Slave state
Before the American Civil War in was United States a slave state , a US state in which the slavery of African Americans were allowed by law, a whereas a free state was a US state where slavery was either banned or eliminated over time. Slavery was one of the causes of the American Civil War and was abolished in 1865 by the 13th Amendment to the US Constitution .
prehistory
The northeast and mid-Atlantic states , including Massachusetts , New York , Pennsylvania, and New Jersey , legally tolerated slavery in the 17th , 18th, and even some 19th centuries , but during the two generations prior to the American Civil War, nearly all were slaves as a result of one Number of laws have been released.
The first US region to be completely free of slavery was the Midwest , organized under the Northwest Ordinance of 1787, just passed before the US Constitution was ratified. The states that were created from this region were Ohio , Indiana , Michigan , Illinois , Wisconsin, and Minnesota . They were mostly settled by New England settlers and veterans of the American Revolutionary War , who were given land there. Because this region was completely free of slaves from the start and cut off from the south by the Ohio River , which pushed for the expansion of legal slavery to the west , the concept of "free states" as opposed to "slave states" developed. The rural Midwest, once in direct east-west rivalry with the trading states in the northeast, realigned itself with the northeastern states that recently became slave-free, and together created the amalgamation of states that prohibited slavery, better known in the Framework of the American Civil War as the free states.
Anti-slave settlers in " Bleeding Kansas " were called free-staters in the 1850s because they had fought successfully so that Kansas was accepted into the Union as a free state.
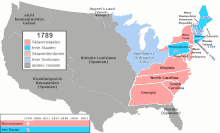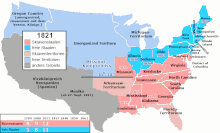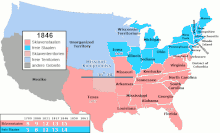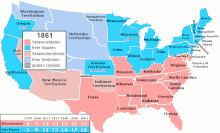
When the American Civil War broke out, there were 19 free states: Maine , Vermont , New Hampshire , Massachusetts, Rhode Island , Connecticut , New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Kansas, Iowa , Oregon and California . New Jersey still had slaves during the American Civil War. New Jersey's law required the gradual release of the slaves, so most (but not all) slaves were released to freedom in that state during the American Civil War.
States
The 15 slave states prior to the American Civil War were Alabama , Arkansas , Delaware , Florida , Georgia , Kentucky , Louisiana , Maryland , Mississippi , Missouri , North Carolina , South Carolina , Tennessee , Texas, and Virginia , including West Virginia , which was not at the time separated from Virginia. Furthermore, slavery was legal in the District of Columbia until April 16, 1862. In addition, slavery was allowed in the two territories of Nebraska and Indian ( Oklahoma ) since the 1850s. The last northern state to abolish slavery was New Jersey in 1804, although that state's laws allowed the keeping of slaves over a certain age as "apprentices for life" until the 13th Amendment of 1865 which is in fact the current one Signed the end of slavery in New Jersey.
Eleven of these states declared their secession in 1860 and 1861 and formed the Confederate States of America . Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland and Missouri did not leave the Union . West Virginia joined the Union as a slave state in 1863 after agreeing to the gradual elimination of slavery and adding the Willey Amendment to the state constitution, after which it ratified it in a referendum on March 26, 1863.
Original state elimination efforts
Before the American Revolution, slavery was allowed in all British colonies in North America , but the War of Independence gave the decisive impetus to a general anti-slavery view. The Northwest Territory , better known as the Midwest, was organized under the Northwest Ordinance of 1787, where slavery was prohibited. Massachusetts adopted the practical abolition of slavery in its 1780 constitution. This constitution served other northern states to pass laws that resulted in the gradual release of slaves. New Jersey was the last state in 1804.
Northern slave states
| Relevant data | VT | PA | MA | NH | CT | RI | NY | NJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European settlement | 1666 | 1638 | 1620 | 1623 | 1633 | 1636 | 1624 | 1620 |
| First record of slavery | around 1760? | 1639 | 1629? | 1645 | 1639 | 1652 | 1626 | 1627 |
| Official end of slavery | 1777 | 1780 | 1783 | 1783 | 1784 | 1784 | 1799 | 1804 |
| Real end of slavery | 1777 | circa 1845 | 1783 | around 1845? | 1848 | 1842 | 1827 | 1865 |
Conflict over the new territories
During the war of 1812 , the British promised freedom to slaves if they would support them. At the end of the war there was a division: one half of the states had already abolished slavery (Northeast), banned it from the beginning (Midwest) or committed to abolishing slavery, and the other half maintained it forever wanted (south).
