Rostock tram
| Rostock tram | |
|---|---|
| Type 6NGTWDE car at Doberaner Platz | |
| Basic information | |
| Country | Germany |
| city | Rostock |
| opening | October 14, 1881 |
| operator | RSAG |
| Transport network | Transport association Warnow |
| Infrastructure | |
| Route length | 35.6 km |
| Gauge | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) 1973–1978 rebuilt from the original 1440 mm |
| Power system | 750 V = , overhead line |
| Operating mode | Furnishing operation |
| Stops | 64 |
| Tunnel stations | 1 |
| business | |
| Lines | 6th |
| Line length | 86.4 km |
| Clock in the peak hours | 10/20 min |
| Clock in the SVZ | 30th min |
| Cruising speed | 20.1 km / h |
| Top speed | 50 km / h route |
| statistics | |
| Passengers | 42 million a year |
| Employee | 750 |
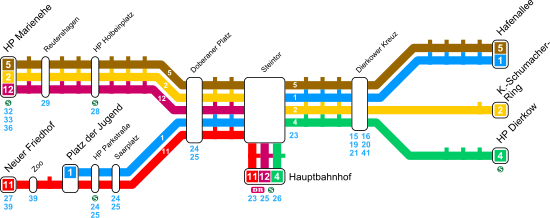
| Network plan 2016 | |
The tram Rostock is next to the Tramway in Schwerin , the only remaining in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern . The network covers a route length of 35.6 kilometers and 64 stops . The first horse tram ran in the city center in 1881, which continues to be the center of the network. The network was gradually expanded until 2006, so that bus traffic only has to cover half of the traffic requirements.
Low-floor articulated trolleys have also been in use since 1992 . Since around 2003 it has been possible to board all journeys without barriers.
history
Until the First World War
In 1881, due to the growing demand for transport, the Mecklenburgische Straßen-Eisenbahn Aktien-Gesellschaft (MSEAG) was founded, which began on August 16, 1881 with the establishment of a horse-drawn tram . Two days after the inaugural voyage on October 14, 1881, regular operations began on three lines:
| 1881 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| 1 | White Cross - Neuer Markt - Hopfenmarkt - Kröpeliner Straße - Schröderplatz - Old Cemetery |
| 2 | Beach (city harbor) - Neuer Markt - Hopfenmarkt |
| 3 | Schröderplatz - Augustenstrasse - New Market - Hop Market |
The drivers also stopped between the stops as soon as they were interested in driving.
In the following years, the routes were adapted to the conditions, which is why, among other things, the trips to the beach were stopped. When today's main train station was built in 1886, the tramway on the Hopfenmarkt - Neuer Markt - Alexandrinenstraße - Bahnhof route was expanded. In 1898 Richard Siegmann became a member of the MSEAG Board of Management, which he remained - with a brief interruption from 1919 to 1921 - until his early dismissal on December 31, 1935. Under his leadership, both the electrification and the further expansion of the tram were promoted.
On May 21, 1904, the first electrically operated tram motor vehicle drove through Rostock. In the course of this, the MSEAG was renamed Rostocker Straßenbahn AG (RSAG). The routes were gradually converted to electrical operation and expanded to Doberaner Platz and further to the new depot in Fahnenstrasse (then Satower Chaussee). By June 18, all lines were covered with the "Electrische". First series railcars were partially in service until 1961. The lines had color names until 1911.
| 1904 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| White Line (1) | Central Station - Steintor - Neuer Markt - Schröderplatz - Doberaner Platz - Old Cemetery - Trotzenburg |
| Red line (2) | Central Station - Augustenstrasse - Schröderstrasse - Doberaner Platz - Kasernenstrasse |
| Green Line (3) | Augustenstraße - City Theater - Mühlendamm - White Cross |
In Hohe Düne and Markgrafenheide , the 4.5 kilometer stretch of the Warnemünde – Markgrafenheide beach railway was opened on July 1, 1910 . The Bäderbahn did not belong to the RSAG, but was operated by the Rostock municipal gas and water works.
