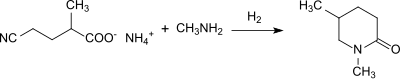2-methylglutaronitrile
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-methylglutaronitrile | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 8 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
clear colorless to brown liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 108.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.95 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−45 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.68 Pa (25 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water: 52.3 g / l (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.434 (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-methylglutaronitrile (MGN) is a racemic dinitrile with a pendant methyl group (α-methyl-valerodinitrile), which is obtained in the large-scale synthesis of adiponitrile and is the starting compound for the vitamin nicotinic acid amide and for the diester dimethyl, which is propagated as a "green" solvent 2-methylglutarate and esteramides is methyl 5- (dimethylamino) -2-methyl-5-oxopentanoate.
Occurrence and representation
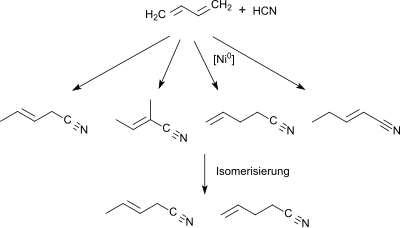
2-methylglutaronitrile is a by-product of the production of adiponitrile, the precursor of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid as building blocks for polyamide 6.6 .
Starting from 1,3-butadiene or a butadiene-rich (> 40 percent by volume) C4 cut from a naphtha steam cracker , the first stage is a hydrocyanation with Ni 0 - phosphine [PR 3 ] catalysts or phosphite [P (OR) 3 ] - or phosphonite [P (OR) 2 R] catalysts obtain a mixture of pentenenitriles which mainly contains trans-3-pentenenitrile in addition to the isomers 2-methyl-2-butenenitrile, 4-pentenenitrile and 2-pentenenitrile.
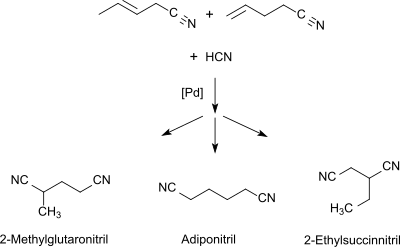
The mixture of monoolefinic C5 mononitriles is isomerized with a hydrocyanation catalyst and a Lewis acid , such as. B. ZnCl 2 is subjected to 3- and 4-pentenenitrile and reacted again in the third stage with hydrogen cyanide to form a mixture of dinitriles which contains adiponitrile and 2-ethylsuccinonitrile in addition to 2-methylglutaronitrile.
2-MGN can be separated from this by fractional distillation.
As an undesirable by-product of adiponitrile production, the 2-MGN-rich fraction with the typical composition of approx. 86% by weight of 2-MGN, 11% by weight of 2-ethylsuccinonitrile and 3% by weight of ADN was incinerated as waste.
properties
2-methylglutaronitrile is a very unpleasant smelling, clear, colorless to brown liquid with a low vapor pressure and a liquid range of> 300 ° C. The compound is very toxic, especially if inhaled.
Applications
2-Methylglutaronitrile can be converted into 3-methylpyridine (β-picoline) by reaction with hydrogen on platinum or palladium contacts at temperatures of 250 to 400 ° C.
In addition to 3-methylpyridine, 3-methylpiperidine is also obtained as a by-product, from which further β-picoline can be obtained by dehydrogenation .
Ammoxidation of 3-methylpyridine on transition metal contacts gives 3-cyanopyridine (nicotinic acid nitrile ) in yields of 95%.
Nitrilase-catalyzed hydrolysis of 3-cyanopyridine by means of immobilized Rhodococcus strains leads to nicotinic acid amide (vitamin B 3 ) in quantitative yield .
Hydrogenation of a solution of 2-MGN in ethanol in the presence of Raney cobalt at 15 bar and 100 ° C. gives 2-methylpentane-1,5-diamine .
2-Methylpentanediamine can be converted into 3-methylpiperidine on a zeolite contact at 300 to 400 ° C. and then dehydrogenated on a palladium contact to form 3-methylpyridine, which can be converted into nicotinic acid amide via nicotinic acid nitrile.
