De Meinweg National Park
| De Meinweg National Park | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Location: | Limburg , Netherlands | |
| Next city: | Roermond | |
| Surface: | approx. 1600 ha | |
| Founding: | 1995 | |
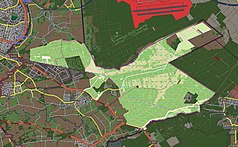
| National park map | ||
The Dutch national park De Meinweg is located in the province of Limburg , municipality of Roerdalen , on the border with the Federal Republic of Germany and is part of the cross-border nature park Maas-Schwalm-Nette . It borders on the villages of Vlodrop , Herkenbosch and Melick . The national park , officially recognized on June 8, 1995, has a total area of around 16 km².
Landscape and nature
The landscape of the national park is characterized by pine forests , heathland and moors . The moors formed due to the sloping terracing of the area from east to west, which is caused by small clumps and geological trenches . The two largest moor lakes, called “vennen” in Dutch, are the “Elfenmeer” and the “Rolvennen” lake.
In the Meinweg area there are still occurrences of the adder and some other snake species .
In order to counteract the encroachment of the heathland, cattle , sheep and horses are allowed to graze in parts of the park in summer . The sheep are tended, cattle and horses, on the other hand, can move freely on large areas delimited by pasture fences and cattle grids . These parts of the national park are not allowed to be used by riders, otherwise there are parts of the park to protect the reptiles, the paths of which are also closed to cyclists.
The exhibition in the national park's visitor center, located on the national road N 570 leading from the border crossing to Germany near Rothenbach to Roermond, shows the natural and cultural history of the area.
history
The heathland and silting are also a result of slash and burn , overgrazing and plague sting of the people who have settled here since the Bronze Age . The name refers to the function as common land in the Middle Ages . The residents of 14 surrounding villages used the area collectively for firewood or as pasture. The barren sandy soil prevented large-scale cultivation for a long time. In the Napoleonic era around 1807 , the land was transferred to state ownership and divided into long, straight parcels, which can still be seen today in the path and border. Population growth , the use of artificial fertilizers and land consolidations led to a decline in nature from the end of the 19th to the middle of the 20th century . Pine plantations served the growing need for pit wood for mine tunnels in the Aachen district and in the Ruhr area . The tracks of the Iron Rhine have been running through the area since 1879 . The reactivation of the single-track railway line for freight traffic between Antwerp and the Ruhr area is a controversial issue today. The planned mining of hard coal was not economically viable. In 1962 , the Beatrix mine was closed shortly before production began.
Direct the former was located since 1909 on the border with Germany Franziskaner - boarding school and convent College of St. Louis . The site is now used by the Maharishi European Research University, MERU, which acquired the land and buildings from the Dutch state in 1984. The listed monastery building was partially destroyed by MERU in 2001 and then finally demolished in 2015 after many years of legal disputes. Today only the rebuilt spire reminds of the monumental neo-Gothic brick building.
On April 20, 2020, a large forest fire broke out in the area of the national park, affecting an area of 170 hectares. The fire spread to the German side of the border, but was quickly brought back under control. The fire lasted longer on the Dutch side. The village of Herkenbosch had to be evacuated, the Red Cross built emergency shelters in gyms. The Dutch army also sent two armored recovery vehicles to support the fire brigade in drawing firebreaks .
gallery
literature
- Venner Gerard: The Meinweg. Research on rights to commons in the former Geldrisch - Jülich border area 1400-1822 (= series of publications of the district of Viersen No. 35). 1985
Web links
- National park website (Dutch)
- Website of the Maas-Schwalm-Nette Nature Park (multilingual)
- Photo gallery of the National Park (German)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Forest fire in the border area: Dutch village evacuated , daily news from April 22, 2020; Accessed April 22, 2020
- ↑ Forest fire: Still no all-clear , RP Online from April 22, 2020; Accessed April 22, 2020