From the First to the Second World War
Due to the difficult supply situation, only a limited service could be offered at the end of the war, which in the meantime even came to a complete standstill for several weeks. After the end of the war, the first requests for a route connection to Dierkow arose , but these had to be postponed due to the financial situation. In addition, there was little need for public transport in the years of inflation, so the network was limited to the main lines.
At the time of the economic boom, the number of passengers rose again. During this time, some changes were made to the network: After accidents at the intersection with the railway line to Warnemünde, line 1 was relocated to Parkstrasse in June 1924 and an underpass was built under the railway line. From September 1925, line 2 also ran on the route of line 1 through the city center. The omitted section of line 2 (main station - Schröderplatz) was taken over by a newly created line 4, which existed until 1928. The Barnstorf route on line 1 was extended to the New Cemetery with a bridge over the Wismar – Rostock railway . When the global economic crisis caused high unemployment in 1930 , the clocks were stretched again and sidecars were no longer used.
In the next few years the population of Rostock skyrocketed to over 100,000. Under National Socialism, aircraft plants were built in Warnemünde and Marienehe. Rostock expanded in Reutershagen, Dierkow and in the Hansa and composers quarter. Therefore, the network was expanded in 1936 and line 2 extended to Marienehe. The beach tram in Markgrafenheide ran all year round from 1936, as demand increased due to the expansion of the air base.
When the long-distance route to Stralsund was built in 1933, tram operations on line 3 to the White Cross had to be stopped. The operation on this route was now covered by buses . Before the Second World War, only two tram lines remained, while the bus network was expanded.
| 1933 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| 1 | Hauptbahnhof - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Zoo - New Cemetery |
| 2 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - shipyard |
From the Second World War to the fall of the Wall

In April 1942 Rostock was the target of British air raids, as a result of which half of the historic city center was destroyed. Attempts were made to keep tram traffic going, but on April 30, 1945, traffic was finally suspended for four months. The RSAG had previously been sold to the city and has since been called the Rostock municipal tram . After the occupation of Rostock by the Red Army on May 1, 1945, the operation of the beach lift was ceased forever.
After the end of the war, the network was quickly rebuilt. On August 13, 1945, limited operations could be resumed on two lines.
| 1945 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| 1 | Hauptbahnhof - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Parkstrasse |
| 2 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Reutershagen |
In the years after the Second World War , the number of passengers rose sharply again. In 1945 and 1946, reversing loops were built in Reutershagen and at Platz der Jugend to ease traffic. In July 1946, track construction work also began for a line to Dierkow. It ran through the old town over the Petri Bridge and on via Dierkow to Gehlsdorf. On April 24, 1950, line 3 to the White Cross was again used by trams. In 1956 buses took over the operation again.
With the determination of Rostock as a district town, the city became more attractive for the settlement of companies from 1952; the population and size of the city grew rapidly. This increased the need for public transport, so that in addition to lines 1 and 2, lines 11 and 12 were created, which condensed the cycle on the original routes to five minutes and drove to areas further out.
| 1959 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| 1 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Tiergartenallee |
| 11 | Hauptbahnhof - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Zoo - New Cemetery |
| 2 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Reutershagen |
| 12 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Reutershagen - Marienehe |
| 4th | Stone gate - Gehlsdorf |
Since May 20, 1961, the trains no longer run through the narrow Kröpeliner Strasse, but on a special track in the middle of the Langen Strasse, which was generously rebuilt in the 1950s.
In 1971 the Reutershagen - Marienehe line was expanded to two tracks, as the demand for the industrial areas there had increased. In addition, further residential areas were planned in the north-west of Rostock. As a result, line 2 to Reutershagen was canceled, all trains on this branch now operated as line 12 to Marienehe. Line 1 was no longer available in the mid-1960s. Since then, all trains to the New Cemetery have operated on this branch. In 1974 the route to Gehlsdorf and with it line 4 was switched on and switched to bus operation. From then until 1987 the Rostock tram only consisted of the two lines 11 and 12.
| 1974 | |
|---|---|
| line | Line route |
| 11 | Hauptbahnhof - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Zoo - New Cemetery |
| 12 | Central station - Steintor - Doberaner Platz - Reutershagen - Marienehe |
In 1983, in the area of the Doberaner Platz transfer station, the Kehre am Brink was built , a connection between the branches in the direction of Marienehe and Neuer Friedhof. Since then, this connection has been used for intermittent and intermittent journeys as well as for construction work and operational disruptions. The turning loop at Schröderplatz could then be omitted and was dismantled in 1984.
In the north-east of the city, new, larger residential areas were built in the 1980s. To connect to the inner city, a new line was built from the Steintor to Dierkow and Toitenwinkel . Unlike the old line 4, which ran on a single track through the narrow streets of the old town, the new route ran east around the old town. At Dierkower Kreuz, the route branches into three branches opened between 1987 and 1990 to the Allee der Bauschaffenden (later Kurt-Schumacher-Ring), to the Dierkow stop and to Toitenwinkel.
In the 1960s Rostock received Gotha cars , mostly articulated trains . Tatra trams of the type T6A2 / B6A2 have only operated in Rostock since 1989 . The Tatra railcars were modernized after the fall of the Wall and remained in use until 2015. Until the T6 / B6 was commissioned, a few LOWA and Reko cars were still in operation. The Gothawagen were used in passenger service until 1996.
Since the turning point
After the construction of the routes to the northeast and the increase in traffic in the northwest to the transfer point in Marienehe, line 5 was the first tram line to operate exclusively in the evening. It led from Marienehe to Toitenwinkel.
| 1992 | ||
|---|---|---|
| line | Line route | comment |
| 1 | Youth Square - Parkstrasse - Doberaner Platz - Lange Str. - Steintor - Dierkower Kreuz - Toitenwinkel, Hafenallee | daily in daytime traffic |
| 2 | Marienehe - Reutershagen - Holbeinplatz - Doberaner Platz - Lange Str. - Steintor - Dierkower Kreuz - Kurt-Schumacher-Ring | |
| 4th | Main station - Steintor - Dierkower Kreuz - HP Dierkow | |
| 5 | Marienehe - Reutershagen - Holbeinplatz - Doberaner Platz - Lange Str. - Steintor - Dierkower Kreuz - Toitenwinkel, Hafenallee | daily in evening traffic |
| 11 | Neuer Friedhof - Zoo - Parkstrasse - Doberaner Platz - Lange Str. - Steintor - Hauptbahnhof | |
| 12 | Marienehe - Reutershagen - Holbeinplatz - Doberaner Platz - Lange Str. - Steintor - Central Station | |
On June 14, 1993, a special night tram line was introduced. Line 3 ran from Marienehe through the city center to the main train station, then to the Dierkow stop and from there to Toitenwinkel. As a result of austerity measures, line 11 was withdrawn to Platz der Jugend from October 24, 1994 after 8 p.m., from January 2, 1995 the daytime lines were operated by lines 81 (Platz der Jugend - Hauptbahnhof - Dierkow) and 82 (Marienehe - Hauptbahnhof - Toitenwinkel) replaced. Night line 3 was given the number 92. With the introduction of the two “Fledermaus” night bus lines, line 92 was discontinued.
The fleet has since 1992 more than 40 modern Duewag - low floor -Gelenkwagen type 6NGTWDE. In addition, the T6 railcars for barrier-free entry have been running with low-floor sidecars since 2002, the Tatra sidecars were then parked.
The citizenship decided in 1993 to expand the tram network to the north-west, which began with the connection from Evershagen in 2000. In 2001, the expansion followed up to Lütten Klein on Rügener Strasse, before the remainder of the route to Mecklenburger Allee in Lichtenhagen was inaugurated on November 28, 2003 .
