Adelite
| Adelite | |
|---|---|
| Pink crystal aggregate from Franklin , Sterling Hill, Sussex County, New Jersey, USA | |
| General and classification | |
| chemical formula |
|
|
Mineral class (and possibly department) |
Phosphates, arsenates and vanadates |
|
System no. to Strunz and to Dana |
8.BH.35 ( 8th edition : VII / B.11b) 41.05.01.01 |
| Crystallographic Data | |
| Crystal system | orthorhombic |
| Crystal class ; symbol | orthorhombic-disphenoidic; 222 |
| Space group | P 2 1 2 1 2 1 (No. 19) > |
| Lattice parameters | a = 7.52 Å ; b = 8.89 Å; c = 5.85 Å |
| Formula units | Z = 4 |
| Frequent crystal faces | {100}, {001}, {110}, {011}, { 2 21} |
| Physical Properties | |
| Mohs hardness | 5 |
| Density (g / cm 3 ) | measured: 3.71 to 3.76; calculated: [3.78] |
| Cleavage | indistinct |
| Break ; Tenacity | uneven to shell-like; brittle |
| colour | colorless, white, gray, bluish gray to yellowish gray, yellow, light green, pinkish brown to brown |
| Line color | White |
| transparency | transparent to translucent |
| shine | Resin gloss |
| Crystal optics | |
| Refractive indices |
n α = 1.712 n β = 1.721 n γ = 1.731 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.019 |
| Optical character | biaxial positive |
| Axis angle | 2V = measured: 68 to 90 ° |
Adelite is a rarely occurring mineral from the mineral class of " phosphates , arsenates and vanadates " with the idealized chemical composition CaMg (AsO 4 ) (OH) or in the crystal-chemical structural formula according to Strunz CaMg [OH | AsO 4 ]. Chemically speaking, Adelit is therefore a calcium - magnesium arsenate with additional hydroxide ions and the arsenate analogue of gottlobite (CaMg (VO 4 ) (OH)).
Adelite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system and although occasionally develops tabular crystals stretched along the a-axis , it is mostly found in the form of hemispherical, granular or massive mineral aggregates . The crystals are brittle, break uneven or shell-like like glass and their surfaces have a resin-like sheen . With a Mohs hardness of 5, Adelite is one of the medium-hard minerals that, like the reference mineral apatite, can still be scratched with a good knife.
In its pure form, Adelit is transparent and colorless. However, due to multiple refraction due to lattice construction defects or polycrystalline formation, it can also appear white and, due to impurities or ion exchange in the compound, take on a gray, bluish-gray to yellowish-gray, yellow, light green or pinkish-brown to brown color, with the transparency decreasing accordingly.
Etymology and history
Adelit was named after the Greek word άδηλος [ˈaðilɔs] for hidden, indefinite or uncertain (also indistinct) based on its often inadequate transparency.
Adelite was first discovered in 1878 or 1888 in the "Kittel Mine" near Nordmark in the Swedish municipality of Filipstad . However, since material from the neighboring Långban was also used for the analysis of the mineral , this place is also considered a type locality . It was first described in 1891 by Hjalmar Sjögren (1856–1922).
The type material (holotype) is stored in the Department of Mineralogy in the Naturhistoriska riksmuseet in Stockholm , Sweden under the collection no. HS 6413 kept.
classification
In the outdated 8th edition of the mineral classification according to Strunz , the Adelite belonged to the department of "Anhydrous phosphates, arsenates and vanadates with foreign anions ", where together with Austinite , Descloizit , Duftite , Gabrielsonite , Konichalcite , Mottramite , Pyrobelonite , Tangeit and Turanite the "Descloizit series" with the system no. VII / B.11b within the “ Tilasite Descloizit Group” (VII / B.11).
In the Lapis mineral directory according to Stefan Weiß, which, out of consideration for private collectors and institutional collections, is still based on this old form of Karl Hugo Strunz's system , the mineral was given the system and mineral number. VII / B.26-10 . In the “Lapis system”, this also corresponds to the section “Anhydrous phosphates, with foreign anions F, Cl, O, OH”, where Adelit gave its name to the “Adelit Group” with the system no. VII / B.26 and the other members Austinit, Cobaltaustinit ( Kobaltaustinit ) Duftit, Gabrielsonit, Gottlobit , Hermannroseit , Konichalcit, Nickelaustinit and Tangeite forms (as 2018).
The 9th edition of Strunz's mineral systematics , which has been in effect since 2001 and was updated by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) until 2009, also assigns the Adelit to the category of “phosphates etc. with additional anions; without H 2 O “. However, this is further subdivided according to the relative size of the cations involved and the molar ratio of the additional anions (OH, etc.) to the phosphate, arsenate or vanadate complex (RO 4 ), so that the mineral can be classified in the sub-section “With medium-sized and mostly large cations; (OH etc.): RO 4 = 1: 1 ”can be found, where it is also named after the“ Adelitgruppe ”with the system no. 8.BH.35 and the other members arsendescloizit , austinite, fragranceite, gabrielsonite, gottlobite, cobaltaustinite, konichalcite, nickelustinite and tangite.
The systematics of minerals according to Dana , which is mainly used in the English-speaking area , also assigns the Adelite to the class of "phosphates, arsenates and vanadates" and there to the category of "anhydrous phosphates, etc., with hydroxyl or halogen". Here, too, he is the namesake of the "Adelit Group" with the system no. 41.05.01 to be found within the subsection of " Anhydrous phosphates etc., with hydroxyl or halogen with (AB) 2 (XO 4 ) Z q ".
