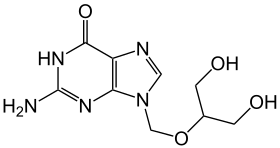
Ganciclovir
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Ganciclovir | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2 - [(2-Amino-6-hydroxy-purin-9-yl) methoxy] propane-1,3-diol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 13 N 5 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
DNA polymerase inhibitor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 255.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
242–255 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
≤ 0.001 hPa (22 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
2.2; 9.4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
heavy in ethanol ; soluble in dilute mineral acids and alkali hydroxide solutions |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Ganciclovir is an analogue of the nucleobase guanine . It is used as an antiviral agent against herpes viruses .
chemistry
Ganciclovir is - like the analogues acyclovir and penciclovir - a derivative of the nucleobase guanine, which occurs as a component of DNA and RNA . Since ganciclovir is weakly acidic (pKa 9.4) due to the NH acidity of the lactam group , it forms a sodium salt that is used therapeutically.
application
Ganciclovir is mainly used for diseases caused by the cytomegalovirus (CMV, synonymous human herpesvirus 5 / HHV 5). CMV infections are of particular importance
- in case of immunodeficiency in the context of transplants or an AIDS disease, as well as
- during pregnancy.
(For details, see the main article on cytomegaly ).
Ganciclovir is also effective against keratitis herpetic ("eye herpes") and can be administered topically in the form of an eye gel.
It is also used experimentally for the treatment of malignant degeneration, e.g. B. in oncolytic viruses . In biochemistry, ganciclovir is used in conjunction with selection markers for negative selection.
Mode of action
Ganciclovir works against all human herpes viruses , but primarily against the cytomegalovirus (CMV) (is about 10 times more phosphorylated in CMV-infected cells, thus more activated than in healthy cells). In infected cells it is first phosphorylated to monophosphate by viral kinases and then phosphorylated by cellular kinases to 5'-triphosphate . Particularly in virus-infected cells, it is first converted by the cell's own guanine kinase into ganciclovir triphosphate, in order to be incorporated into the viral DNA as a synthetic nucleoside analogue , whereby this leads to chain termination as the viral polymerase breaks off a base after incorporation of the ganciclovir .
Administration and pharmacokinetics
Since its oral bioavailability is less than 5%, it is usually given as an infusion in two single doses of 5 mg per kg of body weight each twelve hours apart. With a pH of 11, the solution of its sodium salt is strongly alkaline , so the infusion must be made slowly through a large vein. Misinfusions (into an artery, subcutaneous tissue, or muscle) should also be avoided for the same reason .
In patients, mean plasma concentrations of approximately 6 mg / l were achieved after an infusion time of 60 minutes. The substance is mainly excreted unchanged via the kidneys, the elimination half-life being around 1.5 to 3 hours with normal kidney function. Dose adjustments must be made in the event of impaired creatinine clearance .
For oral administration, 1 g is taken three times a day with meals; Topical applications in gel form in the eye area have been on the German market since 2006.
unwanted effects
Since ganciclovir has significantly higher toxic properties than, for example, acyclovir (it is phosphorylated, i.e. activated, much more strongly than acyclovir in non-infected cells), high side-effect rates are to be expected.
The most commonly observed side effects are neutropenia , thrombocytopenia and anemia , less common: eosinophilia, increase in transaminases or urea and creatinine concentrations in plasma; central nervous side symptoms such as dizziness, headache, hallucinations, cramps; Symptoms related to the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting and diarrhea); Skin manifestations.
Trade names
Cymeven (D), Cymevene (A, CH), Virgan (D)
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet ganciclovir ( memento of the original from February 17, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. at Roche , accessed on February 17, 2017 (PDF).
- ↑ a b c Entry on ganciclovir. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 6, 2019.
- ↑ a b Ganciclovir data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 17, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ pharmazie.com : Cymevene “Roche” 500 mg dry substance for infusion preparation (PDF; 53 kB), accessed on August 29, 2013.