PlayStation
| PlayStation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official PlayStation logo | |||||
| PlayStation from the front | |||||
| Manufacturer | Sony | ||||
| Type | stationary game console | ||||
| generation | 5th generation of consoles | ||||
| publication |
|
||||
| Main processor | 32-bit MIPS RISC (R3000 custom), clock frequency: 33.8688 MHz | ||||
| Storage media | CDs | ||||
| Online service | none | ||||
| Units sold | approximately 102.49 million | ||||
| Most successful game | Gran Turismo (Sold: 10.85 million) | ||||
| predecessor | none | ||||
| successor | PlayStation 2 | ||||
| info | Sony's first game console | ||||
The PlayStation ( Japanese プ レ イ ス テ ー シ ョ ン , Pureisutēshon , official abbreviation : PS , code name : PSX , also called PS1 ) is a stationary game console from the Japanese company Sony , which was first sold in Japan on December 3, 1994 and was manufactured after twelve years of sales in Year 2006, was finally discontinued. The PlayStation is the first game console from the PlayStation brand . With Ken Kutaragi as chairman of the specially founded subsidiary Sony Computer Entertainment , the PlayStation became one of the most successful game consoles of all time (102.5 million units sold worldwide) and overthrew former market leader Nintendo in the home console sector .
history
Originally, Sony was supposed to develop a CD drive (add-on) for Nintendo's 16-bit console Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES), the code name of which was already “ Nintendo PlayStation ”. In return, Sony would be allowed to develop its own console with a CD-ROM drive that could use the valuable SNES technology at the time. When Nintendo announced that it would sign a contract for the "SNES-CD" project with the Dutch company Philips (which was terminated a little later), Sony turned the joint project into a completely independent game console, the internal project title of which was "PlayStation Experimental" should have sounded. Other sources, however, say that the X stands for “Extreme”, while others refer to “Expansion”, as Nintendo also used this abbreviation for its SNES satellite add-on SatellaView-X (BSX). That is why it wore the unofficial abbreviation "PSX" until the PSone and PlayStation 2 were released. With the appearance of the successor "PlayStation 2" in 2000, the device was renamed PSone , which also brought a visual makeover to the device, but the abbreviation PSX continues to last beyond the life of the console. Under the official name " PSX ", Sony released a multimedia hybrid of PS2 and hard disk recorder in Japan.
Sony's aggressive pricing policy is considered a factor in the success of the PlayStation. At E3 1995, Sony surprised everyone with a launch price of the console in North America of $ 299, while Sega introduced its Sega Saturn for $ 399. A year later, Sony announced at E3 that it would cut the price to $ 199. Nintendo had introduced its featured Nintendo 64 at a starting price of $ 249, but ultimately adjusted it to match the PlayStation's new price. For the European launch of the N64 in March 1997, Sony reduced the price of its console to now $ 149 worldwide. With this, Sony put the competitor Nintendo under pressure, which then adjusted its price again: in Germany from 399 DM to 299 DM.
The fact that the games were delivered on CD-ROMs and not on modules, as was the case with most of the older, widespread consoles , certainly contributed to the success of the PlayStation . Not only were the production costs significantly lower, the significantly larger storage space also enabled extensive FMV intermediate sequences and real instrumental music with vocals and voice output to be integrated into the game. The ability of CD-ROMs to be copied onto CD burners , which became widespread from the end of the 1990s , which was only possible with the previous game modules with special peripheral devices, increased consumer popularity, with copies only being made with Modchip , special software such as CloneCD, which " defective sectors "retained when burning on a blank disc (the only copy protection of the PlayStation games at that time), or special boot CD are playable. As an alternative to the boot CD, you can also use the swap trick (CD with the boot sector is required for this).
Although the PlayStation was only able to play games from its own region ex works, the installation of a so-called modchip made it possible to play imported games from all over the world. This inexpensive conversion was popular not least because of the publication policy of most game manufacturers at the time; so were PAL versions usually released months or years partly by the Japanese and North American versions; All too often, the quality of the PAL versions was also poor, as the image resolution and the image repetition rate were usually not adjusted to the television standard used in Europe and Australia. This resulted in wide black borders at the top and bottom of the screen and slowed down the game. Many games, especially text-intensive role-playing games , which would have had to be translated into the various European languages in order to be commercially successful, were not published in Europe at all. These clear disadvantages prompted many players to install a modchip in order to be able to access the worldwide game library in the best quality. A side effect of most of these chips was that the PlayStation could then also play copied games from CDs that you burned yourself.