The racemic diamine can also be used to prepare special polyamides and after reaction with phosgene to form 2-methylpentane diisocyanate as a reaction component in polyurethanes . Nitrilases in α, ω-dinitriles regioselectively hydrolyze the ω-nitrile group without the detectable amide intermediate directly to the carboxy group. This produces 4-cyanopentanoic acid in high yield.
The ammonium salt of 4-cyanopentanoic acid can be converted into 1,5-dimethyl-2-piperidone, an environmentally compatible solvent, by catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of methylamine .
The hydrolysis of both nitrile groups of 2-methylglutaronitrile with z. B. 20% sodium hydroxide solution at 50 ° C and subsequent acidification produces 2-methylglutaric acid .
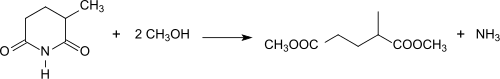
Starting from 2-methylglutaronitrile, hydrolysis to 2-methylglutaric acid can also take place via 2-methylglutarimide, which is obtained in yields of 94% when a 2-MGN / water mixture is heated to 275 ° C. in the presence of a titanium dioxide catalyst.
Hydrolysis in alkaline conditions gives 2-methylglutaric acid.
The reaction of 2-methylglutarimide with e.g. B. Methanol (methanolysis) in the presence of titanium dioxide or lanthanum oxide produces the diester dimethyl-2-methylglutarate, which is an environmentally friendly aprotic dipolar solvent under the name Rhodiasolv ® IRIS with the typical composition 87 - 89% dimethyl-2-methylglutarate, 9 - 11% dimethyl 2-ethyl succinate and 1 - 2% dimethyl adipate as a substitute for acetone , dichloromethane , N-methylpyrrolidone and the like. was commercialized.
The ester mixture is very similar to the so-called dibasic esters as they are commercially available as FlexiSolv ® DBE ® esters.
The diester can be selectively converted with dimethylamine in methanol / sodium methoxide into a mixture of 1- or 5-substituted methyl ester amides, which are used under the name Rhodiasolv ® Polarclean as a formulation aid for crop protection preparations. The ester amides obtained are easily biodegradable and, compared to the frequently used N-methylpyrrolidone, cyclohexanone or isophorone, are good solvents for a large number of different crop protection agents such as insecticides or fungicides .
Other ester amides derive z. B. from 2-MGN, which after alkaline hydrolysis to 2-methylglutaric acid, cyclization with acetic anhydride to 2-methylglutaric anhydride, reaction with dimethylamine to monoamide, acid chloride formation with thionyl chloride and esterification with more hydrophobic alcohols, such as. B. butanols or cyclohexanol are formed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Solvay: GPS Safety Summary, 2-methylglutaronitrile ( Memento of the original dated August 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet 2-methylglutaronitrile 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 28, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Entry on 2-methylglutaronitrile at TCI Europe, accessed on April 28, 2016.
- ↑ a b INVISTA, Technical Information, DYTEK® Methylglutaronitrile (MGN)
- ↑ Patent US5856555 : Process for the hydrocyanation of organic compounds containing ethylenic unsaturation. Applied on April 11, 1997 , published January 5, 1999 , Applicant: Rhone-Poulenc Fiber & Resin Intermediates, Inventor: M. Huser, R. Perron.
- ↑ a b Patent US6242633B1 : Catalyst comprising at least one phosphonite ligand based Nickel (0) complex and method for the production of nitriles. Registered on September 9, 1998 , published on June 5, 2001 , applicant: BASF AG, inventor: J. Fischer, W. Siegel.
- ↑ Patent US7816551B2 : Method for producing dinitriles. Registered on January 27, 2005 , published on October 19, 2010 , applicant: BASF AG, inventors: T. Jungkamp, R. Baumann, M. Bartsch, G. Haderlein, H. Luyken, J. Scheidel.
