Dibenzoyl peroxide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dibenzoyl peroxide | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 10 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless powder with a faint odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Acne medication |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 242.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.33 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
Decomposition from 70 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
<10 Pa |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 5 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(Di) Benzoyl peroxide is a colorless powder with a faint odor. It belongs to the organic peroxides . The powder falls within the scope of the Explosives Act and is classified in Annex II into substance group B.
history
Dibenzoyl peroxide was one of the first organic peroxides to be synthesized. It was first described by BC Brodie in 1858 . The first industrial use began around 1900 as a bleach . With the increased emergence of synthetic plastics from 1940 on, the use of the substance as a radical initiator for polymerization reactions of vinyl monomers increased .
Manufacturing
Benzoyl peroxide can be made from benzoyl chloride and sodium peroxide or hydrogen peroxide .
properties
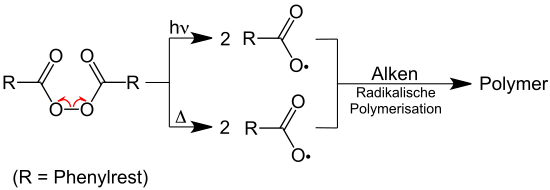
The bond between the two oxygen atoms is unstable and splits homolytically with low expenditure of energy, e.g. B. by light irradiation (photolytic) or supply of heat (thermolytic). The formation of benzoyloxy radicals plays an important role in the radical polymerization of alkenes :
Benzoyl peroxide breaks down easily into two benzoyloxy radicals , which further break down into phenyl radicals with splitting off of CO 2 . The phenyl radicals can then dimerize to biphenyl :
In the dermatological application, it may therefore be phototoxic come effects. As a potent oxidizing agent, benzoyl peroxide has an antibacterial and keratolytic effect . The amino acids of the bacteria are oxidized. After the release of benzoic acid and oxidative cleavage of the lipid bridges of the keratin , keratolysis occurs. By reducing free oxygen radicals , there is also an anti-inflammatory effect .
Benzoyl peroxide can explode if heated. Therefore, commercially available benzoyl peroxide always contains phlegmatizers (e.g. 20% water) or plasticizers for stabilization.
use
Benzoyl peroxide is used as an active ingredient in dermatology and here in particular in the topical therapy of acne . Benzoyl peroxide preparations are available without a prescription in concentrations of up to 10% in many countries - not in Austria or Switzerland.
Cosmetic articles must not contain benzoyl peroxide.
In organic chemistry , benzoyl peroxide is used as a radical starter z. B. for radical polymerizations , used (for example in synthetic resins based on methyl methacrylate to create industrial floors or as a component of two-component adhesives ). Benzoyl peroxide is no longer used industrially as an initiator in acrylic resin production, since then approx. 0.2% (toxic) benzene is contained as a decomposition product in the synthetic resins. As an alternative z. B. dicumyl peroxide is used.
See also
Trade names
As a medicine
Aknefug BP (CH), Aknefug oxide (D), Akneroxid (A, D, CH), Benzac (CH), Benzaknen (D), Benzoyt (D), Brevoxyl (D), Cordes BPO (D), Klinoxid (D ), Lubexyl (CH), Marduk (D), PanOxyl (D), Sanoxit (D)
Acne Crème plus (CH), Acne Plus (A, D), Duac (D), Epiduo (D, CH)
As a radical starter
Basiron, Stioxyl, Panoxyl, Perkadox L-W75
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on dibenzoyl peroxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on benzoyl peroxide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 29, 2017.
- ↑ Entry on dibenzoyl peroxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Schweizerische Unfallversicherungsanstalt (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 94-36-0 or dibenzoyl peroxide ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ^ Sprengstoffgesetz - SprengG , accessed on November 4, 2018
- ^ BC Brodie: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 108 (1858) 79.
- ↑ a b c H. Klenk; PH Goetz; R. Siegmeier; W. Mayr: Organic Peroxy Compounds , in: Ullmanns Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie , Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 2012; doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a19_199 .
- ↑ Fanta, D., Messeritsch-Fanta, C .: Acne 1999: do we still need a dermatologist? In: dermatologist . tape 50 , no. December 12 , 1999, pp. 900-11 , doi : 10.1007 / s001050051009 .
- ↑ Red List online, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland, as of September 2009.