In addition, the PlayStation could play audio CDs; Since the console does not have its own loudspeakers or controls designed for this purpose, the television set usually had to be switched on as the playback medium; The sound could only be reproduced via loudspeakers by inconveniently wiring two of the three cinch plugs to the stereo system and the third to the television, or by using an RGB cable with separate audio outputs. But even then, the joypad had to be controlled via menus displayed on the screen, there was no remote control. As a bonus, from a later revision, the PlayStation was able to display a light show with changing colors and shapes to the rhythm of the music.
In contrast to the SNES, Nintendo's only competing product at the time (although it must be mentioned that the SNES was released in 1991), and the still available Sega Mega Drive from 1989, the PlayStation (as well as the Sega Saturn, 3DO and also Atari Jaguar ) already come up with hardware specially developed with regard to 3D applications. It took some time before Nintendo countered with the Nintendo 64 in 1996.
equipment
The PlayStation offers two connections for various controllers with which the characters in a game are controlled. The original PlayStation joypad offers four main buttons (cross, circle, triangle, square) for the thumb of the right hand, which trigger actions in most games, two selection buttons (Select and Start), which are located in the middle, and four shoulder buttons (L1, L2 as well as R1 and R2), which are operated with the index fingers and often take on secondary control tasks. Directions are indicated with the thumb of the left hand on a 4-way control pad, diagonals are reached by pressing two directions at the same time (for example, up and right = diagonally to the top right). On April 25, 1997, an analog controller was also introduced, which took over Nintendo's idea of analog sticks, but offered two of these sticks at the same time. These small control sticks allowed a stepless directional indication with different impact strengths, which allows a more sensitive control compared to a control pad. The design of the PlayStation joypad remained largely unaffected, because the two analog sticks were only added to the lower part of the joypad during development. However, the rear shoulder buttons (L2, R2) have been enlarged quite a bit to increase comfort, and the joypad has two more buttons. L3 and R3 are under the analog sticks and are activated when one of the analog sticks is pressed down.

The dual shock controller, which was introduced on November 20, 1997 with the Gran Turismo game , quickly replaced the analog controller . Its structure was the same, but it offered an optional rumble function. This technique used semicircular metal blocks that were built into the joypad to rotate. The resulting imbalance caused the joypad to vibrate in certain game scenes. By vibrating the joypad in the player's hands, the impression of action-packed game scenes should be increased again, which was very popular with both software manufacturers and gamers and was used in almost every game of the fading PlayStation 1 era. After a short time, the DualShock controller was declared the PlayStation's standard joypad, so that new devices were only delivered with this joypad. Some games created late in the system's life cycle even require an analog controller. The design and technology can also be found in PlayStation 2 and PlayStation 3 controllers, the DualShock 2 , the Sixaxis and the DualShock 3 ; However, with these versions, the former digital buttons are also continuously analogue, Sixaxis and DualShock 3 are even wireless and sensitive to movement.
Further peripherals for the Sony PlayStation are:
- The multi tap. This allows z. B. expand the number of controllers to five and the number of memory cards to four. With two multi taps, even up to eight players with eight memory cards can compete with one another. However, this is only supported by a few games (e.g. Soccer Live ).
- Light guns (e.g. Just! A Gun, Namco G-con 45)
- Dance mats
- PlayStation mouse
- wireless joypads
- Arcade joypads
- Dual analog joystick
- other so-called freakware such as B. small pseudo-electric guitars that are required for playing certain software titles.
- various cheat modules for the expansion slot in the back
- a module for the expansion slot at the back to play VCDs
- Third-party controllers in various colors and shapes, design often similar to that of the original
- Link cable
- colored housings (including transparent ones) from third-party manufacturers
- Modchips, Ghostchips for playing import games or backup copies
- Cheat module replacement for the PSone in the form of a CD
- Memory cards from Sony in various colors with a size of 120 kilobytes (15 blocks of 8 KB each)
- Third-party memory cards in sizes of several megabytes
- Adapter for playing Game Boy games for the expansion slot (from third-party manufacturers)
- DexDrive floppy disk drive for backing up saved games on standard 3.5 "floppy disks (from third-party manufacturers)
- various Sony and third-party liquid crystal displays that can be attached to the PSone
- PSIO, a plug-in module for the PlayStation Parallel I / O Port, which allows homebrews and backups to be started from an SD
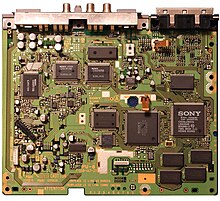
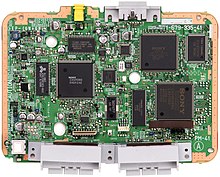
hardware
Technical specifications
PlayStation specifications. These apply to the PlayStation (PS) and the slightly smaller PlayStation One (PSone).
