Furfuryl alcohol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Furfuryl alcohol | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 6 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, almost odorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 98.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.13 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−31 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
171 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
53 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.487 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 10 ml m −3 or 40 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Furfuryl alcohol is a chemical compound from the group of alcohols and substituted oxygen heterocycles . It is derived from furan and differs from it by an additional hydroxymethyl group .
Extraction and presentation
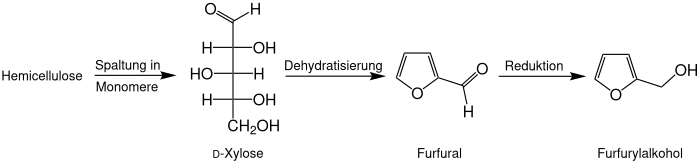
Furfuryl alcohol is obtained industrially from furfural by catalytic reduction . Since hemicellulose furfural from agricultural residues such as corn cobs ( English corn cob ) or bagasse is obtained, also furyl alcohol is produced entirely from renewable raw materials. It can therefore be made entirely from renewable raw materials.
Furfuryl alcohol can also be produced by means of a Cannizzaro reaction by disproportionation of furfural, whereby 2-furancarboxylic acid is also formed.
properties
Furfuryl alcohol is a colorless to clear-yellow liquid with a slightly pungent odor. Upon contact with air or light, the compound turns brown to red-brown. It is readily soluble in many organic solvents (e.g. ethanol, diethyl ether) and soluble in chloroform . The vapors of furfuryl alcohol can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 75 ° C, ignition temperature 390 ° C).
The connection is multifaceted. Mesomeric-stabilized carbenium ions can be formed in an acidic medium . These are the starting point for condensation reactions in which linear oligomers of different lengths and linked are formed ( furan resins ). Most of the furan rings are linked via methylene groups (–CH 2 -), but there are also links via dimethylene ether groups (–CH 2 –O – CH 2 -). However, especially under strongly acidic conditions, formaldehyde is split off from these and methylene groups are formed again.
use
Furfuryl alcohol is mainly used for the production of furan resins, which have a wide range of applications. It also serves as a solvent and reactive thinner in other resins and is used in wetting agents . It has recently also been used in chemical wood modification in the production of furfurylated wood .
Risk assessment
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified furfuryl alcohol as a possible carcinogen in 2017.
Furfuryl alcohol was included by the EU in 2012 in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) in the context of substance evaluation in the Community's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ). The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. Furfuryl alcohol uptake was caused by concerns about its classification as a CMR substance, consumer use , environmental exposure, worker exposure , high (aggregated) tonnage and widespread use. The re-evaluation took place from 2013 and was carried out by Poland . A final report was then published.
See also
Web links
- Joint FAO / WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), Monograph for Furfuryl Alcohol and Related Substances
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on furfuryl alcohol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 27, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Gerhard W. Becker, Dietrich Braun, Wilbrand Woebcken; Kunststoff Handbuch 11 vols. In 17 tl.-vols., Vol. 10, thermosets: BD 10; ISBN 3-446-14418-8 .
- ↑ Entry on Furfuryl alcohol in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 98-00-0 or furfuryl alcohol ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b c Oliver Türk: Material use of renewable raw materials. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden, 2014, ISBN 978-3-8348-1763-1 , pp. 443-454.
- ↑ a b c Entry on furfuryl alcohol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 13, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-266.
- ↑ JB Barr & SB Wallon: The Chemistry of Furfuryl Alcohol Resins . In: Journal of Applied Polymer Science . tape 15 , 1971, p. 1079-1090 , doi : 10.1002 / app.1971.070150504 .
- ↑ a b R. H. Kottke: Furan Derivates. In: Encyclopedia of chemical technology. Raymond Eller Kirk & Donald Frederick Othmer, December 4, 2000, accessed August 16, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Alessandro Gandini & Mohamend Naceur Belgacem: Furans . In: Hanna Dodiuk & Sidney H. Goodman (Eds.): Handbook of Thermoset Plastics . Elsevier, Amsterdam 2014, ISBN 978-1-4557-3107-7 , pp. 93-110 .
- ^ A b Alessandro Gandini & Mohamend Naceur Belgacem: Furans in Polymer Chemistry . In: Progress in Polymer Science . tape 22 , no. 6 , 1997, pp. 1203-1379 , doi : 10.1016 / S0079-6700 (97) 00004-X .
- ↑ Yann Grosse, Dana Loomis, Kathryn Z Guyton, Fatiha El Ghissassi, Véronique Bouvard, Lamia Benbrahim-Tallaa, Heidi Mattock, Kurt Straif: Some chemicals that cause tumors of the urinary tract in rodents. In: The Lancet Oncology . 18, 2017, pp. 1003-1004, doi: 10.1016 / S1470-2045 (17) 30505-3 .
- ↑ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Conclusion and Evaluation Report .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Furfuryl alcohol , accessed on March 26, 2019.