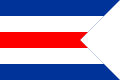
Service flag of the naval forces of the Bundeswehr

The service flag of the naval forces of the Bundeswehr was determined by order of May 25, 1956 ( Federal Law Gazette p. 447), the federal service flag in the form of a double stand by Federal President Theodor Heuss .
arrangement

The "Order of the Federal President on the service flag of the naval forces of the Bundeswehr" (BPäsFlaggenAnO) of May 25, 1956, was published in the Federal Law Gazette, Part III, structure number 1130-5 (text valid from: January 1, 1964). It says:
(1) I choose the federal service flag in the form of a double stand as the service flag of the naval forces of the Bundeswehr.
(2) The side of the flag facing away from the pole is jagged. The vertex of the right-angled incision is in the middle of the red field. The distance between the vertex and the federal shield is slightly less than the distance between the federal shield and the pole.
The order is signed by Federal President Theodor Heuss, Federal Chancellor Konrad Adenauer and the Federal Minister of Defense Theodor Blank .
Regulations


The flagging of ships and boats is regulated in the Marine Service Regulation (MDv) 161/1 “Flag, Salute and Visiting Regulations for Ships / Boats of the Bundeswehr (FlaSBO)” in the version dated November 28, 2005. It contains provisions on the waving of flags in accordance with international custom on board war and auxiliary ships of the Navy. The central guideline A2-2630 / 0-0-3 "Military forms and celebrations of the Bundeswehr" (formerly ZDv 10/8) applies to land services of the Navy .
The service flag of the naval forces and the federal service flag are set in a reduced form on the ships and boats authorized to operate them as a jack (bow flag) . Warships that are landed or anchored, set the service flag of the naval forces and the jack from 7:00 a.m. in the summer half-year April to September or 8:00 a.m. in the winter half-year October to March until sunset, at the latest by 8:00 p.m. Warships in motion always carry the service flag of the naval forces, even in the dark.
Civilian auxiliary ships of the Navy fly the normal federal service flag.
role models
With the form of the double stand, the Bundeswehr abandoned the rectangular tradition of the German war or service flags ( Reichskriegsflagge ) of the Reich and Bundesflotte ( Navy of the North German Confederation ) as well as the Kaiserreich ( Imperial Navy ) and later the German Empire ( Reichsmarine and Kriegsmarine ).
Vice-Admiral Friedrich Ruge , the first inspector of the German Navy, posed as the inventor .
“On the occasion of the takeover of the first boats from the Americans in Bremerhaven, I gave a speech; then the federal flag was hoisted: black-red-gold with the federal eagle in the coat of arms in the middle. As a difference from the federal service flag, I had arranged on my own that the flag was jagged like that of the Nordic navies. No one has ever commented on this ... "
However, other information indicates that the frigate captain Theodor von Mutius was the designer of the sea flag. At the corresponding time, he was working in Department VII-Marine , Internal Management Department , of the Federal Ministry of Defense.
Presumably three aspects were "godfathers" when choosing the shape for the sea flag:
- the model intended for the European Defense Community
- the traditional double stand of the Nordic navies
- the war flag of the Prussian Navy .
Already from 1946 to 1949 there was by order of the Allied Control Council in the Control Council Act No. 39 that all German (merchant) ships had to carry the international signal flag of the letter "C" with a triangular cutout for identification , the so-called C double stand. The colors blue, white and red represent the national colors of the four allies: United States , United Kingdom , France and the Soviet Union . This stander was not allowed to be greeted at sea, or certificates of honor were not given to him.
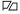
 ? C double stand; Identification flag for German merchant ships 1946–1949
? C double stand; Identification flag for German merchant ships 1946–1949
- Double stander of the Nordic navies
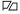 Finnish Navy (1920–1978)
Finnish Navy (1920–1978)
See also

Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Order of the Federal President on the service flag of the naval forces of the Bundeswehr on gesetze-im-internet.de
- ↑ Inland protocol of the federal government - flagging in the German Navy. February 12, 2011
- ↑ a b Seeflagge on marine.de
- ↑ Control Council Act No. 39 . Constitutions of the world; accessed on June 28, 2014