- CPU : 32-bit MIPS RISC (R3000A custom), clock frequency: 33.8688 MHz (30 MIPS performance)
- RAM : 2 MB (1.5 MB RAM + 512 kB ROM)
- ROM : 512 kB
-
Graphics : PlayStation GPU , 1 MB graphics RAM
- Color depth: 4 bit to 24 bit (16.7 million colors)
- Resolution: 320 × 240 to 640 × 480 (NTSC, interlaced) or 512 × 384 (PAL) pixels
- Texture mapping and flat - or Gouraud shading
- MDEC chip for hardware decoding of films (e.g. full motion video )
- Sound : SPU ADPCM, 24 channels, 512 kB sound RAM, MIDI support
-
Drive : 2-way CD-ROM drive, 32 kB buffer, 660 MB storage space
-
European models
- The KSM-440ACM drive was used on the PlayStation model SCPH-1002.
- The KSM-440ADM drive was used on the PlayStation models SCPH-5502, SCPH-5552 and SCPH-7002.
- The KSM-440AEM drive was used on the PlayStation models SCPH-7502 and SCPH-9002.
- The KSM-440BAM drive was used for the PSone, which bears the model number SCPH-102.
-
European models
Interfaces
- 2 × controller connections
- 2 × memory card slots
- AV-Multi-Out (proprietary connection via which stereo sound, composite video , S-video and RGB signals are output)
- AV cinch outputs for stereo sound and composite video (only with the SCPH-1002)
- S-Video Hosiden Jack (only on models for the Japanese market)
- Serial I / O for multiplayer (not with the PSone)
- Parallel I / O for external modules (e.g. so-called fake modules e.g. " Xploder ", has been omitted in the last version SCPH-9002)
Dimensions
(Height × width × depth)
- PS: 60 × 270 × 188 mm³
- PSone: 38 × 194 × 146 mm³ (approx. 35% of the volume of the original PS)
PSone
In December 1994 the first PlayStation (PS) appeared in Japan for ¥ 35,820 (at that time approx. 573 DM - the price for an import was up to 2,800 DM), in September 1995 it was introduced in Europe (price: 599 DM). It has undergone several small redesigns over the years, mainly connections such as B. the cinch outputs were saved. However, the main design of the device remained untouched. It was not until 2000 that Sony redesigned the look of the device, which was mainly reflected in its size. The PlayStation, which was equivalent in terms of functions, but was significantly reduced in size, was called PSone from that point on. In common parlance, both consoles are often referred to as PSone in order to be able to clearly differentiate them from PS2 games for the successor console, the PlayStation 2 .
Obvious differences between the PSone and the PS:
- smaller
- lighter
- Color white (PS: gray)
- white DualShock controller
- Parallel port (e.g. for cheat modules) has been removed
- no restart button (reset)
- external power supply
Console version history
The circuit board of the PlayStation has been made considerably smaller due to technical progress and several chips have been combined in one housing. In addition, many connections have been rationalized away , the cinch connections from the 5502 series, the parallel port from the 9002 series and the connection option (serial connection) from the SCPH 102 series (PSone).
- PlayStation (launched in Japan on December 3, 1994, USA and Europe 1995)
- PSone (market launch: 2000, new design, technically the same as the original PlayStation)
- The name PlayStation was also used by Sony for all later consoles of its own, i.e. the PlayStation 2 (PS2), the PlayStation Portable (PSP), the PlayStation 3 (PS3), the PlayStation Vita (PSV), PlayStation 4 (PS4) and PlayStation 4 Pro (PS4 Pro)
There were a total of five versions of the PlayStation:
- the normal PlayStation (model numbers SCPH-xxxx) in the gray housing
- the small PSone (model numbers SCPH-1xx)
- a so-called Net Yaroze (model number DTL-H300x) with a black housing
- the so-called debugging station (DTL-H100x or DTL-H110x or also DTL-H1200) in a blue or green housing
- a white version (model number SCPH-5903) with video CD playback capability
Normal version (gray housing)
The first version released in Europe was SCPH-1002 in a light gray case. Later models with this housing design lack the cinch connections for cost reasons , so that the sound could no longer be tapped separately, but was only output through the A / V multi output. The model SCPH-9002 also lacks the parallel interface (expansion port ), so that the use of cheat modules was impossible. Rumors say that the parallel port was also removed because various cheat modules facilitate the so-called "swap trick", which allows copied CD-R games to be started without a modchip. Starting with the SCPH-7502 model, a new dark blue user interface was introduced for the memory card manager and the CD player, although the audio playback effects of the predecessor were removed. From this model onwards, visualizations could also be selected during music playback.