Chemism
The idealized (theoretical) composition of Adelit (CaMg (AsO 4 ) (OH)) consists of 18.19% calcium (Ca), 11.03% magnesium (Mg), 34.01% arsenic (As), 36.31 % Oxygen (O) and 0.46% hydrogen (H). When analyzing the type material from Långban (Sweden), minor additions of manganese, lead, chlorine, copper, iron and aluminum as well as traces of barium were also measured.
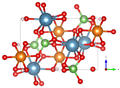
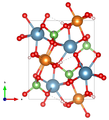
Crystal structure
Adelite crystallizes orthorhombically in the space group P 2 1 2 1 2 1 (space group no. 19) with the lattice parameters a = 7.52 Å , b = 8.89 Å and c = 5.85 Å as well as 4 formula units per unit cell .
The crystal structure of Adelit consists of 6-fold coordinated magnesium octahedra , which are connected to each other via shared edges and form chains parallel to the c-axis. These chains form via corner linked AsO 4 - tetrahedron a scaffold, the large cations are distributed in the gaps.
| Crystal structure of Adelit |
|
|
| Color table: __ Ca __ Mg __ As __ O __ O __ H |
Education and Locations
Adelite forms, in metamorphic Iron - manganese - ore bodies , where it usually in a separate from the iron ore layer together with hausmannite occur and other manganese ores. Depending on the locality adelite can also with other minerals in mineral assemblage are found, such as, among others, with Arsenoklasit , Braunit , Hedyphan , Fredrikssonit and Sarkinit in Långban; Hausmannite, magnetite and solid copper in the “Kittel Mine” as well as allactite , alleghanyite , barite , calcite , chlorophoenicite , franklinite , hodgkinsonite , johnbaumite , kraisslite , rhodochrosite , sphalerite , svabit , willemite and zincite in Franklin and Sterling Hill in the US state New Jersey .
As a rare mineral formation, Adelite could only be detected at a few sites, of which around 10 are known (as of 2011). In addition to its type localities "Kittel Mine" and Långban, the mineral was also found in the "Jakobsberg Mine", the "Moss Mine" and the "Harstigen Mine", all of which are located in the Filipstad municipality.
In Germany the mineral occurred near Sankt Andreasberg in Lower Saxony's Harz Mountains and in the "Grube Glücksstern" at Gottlob near Friedrichroda in Thuringia and in the USA, in addition to the previously mentioned sites Franklin and Sterling Hill in New Jersey, it was also found in the "Mercur Mine" in Oquirrh- Mountains exposed in Utah.
See also
literature
- H. Sjögren: Contributions to Swedish mineralogy Part I: 8. Adelite a new basic arseniate from Nordmarken, Jakobsberg and Långban, Vermland . In: Bulletin of the Geological Institution of the University of Upsala . tape 1 , 1892, p. 56–64 (English, rruff.info [PDF; 375 kB ; accessed on January 7, 2020]).
- H. Effenberger, W. Krause, H.-J. Bernhardt: Structural investigations of adelite and cobaltaustinite, two members of the adelite-descloizite group . In: Experimental Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry . tape 9 , 2002, p. 30 (English, rruff.info [PDF; 1.6 MB ; accessed on January 7, 2020]).
Web links
- Mineral Atlas: Adelit (Wiki)
- Adelite search results. In: rruff.info. Database of Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and chemistry of minerals (RRUFF), accessed on January 7, 2020 .
- American-Mineralogist-Crystal-Structure-Database - Adelite. In: rruff.geo.arizona.edu. Accessed January 7, 2020 (English).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Malcolm Back, William D. Birch, Michel Blondieau and others: The New IMA List of Minerals - A Work in Progress - Updated: November 2019. (PDF 1720 kB) In: cnmnc.main.jp. IMA / CNMNC, Marco Pasero, November 2019, accessed January 7, 2020 .
- ↑ a b c d e Hugo Strunz , Ernest H. Nickel : Strunz Mineralogical Tables. Chemical-structural Mineral Classification System . 9th edition. E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagbuchhandlung (Nägele and Obermiller), Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-510-65188-X , p. 458 (English).
- ^ A b H. Sjögren: Contributions to Swedish mineralogy Part I: 8. Adelite a new basic arseniate from Nordmarken, Jakobsberg and Långban, Vermland . In: Bulletin of the Geological Institution of the University of Upsala . tape 1 , 1892, p. 58 (English, rruff.info [PDF; 375 kB ; accessed on January 7, 2020]).
- ^ A b David Barthelmy: Adelite Mineral Data. In: webmineral.com. Accessed January 7, 2020 (English).
- ↑ a b c Adelite . In: John W. Anthony, Richard A. Bideaux, Kenneth W. Bladh, Monte C. Nichols (Eds.): Handbook of Mineralogy, Mineralogical Society of America . 2001 ( handbookofmineralogy.org [PDF; 65 kB ; accessed on January 7, 2020]).
- ↑ a b c d e f Adelite. In: mindat.org. Hudson Institute of Mineralogy, accessed January 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Biography of Hjalmar Sjögren (1856-1922). In: www.nrm.se. Naturhistoriska riksmuseet , November 7, 2014, accessed on January 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Catalog of Type Mineral Specimens - A. (PDF 85 kB) In: docs.wixstatic.com. Commission on Museums (IMA), December 12, 2018, accessed January 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Stefan Weiß: The large Lapis mineral directory. All minerals from A - Z and their properties. Status 03/2018 . 7th, completely revised and supplemented edition. Weise, Munich 2018, ISBN 978-3-921656-83-9 .
- ↑ Ernest H. Nickel, Monte C. Nichols: IMA / CNMNC List of Minerals 2009. (PDF 1816 kB) In: cnmnc.main.jp. IMA / CNMNC, January 2009, accessed January 7, 2020 .