Eifelit
| Eifelit | |
|---|---|
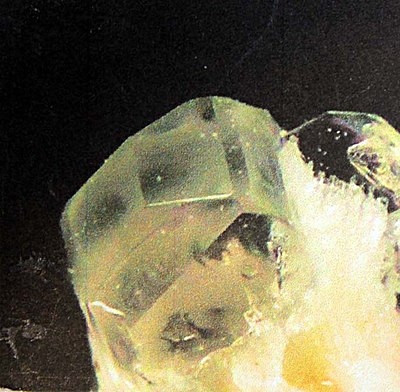
| Eifelite crystal from the Ettringer Bellerberg type locality in the Eifel | |
| General and classification | |
| other names |
IMA 1980-097 |
| chemical formula | KNa 2 MgNaMg 3 Si 12 O 30 |
|
Mineral class (and possibly department) |
Silicates and germanates - ring silicates |
|
System no. to Strunz and to Dana |
9.CM.05 ( 8th edition : VIII / E.22) 63.02.01a.04 |
| Crystallographic Data | |
| Crystal system | hexagonal |
| Crystal class ; symbol | dihexagonal-dipyramidal; 6 / m 2 / m 2 / m |
| Space group | P 6 / mcc (No. 192) |
| Lattice parameters | a = 10.14 Å ; c = 14.22 Å |
| Formula units | Z = 2 |
| Frequent crystal faces | {10 1 0}, {0001}, subordinate {11 2 0}, {10 1 2} |
| Physical Properties | |
| Mohs hardness | Please complete |
| Density (g / cm 3 ) | 2.67 |
| Cleavage | not observed |
| colour | colorless |
| Line color | White |
| transparency | transparent |
| shine | Glass gloss |
| Crystal optics | |
| Refractive indices |
n ω = 1.5458 to 1.5443 n ε = 1.5445 to 1.5430 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.001 |
| Optical character | uniaxial positive |
| Pleochroism | - |
The mineral Eifelit is a very rare ring silicate from the milarite group and has the simplified chemical composition K Na 2 MgNa Mg 3 Si 12 O 30 . It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system and develops colorless, six-sided, platy to prismatic crystals .
Etymology and history
Was discovered in 1983 in a Eifelit gneiss - Xenolith from Ettringer Bellerberg in the Eifel , Germany and was named by K. Abraham, W. Gebert, O. Medenbach, W. Schreyer and G. Hentschel after its place, the Eifel region of Germany.
21 years later, in 2004, the Stardust space probe collected dust samples in the tail of comet 81P / Wild 2 , in which Eifelite could be detected.
classification
In the outdated but still partially in use 8th edition of the mineral classification by Strunz of Eifelit belongs to the general ward of the " Ring silicates (cyclo silicates)" where he collaborated with Almarudit , Armenit , Berezanskit , Brannockit , Chayesit , Darapiosit , Dusmatovit , Emeleusit , Faizievit , Merrihueit , Oftedalit , Osumilith , Osumilith- (Mg) , Poudretteit , Roedderite , Shibkovite , Sogdianite , Sugilite , Trattnerite and Yagiite the " Milarite-Osumilite-Group " with the system no. VIII / E.22 forms.
The 9th edition of Strunz's mineral systematics , which has been in effect since 2001 and is used by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA), also classifies Eifelit in the "ring silicates" section. This is, however, further subdivided according to the structure of the rings, so that the mineral can be found in the sub-section "[Si 6 O 18 ] 12− -six double rings" according to its structure . It belongs to Almarudit, Armenit, Berezanskit, Brannockit, Chayesit, Darapiosit, Dusmatovit, Friedrichbeckeit , Klöchit , Merrihueit, Milarit, Oftedalit, Osumilith, Osumilith- (Mg), Poudretteit, Roedderit, Shibkattite, Sogdianit, Sugil " Milaritgruppe " with the system no. 9.CM.05 .
The systematics of minerals according to Dana , which is mainly used in the English-speaking world , assigns the Eifelite to the class of "silicates and Germanates", but there it is in the more finely divided division of "ring silicates: condensed rings". Here it is in the " Milarite Osumilith Group (Milarite Osumilith Subgroup) " with the system no. 63.02.01a can be found in the subsection “ Ring Silicates : Condensed, 6-membered Rings”.
Chemism
Eifelite is the Na-rich end link of the complete Roedderite-Eifelite mixed crystal series. The measured composition from the type locality is [12] (K 0.92 Na 0.08 ) [9] (Na 1.82 □ 0.18 ) [6] (Mg 1.20 Na 0.80 ) [4] ( Mg 2.78 Zn 0.05 Cu 0.02 Mn 2+ 0.08 Fe 2+ 0.03 Al 0.04 ) [4] (Si 11.92 Al 0.08 ) O 30 , whereby in the square brackets the coordination number of the respective position in the crystal structure is given.