- ↑ a b Patent US8053594B2 : Preparation of diesters from imide / dinitrile compounds. Filed July 5, 2007 , published November 8, 2011 , Applicant: Rhodia Operations, Inventors: P. Leconte, P. Marion, R. Jacquot.
- ↑ a b c Sustainable solvents, products and process innovations. (PDF; 1 MB) (No longer available online.) In: chemspeceurope.com. Rhodia, member of the Solvay group, archived from the original on May 12, 2016 ; accessed on April 28, 2016 .
- ↑ Patent CH654576A5 : Process for the production of 3-methylpyridine. Applied on July 29, 1982 , published on February 28, 1986 , applicant: Lonza AG, inventor: EJ Newson, T.-B. Truong.
- ↑ Patent US4876348 : Process for making 3-cyanopyridine. Filed October 29, 1985 , published October 24, 1989 , Applicant: The Standard Oil Co., Inventor: R. DiCosimo, JD Burrington, DD Suresh.
- ↑ a b Patent US5719045 : Process for preparing nicotinamide. Applied on October 31, 1996 , published on February 17, 1998 , applicant: Lonza AG, inventors: J. Heveling, E. Armbruster, L. Utiker, M. Rohner, H.-R. Dettwiler, RJ Chuck.
- ↑ Patent US4987263 : Preparation of 2-methylpentadiamine. Applied on August 12, 1988 , published January 22, 1991 , applicant: Rhone-Poulenc Chimie, inventor: G. Cordier.
- ↑ Patent WO2008074645A1 : Process for preparing 2-methylpentane-1,5-diisocyanate from methylglutaronitrile. Registered on December 6, 2007 , published on June 26, 2008 , applicant: BASF SE, inventors: P. Pfab, E. Ströfer, C. Knösche, E. Schwab, M. Klötzer, G. Georgi.
- ↑ Patent US6551804 : Process for preparing 4-cyanopentanoic acid. Applied January 22, 2001 , published April 22, 2003 , Applicant: EI Du Pont de Nemours and Co., Inventors: R. DiCosimo, RD Fallon, JE Gavagan.
- ↑ Patent US5814508 : Preparation of lactams from aliphatic α, ω-dinitriles. Filed August 13, 1997 , published September 29, 1998 , Applicant: EI Du Pont de Nemours and Co., Inventors: R. DiCosimo, RD Fallon, JE Gavagan, FE Herkes.
- ↑ FB Cooling et al .: Chemoenzymatic production of 1,5-dimethyl-2-piperidone . In: J. Mol. Cat. B : Enzymat. tape 11 , no. 4-6 , 2001, pp. 295-306 , doi : 10.1016 / S1381-1177 (00) 00150-8 .
- ↑ Patent US6261381B1 : Composition and process for cleaning inks from various substrates including printing plates. Filed November 9, 2000 , published July 17, 2001 , applicant: MacDermid, Inc., inventor: G. Wojcik.
- ↑ Patent US20150175515A1 : Process for preparing diacid compounds. Filed June 26, 2013 , published June 25, 2015 , Applicant: Rhodia Operations, Inventor: R. Jacquot, B. Rhers.
- ↑ Patent US20120071686A1 : Production of diesters from dinitrile compounds. Filed October 21, 2008 , published March 22, 2012 , inventors: R. Jacquot, P. Leconte.
- ↑ Solvay: GPS Safety Summary, Dimethyl 2-methylglutarate ( Memento of the original from August 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ INVISTA's DBE ® esters, FlexiSolv ® DBE ® ester
- ↑ Patent US20130237722A1 : Process for preparing esteramide compounds. Registered on June 9, 2011 , published on September 12, 2013 , Applicant: Rhodia Operations, Inventors: T. Vidal, R. Rached, M. Guglieri.
- ↑ Patent US20140221211A1 : Use of esteramides as solvents, novel esteramides and process for preparing esteramides. Registered on April 9, 204 , published on August 7, 2014 , applicant: Rhodia Operations, inventor: O. Jentzer, M. Guglieri.