Doxycycline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Doxycycline | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(4 S , 4a R , 5 S , 5a R , 6 R , 12a S ) -4-dimethylamino-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4, 4a, 5.5a, 6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Inhibition of ribosomal protein synthesis |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
201 ° C (charring) (doxycycline hemiethanolate hemihydrate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water (0.63 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Doxycycline is an antibiotic belonging to the tetracycline class . It has a broad spectrum of activity and shows a bacteriostatic effect on gram-positive , gram-negative and cell wallless germs. It is also effective against Plasmodium sp., But shows only slight tuberculostatic activity.

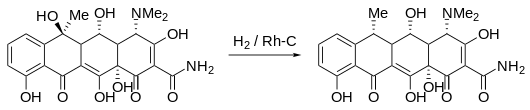
synthesis
Doxycycline can be obtained from oxytetracycline by direct hydrogenation with rhodium as a catalyst .
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of doxycycline is based on an inhibition of protein synthesis . The elongation of the peptide chain is interrupted by reversible blocking of the binding site of the aminoacyl-t-RNA on the 30S subunit of the ribosome . Doxycycline is primarily bacteriostatic.
application areas
According to its spectrum of activity, doxycycline is used to treat respiratory diseases , infections of the urogenital tract , infections of the gastrointestinal tract , biliary tract infections, acne , rosacea , chlamydial infections, borreliosis and numerous rare infections such as plague and anthrax . Doxycycline is also used by the WHO and the German Society for Tropical Medicine and International Health. V. (DTG) for malaria prophylaxis , but there are no approved finished medicinal products for this indication in Germany .
Side effects
Photosensitization has been observed in some patients while taking tetracyclines, including doxycycline . A pronounced sunburn occurs after exposure to sunlight or UV radiation . Patients who may be exposed to direct sunlight or UV radiation should be informed about this typical tetracycline reaction. Treatment should be discontinued at the first signs of reddening of the skin. In addition, acute hypersensitivity reactions with swelling of the tongue and larynx can occur, which lead to dyspnoea and possibly life-threatening shock.
Rare side effects are inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat, headache , nausea , vomiting and (not always reversible) loss or change in the sense of smell and taste as well as inflammation of the pancreas . Liver and kidney damage can occur, especially in the event of an overdose. Simultaneous consumption with milk and milk products as well as other calcium- or magnesium-containing medicines or foods can reduce the absorption of doxycycline from the gastrointestinal tract (formation of poorly soluble complexes ) and thus reduce the therapeutic effect. When taking alcohol at the same time, the increased metabolic rate of the liver causes the drug to break down faster. An effective concentration is no longer achieved as a result. The drug is subject to a doctor's prescription .
Doxycycline is contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding and in children under 8 years of age, as the accumulation of doxycycline can cause tooth discoloration , damage to tooth enamel and a delay in bone growth in fetuses from the 4th month of age and in infants and children up to the age of 8 .
If oral contraceptives are used at the same time , their effect can be canceled.
Trade names
Aknefug Doxy (D), Antodox (D), Atridox (A), Doxakne (D), Dotur (A), Doxybene (A), Doxyclin (CH), Doxyderma (D), DoxyHexal (D), Doxylag (CH) , Doxymono (D), Doxysol (CH), Oraycea (D, A), Periostat (A), Rudocycline (CH), Supracycline (CH), Tasmacyclin (CH), Vibramycin (A, CH), Vibravenous (A, CH ), Zadorin (CH), various generics (D, A, CH)
Ambrodoxy (D), Ambroxol comp. (D)
- Veterinary medicine
Centidox, Doxy, HydroDoxx, Pulmodox, Ronaxan, Soludox, Powdox
Web links
- Entry on Doxycycline at Vetpharm, accessed April 18, 2012.
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index : An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , pp. 582.
- ↑ a b Entry on doxycycline in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet Doxycycline hyclate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 28, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Science-Online-Lexika: Entry on Doxycycline in the Lexikon der Biologie. Retrieved September 2, 2009.
- ↑ a b G. Füllgraf, Björn Lemmer : Pharmakotherapie: Klinische Pharmakologie. 13th edition, Springer, 2006, ISBN 978-3-540-34180-2 , pp. 135-136.
- ↑ Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel: Active pharmaceutical ingredients: syntheses, patents, applications . 2nd Edition. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York 1982, ISBN 3-13-558402-X , p. 339-340 .
- ↑ Thomas Karow, Ruth Lang-Roth: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. 21st edition, Pulheim 2012, p. 767.
- ^ German Society for Tropical Medicine and International Health eV (DTG): Medicines for Malaria prophylaxis .
- ↑ Specialist information from the Swiss drug compendium.
- ↑ Red List
- ↑ Rote Liste Service GmbH (Ed.): Rote Liste 2017 - drug directory for Germany (including EU approvals and certain medical devices) , Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt / Main, 2017, edition 57, ISBN 978-3-946057-10 -9 , p. 358.