Neisseria gonorrhoeae
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

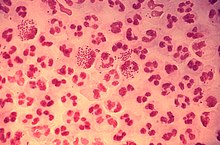
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gram stain) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | ||||||||||||
| ( Zopf 1885) Trevisan 1885 |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (syn. Gonococcus neisseri , Micrococcus gonorrhoeae ; gonococcus ) is a gram-negative , immobile bacterium . Gonorrhea are the triggers of gonorrhea (syn. Tripper ) and other conditions.
properties
Gonococci are gram-negative, aerobic diplococci . Gonococci are very sensitive to environmental influences, especially to dehydration. Gonococci are catalase and cytochrome oxidase positive.
In contrast to Neisseria meningitidis, gonococci lack a real capsule . The membrane of the gonococci, however, contains lipooligosaccharides (LOS), of which certain sub-forms can bind sialic acid and thus build up a capsule-like structure that enables serum resistance and extracellular survival in the host. Gonococci effectively evade the host's humoral immune response. Direct contact with the host cells takes place via type IV pili and so-called OPA proteins (OPA = opacity, since they make the colonies appear cloudy). Gonococci have different OPA proteins in their genome. These are usually not expressed at the same time. The type of OPA protein expressed is responsible for the organotropism of the germ. The germs bind through the OPA proteins to CD66, heparan sulfate proteoglycan receptors and CGM1 on fibroblasts , epithelial cells and macrophages . In addition, these proteins induce phagocytosis . Each OPA gene has several repetitive sequences (repeats) of 5 nucleotides. These are regularly cut out or duplicated, which changes the reading frame and creates new variants of the OPA proteins. This mechanism is called antigenic variation . Since iron intake is essential for gonococci , there are also transporters for transferrin and lactoferrin on their surface .
Gonococci have type IV pili made up of pilin . These pili can be used to move (twitching motility) over surfaces. Through cycles of lengthening, binding of the pilus to the surface and shortening of the pilus, the cell body is drawn over the substrate, causing a twitching movement.
Gonococcal strains form e.g. T. penicillinase and thus escape the previously common therapy using penicillin . Penicillinase is usually plasmid- coded.
In addition, gonococci produce an IgA1 protease . This can cleave IgA antibodies . Gonococci thereby override an important defense mechanism of the mucous membranes . The IgA1 protease cleaves the constant part, Fc fragment, of the antibody from the antigen-binding part, Fab fragment . The Fc fragment is used to bind to the Fc receptor of phagocytic cells. This binding and thus the subsequent phagocytosis of the pathogen does not occur due to the cleavage of the antibody. The Fab fragment nevertheless recognizes specifically the epitopes of the bacteria and binds to them. The result is that the bacteria are masked by the body's own proteins (Fab fragments) and are no longer recognized as foreign by the immune cells. The bacterium thus escapes the immune cells and the disease becomes chronic .
Spread
Gonococci have a worldwide distribution. The reservoir is exclusively the infected person. It is questionable whether there are transmission options such. B. from or to the pet.
frequency
Gonorrhea is a common infection. An infection peak occurs in young adulthood. The infection can cause few or uncharacteristic symptoms, especially in women. Therefore, a high number of unreported cases is assumed. There is a high infection rate in countries with poor health care. Along with Chlamydia trachomatis, gonorrhea is the most common sexually transmitted disease worldwide .
Gonococcal diseases
Gonorrhea : In men, gonorrhea usually takes the form of painful and purulent urethritis . If the disease ascends via the urethra, gonorrheic prostatitis and epididymitis can occur. Urethral strictures and infertility can result. Symptoms can go away after weeks.
In women, the majority of infections proceed without any significant symptoms. The remaining patients have discharge , painful micturition and purulent secretions from the urethra . Increases the infection in women, then one can pelvic inflammatory disease or salpingitis and a so-called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) ( pelvic inflammatory disease ) develop. This can result in sterility . The risk of this is increased in pregnant women. In addition, the fruit and the amniotic sac can be infected ( chorionamnionitis ) with the risk of an abortion .