Eifelite forms a complete mixed crystal row with Roedderite ( C K B (□ Na) A Mg 2 T2 Mg 3 T1 Si 12 O 30 ) according to the exchange reaction B □ + A Mg = B Na + A Na.
Crystal structure
Eifelite crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system in the space group P 6 / mcc (space group no. 192) with the lattice parameters a = 10.14 Å and c = 14.22 Å as well as two formula units per unit cell .
Eifelite is isotypic to milarite , i.e. i.e., it crystallizes with the same structure as milarite. The 12-fold coordinated C position is almost fully occupied with potassium (K + ). The 9-fold coordinated B-position is also fully occupied with sodium (Na + ). Magnesium (Mg 2+ ) and sodium fill the 6-fold coordinated A position in approximately equal parts and the tetrahedrally coordinated T2 position contains magnesium (Mg 2+ ) and small amounts of other divalent cations. The T1 position, which builds up the double rings, contains only silicon (Si 4+ ). Eifelite is one of the few silicates in which sodium is incorporated with octahedral coordination.
Education and Locations
The so far only documented terrestrial occurrence of Eifelite with almost terminal composition is its type locality , the quarry of the company A. Casper at Ettringer Bellerberg , 2 km north of Mayen , in the Laacher See region of the Eifel , Rhineland-Palatinate , Germany . This very mineral-rich site is the type locality of 13 minerals (as of 2016), 4 of which are from the milarite group: Almarudite , Eifelite, Friedrichbeckeit and Osumilith- (Mg) . The milarite group minerals chayesite, merrihueit, roedderite and trattnerite were also detected here.
There the mineral was found in cavities of a silicate-rich rock inclusion ( xenolite ) in leucite - tephrite - lava . It occurs together with quartz , sanidine , clinopyroxene , amphibole , tridymite , hematite and pseudobrookite . This occurrence corresponds to those of the other minerals from the milarite group that were previously found in the Vulkaneifel : Almarudite, Roedderite , Osumilith and Osumilith- (Mg).
Eifelite forms contact metamorphic at high temperatures around 900 ° C and low pressure. It is assumed that it is deposited directly from an alkali-rich , silicon and magnesium-containing and low-aluminum gas phase.
When examining dust samples from comet 81P / Wild 2, Eifelite of extraterrestrial origin was found. Eifelite is therefore a condensate from the gas phase of solar nebulae and, together with potassium feldspar, an essential carrier of potassium , which could be detected spectroscopically in the tail of comets.
See also
literature
- Eifelite . In: John W. Anthony, Richard A. Bideaux, Kenneth W. Bladh, Monte C. Nichols (Eds.): Handbook of Mineralogy, Mineralogical Society of America . 2001 ( handbookofmineralogy.org [PDF; 67 kB ; accessed on August 17, 2017]).
Web links
- Mineral Atlas: Eifelit (Wiki)
- Mindat - Eifelite (English)
- American-Mineralogist-Crystal-Structure-Database - Eifelite (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w K. Abraham, W. Gebert, O. Medenbach, W. Schreyer, G. Hentschel: Eifelite, KNa 3 Mg 4 Si 12 O 30 , a new mineral of the osumilite group with octahedral sodium . In: Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology . tape 82 , 1983, pp. 252-258 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01166619 , bibcode : 1983Comp ... 82..252A .
- ↑ Webmineral - Eifelite (English)
- ↑ a b c d e f g PJ Dunn, GY Chao, JD Grice, JA Ferraiolo, M. Fleischer, A. Pabst, JA Zilczer: New Mineral Names . In: American Mineralogist . tape 69 , 1983, pp. 565-569 ( minsocam.org [PDF; 658 kB ; accessed on August 17, 2017]).
- ↑ a b M. Fulle, P. Molaro, L. Buzzi, and P. Valisa: Potassium detection and Lithium depletion in comets C / 2011 L4 (Panstarrs) and C / 1965 S1 (Ikeya-Seki) . In: Astrophysical Journal Letters . tape 771 , 2013 ( iop.org [PDF; 371 kB ; accessed on August 17, 2017]).
- ↑ a b ME Zolenskyet et al .: Mineralogy and Petrology of Comet 81P / Wild 2 Nucleus Samples . In: Science . tape 314 , 2006, pp. 1735 , doi : 10.1126 / science.1135842 , bibcode : 2006Sci ... 314.1735Z .
- ↑ Webmineral - New Dana Classification of Cyclosilicates cyclosilicates Condensed ring
- ↑ Caspar Quarry, Bellerberg volcano, Ettringen, Mayen, Eifel, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany