4-hydroxybenzoic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
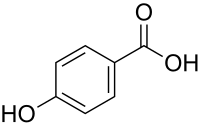
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
monoclinic prismatic |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 6 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, odorless, flammable solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 138.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.46 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
213-215 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
decomposition |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a chemical compound belonging to the group of hydroxybenzoic acids . It is a breakdown product and intermediate in the metabolism of quinones in eukaryotes .
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid ( para -hydroxybenzoic acid ) was also previously known as catalpic acid because it is found in the leaves and fruits (pods) of the trumpet trees ( Catalpa spp.). The term catalpic acid is now used to refer to the fatty acid contained in larger quantities in the seed oil of species ( Catalpa spp. And others) of the trumpet tree family (Bignoniaceae) . p -hydroxybenzoic acid is the name to the substance group of parabens ( para -hydroxy ben benzoic acid).
presentation
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is produced commercially from potassium phenate and carbon dioxide in a Kolbe-Schmitt reaction :
In the laboratory, the preparation takes place by heating potassium salicylate with potassium carbonate to 240 ° C, followed by treatment with acid ( hydrochloric acid ).
biosynthesis
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid arises from several substances: in plants from its adduct with coenzyme A , which in turn arises from 4-cumaroyl-CoA; in bacteria during the oxidation of benzoic acid ( EC 1.14.13.12 ) or during the breakdown of chorismic acid ( EC 4.1.3.40 ), 4-methoxybenzoic acid ( EC 1.14.99.15 ), 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde ( EC 1.2.1.64 ) or 4-chlorobenzoic acid ( EC 3.8.1.6 ). It can also be decarboxylated to phenol or oxidized to 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. In the biosynthesis of the ubiquinones , it is linked to a polyprenyl radical.
properties
The aqueous solution of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid reacts acidic ( pH value : 3.3 at a measuring temperature of 20 ° C and a concentration of 1 g / l).
use
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is mainly used technically for the production of its esters , which are used as preservatives .
Health hazards
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid was included by the EU in 2012 in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of the substance evaluation in the Community's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ). The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid were concerns about consumer use and high (aggregated) tonnage as well as the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of CMR substances and as a potential endocrine disruptor . The re-evaluation took place from 2014 and was carried out by the Czech Republic . A final report was then published.
Web links
- OECD : Screening Information Dataset (SIDS) Initial Assessment Report (SIAR) for Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed December 8, 2019.
- ↑ E. Winterstein, G. Trier: The alkaloids: a monograph of natural bases. Borntraeger, 1910, p. 305.
- ↑ Entry on 4-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 21, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 8, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on May 1, 2009.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification . Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ^ CA Wachtmeister: Studies on the Chemistry of Lichens. X. The Structure of Porphyrilic Acid. In: Acta Chem. Scand. 10, 1956, pp. 1404-1413, doi : 10.3891 / acta.chem.scand.10-1404 , ( PDF ; 1.4 MB).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-288.
- ↑ Walter Karrer : Constitution and occurrence of organic plant substances. Springer, 1958, ISBN 978-3-0348-6795-5 (reprint), p. 356.
- ↑ YPS Bajaj: Medicinal and Aromatic Plants VIII. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry 33, Springer, 1995, ISBN 978-3-642-08201-6 , p. 142 f.
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum . 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig / Berlin / Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 978-3-335-00343-4 , pp. 351-352.
- ^ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Report and Conclusion Document .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): 4-hydroxybenzoic acid , accessed on March 26, 2019.


