Nemours and Co., Inventor: WC Drinkard, Jr., RV Lindsey, Jr
- ↑ Solvay: GPS Safety Summary, 2-methylglutaronitrile ( Memento of the original from August 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Patent US3752839 : Hydrocyanation olefins. Filed on July 2, 1970 , published on August 14, 1973 , Applicant: you EI DuPont de Nemours and Co., Inventor: WC Drinkard, Jr., RV Lindsey, Jr
- ↑ Patent EP0395038A2 : Preparation of adipic acid from lactones. Applied on April 26, 1990 , published October 31, 1990 , applicant: EI Du Pont de Nemours and Company, inventor: PM Burke.
- ↑ Solvay: GPS Safety Summary, Dimethyl 2-methylglutarate ( Memento of the original from August 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Patent US7863232B2 : Treatment / cleaning of textile materials utilizing formulations of branched carboxylic acid diesters. Filed July 16, 2008 , published January 4, 2011 , applicant: Rhodia Operations, inventor: J.-E. Zanetto, S. Nair, S. Mutoy.
- ↑ Patent US20130237722A1 : Process for preparing esteramide compounds. Registered on June 9, 2011 , published on September 12, 2013 , Applicant: Rhodia Operations, Inventors: T. Vidal, R. Rached, M. Guglieri.
- ↑ a b Patent US20140221211A1 : Use of esteramides as solvents, novel esteramides and process for preparing esteramides. Registered on April 9, 2014 , published on August 7, 2014 , applicant: Rhodia Operations, inventor: O. Jentzer, M. Guglieri.
- ↑ Patent WO2013153147A1 : Polyesters comprising 2-methylglutaric acid, process for production of the said polyesters and products obtained therewith. Filed April 11, 2013 , published October 17, 2013 , Applicant: Novamont SPA, Inventor: T. Milizia, R. Vallero.
- ↑ Patent WO9912993 : Manufacture of branched polyamides. Filed September 3, 1998 , published March 18, 1999 , applicant: Dupont Canada, Inc., inventor: H. Ng.