Gonoblennorrhea : This is purulent keratoconjunctivitis of the newborn. The eye infection occurs during the birth process in an infected mother. There is a risk of perforation and blindness. For this reason, Credé prophylaxis with silver nitrate or penicillin has been carried outsince the 19th century.
In addition, gonococci can infect the conjunctiva (such as the conjunctiva ), the pharynx (especially the oropharynx, the pharynx ) and the rectum . There is also a disseminated infection with infestation e.g. B. of joints, lungs and other organs. Also, endocarditis and meningitis may be a result of infection with gonorrhea.
transmission
The transmission of the gonococci usually takes place as a smear infection during sexual intercourse . Newborn babies are infected by vaginal smear infection at birth. As a prophylaxis, an antibiotic solution with erythromycin (formerly: silver nitrate) is dripped into the eyes of newborns (in Austria and Switzerland) .
incubation period
The incubation period is between two and five days for men and up to three weeks for women.
Pathogenesis
Gonococci attach themselves to the mucous membrane cells of the urethra or the cervix via special pili . The adhesin pillin plays a major role in this. Some gonococci induce endocytosis in mucous membrane cells through the opa proteins and are ejected on the side facing away from the lumen (so-called transcytosis ). Gonococci are phagocytosed by granulocytes and can usually be killed. Only some of the gonococci survive intracellularly. The tissue damage occurs through the induction of a purulent inflammation and complement activation and the resulting destruction of the affected epithelium . But v. a. the lipopolysaccharide of the bacterial cell wall play a major role.
therapy
Because of the increasing prevalence of penicillinase-forming gonococci, therapy is carried out with ceftriaxone or a third-generation cephalosporin , with strains resistant to all cephalosporins being found in Japan . Since a double infection with chlamydia can often be found, azithromycin or doxycycline is also used. A co-infection with syphilis should be excluded. The success of the therapy is checked after a week with a smear . The partner treatment is also important in order to rule out cross infections (so-called ping-pong gonorrhea). The Credé prophylaxis is the preventive treatment of newborn babies with 1% silver nitrate solution or erythromycin . A vaccine is not available because of the high variability of the opa and pillin proteins.
Diagnosis
The proof of a gonococcal infection is usually made microscopically . The typical roll-shaped diplococci are usually found inside granulocytes . To secure the diagnosis, an exciter cultivation takes place z. B. on cooked blood agar . In women, the microscopy of a cervical smear can be negative, since the pathogens can reside deep in the crypts. Today, the detection of gonococci is often carried out using PCR .
Reporting requirement
In Switzerland, the positive laboratory analysis findings to be Neisseria gonorrhoeae Laboratory notifiable and that after the Epidemics Act (EpG) in connection with the epidemic Regulation and Annex 3 of the Regulation of EDI on the reporting of observations of communicable diseases of man .
Historical
Albert Neisser discovered the gonococci in a patient's urethral swab in 1879. Carl Siegmund Franz Credé introduced the prophylaxis named after him in 1881 . Ernst Bumm succeeded in growing gonococci for the first time in 1885.
literature
- Michael Sachs: Gonococci. In: Werner E. Gerabek , Bernhard D. Haage, Gundolf Keil , Wolfgang Wegner (eds.): Enzyklopädie Medizingeschichte. De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2005, ISBN 3-11-015714-4 , p. 502.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Marianne Abele-Horn: Antimicrobial Therapy. Decision support for the treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases. With the collaboration of Werner Heinz, Hartwig Klinker, Johann Schurz and August Stich, 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Peter Wiehl, Marburg 2009, ISBN 978-3-927219-14-4 , p. 200 f.
- ↑ Emerging Infectious Diseases : Vol. 17, No. January 1, 2011
- ↑ Marianne Abele-Horn (2009), p. 200.