A peculiarity of the SCPH-1002 was a design flaw in the power supply, which led to overheating and thus to reading errors with increasing age of the console. The problem can be circumvented by placing the console upside down or to the side.
PSone
This last PlayStation was released shortly before the appearance of the PS2 and differs from the other models in its much smaller dimensions, a rounded housing shape and the external power supply. However, the serial port was also removed here to save costs, so that the link mode capability was omitted. Thanks to the outsourced power supply unit, it was now also possible to install a PSone in the car.
Net Yaroze
The so-called Net Yaroze (model number DTL-H300x) was housed in a black case. With this it was possible to program your own games, which also required a PC with internet connection and knowledge of the C programming language . Due to the high price of US $ 750 and the fact that very few households had an Internet connection at that time, this version of the PlayStation could not establish itself. Programming on the "Net Yaroze" was also quite difficult, even if you had programming knowledge beforehand, and the games rarely had 3D graphics due to the limited developer tools (in contrast to the official, much more expensive developer tools). For a long time, demo CDs from the official PlayStation magazine occasionally featured a few games programmed with a Net Yaroze.
In terms of hardware, the Net Yaroze, in contrast to the PlayStation, was able to play games in all image formats. On delivery, the only other difference was the included Net-Yaroze tools ( boot CD , compiler , access card ). In contrast to the Debugging Station, the Net Yaroze could not play CD-R copies. Many programmers from the demo / homebrew scene also use illegally copied Net-Yaroze compilers and cracked Net-Yaroze boot CDs in connection with normal PlayStations, which were equipped with a modchip, because the Net Yaroze was too expensive for them.
Debugging station
The so-called debugging station (DTL-H100x or DTL-H110x or also DTL-H1200) had a blue or green housing and could play games in all image formats and also burned copies on CD-R (without modchip or modifications, directly from the Factory out). This was important as beta versions were tested on CD-Rs. However, it was never available to the end user, but was only given to licensed developers and editors of video game magazines. For this reason it is a sought-after rarity.
White PlayStation
The white PlayStation (model number SCPH-5903) was able to play video CDs without an additional expansion card, but was only released in Asia and is a coveted collector's item due to the low edition of 10,000 pieces.
Games
Over 4,000 games have appeared for the PlayStation over the years, including some that have created entirely new genres. For the launch of PlayStation in 1994 the racing game was Ridge Racer from Namco released, what ever is considered the very first PlayStation game. Although there was only one route (which could be traveled in different lengths and in mirror image), it became a hit and generated high sales of games such as consoles. The most important publications in 1995 include the action racing game Destruction Derby , which impressed with a sophisticated damage model for the vehicles at the time, the multiplayer strategy game Worms , and the futuristic glider race WipEout . The first part of the Tekken series, which is still successful to this day, as well as the sports games of the FIFA Soccer and NBA Live series from Electronic Arts , which are updated each year, appear for the first time that year.
Probably the most sustainable release of 1996's Resident Evil by Capcom , which sold millions of copies worldwide and several sequels moved to it. Another million seller is the action adventure Tomb Raider , whose heroine Lara Croft became one of the most famous figures in pop culture. Other hits of the year are the Jump 'n' Run Pandemonium , the film adaptation Die Hard Trilogy , the Formula 1 racing game Formula 1 , which comes up with a realistic commentary, and the technically advanced sequels Tekken 2 and WipEout 2097 .
The biggest hit of 1997 was Final Fantasy VII , an RPG epic that also sets new standards in terms of presentation. In addition, critics and fans praise the racing game Porsche Challenge , the Beat'em Up Soul Blade and the innovative Jump'n'Run Oddworld: Abe's Oddysee . The first part of the Grand Theft Auto series is also published. The racing simulation Gran Turismo became a millionaire hit in 1998, alongside the extremely successful sequels Resident Evil 2 , Tekken 3 , Need for Speed III: Hot Pursuit and the stealth game Metal Gear Solid .