The potential for political conflict over the issue of slavery at the federal level raised concerns among politicians about the balance of power in the US Senate , where each state was represented by two senators. With an equal number of slave states and free states, the US Senate was also divided. When the population of the free states grew faster than the slave states, it resulted in the free states taking control of the US House of Representatives , while the slave states' politicians in the US Senate were concerned with a Congressional veto on federal laws on slavery maintain. As a result, slave states and free states were often admitted to the Union in pairs in order to maintain the existing balance in the US Senate.
Missouri Compromise
The dispute over whether Missouri should be admitted to the Union as a slave state resulted in the Missouri Compromise of 1820. There it was determined that the Louisiana Purchase Territory north of 36 ° 30 ', which describes Missouri's southern border, was used to organize free States and the territory south of this border would be reserved for slave states. As part of this compromise, Maine was added as a free state and Missouri as a slave state in order to maintain the balance.
Status of Texas and the Mexican Cession States
The admission of Texas into the Union and the acquisition of vast new western territories after the Mexican-American War fueled the dispute. Although the populated part of Texas an area rich in cotton - plantations and was dependent on slavery, the acquired territory that today appeared New Mexico belongs, not for cotton or slavery favorable. In the compromise of 1850 , California was admitted to the Union as a free state without an additional slave state as compensation. This would have meant a majority for the free states in the US Senate, but California agreed to send a pro-slavery and an anti-slavery Senator to Washington, DC . So California's concern added to the fear of pro-slavery politicians, but it did not change the balance in the US Senate.
Final battles
The difficulty of identifying any territory that could be organized as another slave state stalled the process of opening the western territories to settlement, for which the slave state politicians were seeking a solution. There were efforts to acquire Cuba and annex Nicaragua , both for the slave states. In 1854 the Missouri Compromise of 1820 was lifted and an attempt was made to organize Kansas as a slave state. Kansas was intended for admission to the Union with Minnesota, but the admission of Kansas as a slave state was blocked by the question of the admissibility of its slave state constitution. When Minnesota was admitted to the Union in 1858, the balance in the US Senate was lost, the loss due to the subsequent admission of Oregon in 1859 brought the final blow.
Admission of states in pairs
Before 1812 there was no need for a balance between slave states and free states. The following table shows how the states were organized up to 1812:
| Slave states | year | Free states | year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delaware | 1787 |
New Jersey (slaves until 1804) |
1787 |
| Georgia | 1788 | Pennsylvania | 1787 |
| Maryland | 1788 | Connecticut | 1788 |
| South carolina | 1788 | Massachusetts | 1788 |
| Virginia | 1788 | New Hampshire | 1788 |
| North Carolina | 1789 |
New York (slaves until 1799) |
1788 |
| Kentucky | 1792 | Rhode Island | 1790 |
| Tennessee | 1796 | Vermont | 1791 |
| Louisiana | 1812 | Ohio | 1803 |
After 1812 and until the American Civil War, the balance of free states and slave states was maintained within the federal government, states were typically admitted to the union in pairs:
| Slave states | year | Free states | year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mississippi | 1817 | Indiana | 1816 |
| Alabama | 1819 | Illinois | 1818 |
| Missouri | 1821 | Maine | 1820 |
| Arkansas | 1836 | Michigan | 1837 |
| Florida | 1845 | Iowa | 1846 |
| Texas | 1845 | Wisconsin | 1848 |
|
California (A Pro-Slavery Senator) |
1850 | ||
|
Kansas (blocked) |
Minnesota | 1858 | |
| Oregon | 1859 | ||
| Kansas | 1861 |
End of the slave states
Maryland and the pro-union government of Missouri abolished slavery during the American Civil War. The 13th Amendment, ratified December 6, 1865, abolished slavery in all of the United States, without exception. The ratification of the 13th Amendment was a condition for the return to the Union of the states that had declared their secession.
Individual evidence
- ↑ "The children of slaves born within the limits of this State after the fourth day of July, eighteen hundred and sixty-three, shall be free; and all slaves within this State who shall, at the time aforesaid, be under the age of ten years, shall be free when they arrive at the age of twenty-one years; and all slaves over ten and under twenty-one years shall be free when they arrive at the age of twenty-five years; and no slave shall be permitted to come into the State for permanent residence therein. " Fast, Richard Ellsworth & Hu Maxwell, The History and Government of West Virginia , Morgantown, 1906, pg. 109
Web links
- Slavery in the North (Engl.)
- Report of the Brown University Steering Committee on Slavery and Justice (PDF; 5.9 MB)