In 1999, two genre-defining games were released with Silent Hill and Tony Hawk's Skateboarding . Dino Crisis relocates the successful Resident Evil concept in a dinosaur scenario and the racing game Driver offers previously unknown freedom of movement in virtual cities. Also, Gran Turismo 2 and Final Fantasy VIII , the agent game Siphon Filter , that of Steven Spielberg's film company DreamWorks co-produced first-person shooter Medal of Honor and the action-packed flight simulator Ace Combat 3 provide still continued high sales of software and hardware.
In 2000 , the year PlayStation 2 was released, the innovative action adventure Fear Effect and the sequels Dino Crisis 2 , Final Fantasy IX and Medal of Honor: Underground, which are still selling very well, are released . In 2001, Fear Effect 2 and C-12: Final Resistance are the last major, lavishly produced games. After that, most of the big game publishers concentrate exclusively on the new PlayStation 2. The appearance of two retro game hits in 2003 went almost unnoticed by the players: the Beat'em Up International Karate Plus and the Jump ', designed as a James Bond parody. n 'Run James Pond 2 was released many years earlier for the C64 and Amiga .
emulation
The first working attempts to emulate PlayStation games on the PC were made in the late 1990s. The Bleem! was groundbreaking here; thanks to the programming in assembler , it ran surprisingly smoothly even on less powerful computers. Bleem was sold commercially from 1999. Sony filed a lawsuit against the makers of Bleem, but lost on all counts. In the end, however, the legal dispute meant the end of the emulator , as the legal costs for the two-man company could not be borne.
There were three special Dreamcast versions of the emulator called Bleemcast. However, each of the three bleemcasts was only compatible with one specific game; the games supported were Metal Gear Solid , Tekken 3 and Gran Turismo . The graphic quality of these titles was also significantly improved by Bleemcast, which was noticeable through a higher resolution and mip mapping on the textures. Today the PlayStation can be emulated almost perfectly on the PC. The most popular and powerful emulator is ePSXe ; however, this has the disadvantage of requiring an image file of the PlayStation's BIOS . Another popular emulator is PCSX , which is not as compatible as ePSXe, but does not require a BIOS image.
Various emulators from some older systems can also be played on the PlayStation itself; Particularly noteworthy is the very accurate emulation of the NES by It Might Be NES . An adapter for playing Nintendo Game Boy games has also appeared; The Game Boy hardware is not used in the adapter, but its functions are emulated. However, the emulation does not work perfectly.
Web links
- Official Sony PlayStation website
- Link catalog on the subject of Sony game consoles at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
Individual evidence
- ↑ http://www.scei.co.jp/corporate/data/bizdatajpn2004_e.html ( Memento from June 29, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ http://www.scei.co.jp/corporate/data/bizdatausa_e.html ( Memento from March 6, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ http://scei.co.jp/corporate/data/bizdataeu_e.html ( Memento from July 28, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ SCEE 1995 — Key Facts and Figures . Sony Computer Entertainment. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009. Retrieved November 16, 2015.
- ^ PlayStation Cumulative Production Shipments of Hardware . Sony Computer Entertainment. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved May 12, 2012.
- ↑ Best Selling PlayStation Games. listal.com, January 6, 2009, accessed January 4, 2017 .
- ↑ a b SCPH @ PlayStation. Retrieved May 2, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Brendan Sinclair: Sony stops making original PS. GameSpot, March 23, 2006, accessed April 1, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Individual region / Japan (1994-2004) | Sony Computer Entertainment Inc. June 29, 2013, accessed May 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Sales figures of the world's best-selling game consoles up to February 2020. In: Statista . March 2020, accessed on August 5, 2020 .
- ↑ Edge editorial team: The Making Of: PlayStation ( English ) In: Edge magazine . Future, plc. April 24, 2009. Archived from the original on May 16, 2012. Retrieved on April 8, 2011.
- ↑ Video game decisions (1): Nintendo decides to use modules for the N64. In: retrovideospiele.com. Retrieved May 22, 2019 .
- ↑ SCPH @ PlayStation. Retrieved May 2, 2019 .
- ↑ Analog Joypad To Go On Sale In Japan. IGN, April 3, 1997, accessed April 7, 2017 .
- ↑ SCPH @ PlayStation. Retrieved May 2, 2019 .
- ↑ PSIO. Retrieved June 4, 2019 (American English).
- ↑ Up2Games.de: Technical data of the PlayStation
- ↑ Tom Rhodes: Best Little Emulator Ever Made! The Escapist, October 2, 2007, accessed April 1, 2017 .