The tram was also expanded to the southern part of the city. For the IGA 2003 in Rostock, the tram was passed under the modernized main station and then extended to the cafeteria and the south view. This section was opened on April 12, 2003.
In 2005, construction began on the connection from Doberaner Platz via Schröderplatz to the main train station, which was completed on October 14, 2006. This had been planned for a long time, so when the Vögenteich road was built, enough space was left for a double-track stretch on the green strip. In addition, a pedestrian underpass was built at Augustenstrasse to enable passengers to access the planned tram stop without having to cross the busy lane. When this tram section was later built, this underpass was dismantled and instead the stop a little further south at Goetheplatz was set up with traffic lights for crossing the street at the same level.
The network has not changed since then. Only adjustments and optimizations were made to the line routes. With the reconstruction of the road layout in the area of the Kröpeliner Tor, the route of the tram route also had to be adapted. It no longer runs in an elongated curve along the hotel, but only turns before the Patriotic Way. The old course of the street and the tram route can still be guessed at the curvature of the hotel building. The Kröpeliner Tor tram stop was relocated to the northeast at the beginning of Langen Straße.
In 2002, work began on increasing the contact wire voltage from 600 to 750 volts . For this purpose, contact line material was exchanged and new substations built. In 2017, the voltage changeover with the sections from the town hall via Steintor to the northeast and from Kröpeliner Tor to the Steintor was completed.
Today's line network
For the new 2016 annual timetable, the MOBIL 2016 traffic concept was developed for Rostock , which was supposed to adapt the traffic offer to the changed demand. In the course of this, there were major reorganizations in the tram network for the first time since 2003. On weekdays, this means that almost all routes run at least every ten minutes during the day. Line 4 no longer leads to Lichtenhagen, but via Lange Straße and Goetheplatz to the cafeteria (stop name changed to Campus Südstadt on March 17, 2018). Line 2 runs via the main station, but no longer to Südblick, but to Reutershagen. In addition, line 3 now also runs daytime on weekdays.
- Lines or line portions with 10 minute intervals are bold shown
- Lines or line sections with 20-minute intervals are shown with the same font
- Lines or line segments with 30-minute intervals are in italics shown
- (valid Mon-Fri approx. 6:30 a.m. to 6:00 p.m.)
Planned expansion
On November 30, 2015 it was announced that the Rostock tram network would be expanded further in order to be able to better reduce vehicle traffic. Therefore, the tram should take around 50 Pick up 000 commuters far from the gates of the city of Rostock and transport them directly to the city center.
The Rostock Environment and Building Senator Holger Matthäus made the following suggestions for network expansion:
- to the Hansecenter in Bentwisch
- to the Ostseepark in Sievershagen
- to Globus in Roggentin
At the same time, Rostocker Straßenbahn AG (RSAG) noted that it is currently focusing more on a new tram route along the Rostock city port . According to previous plans, this project should be around 10 Cost millions of euros. In the course of the development of the city port, the further expansion of the tram tracks between Kanonsberg and Werftdreieck could become more likely.
In October 2016, plans were presented to build a new district between Südstadt and Gartenstadt. In this context, the final stops Neuer Friedhof and Südblick are to be connected by a new tram line. As part of the draft plan of the “Mobility Plan Future” of the city of Rostock, this tram ring connection Groß-Biestow and the above-mentioned tram connection Reutershagen - Ostseepark are in a list of 14 key measures with high priority, the implementation of which should be the focus in the near future .
Further plans were announced in early August 2018. These would be the first new routes since the tunnel under the main station was built in 2006. The first priority is the route from Evershagen to Sievershagen (Ostseepark). Another focus is the above-mentioned project to develop the Groß-Biestow tram ring (from the south view to the new cemetery). Further lines could be planned from the zoo to Reutershagen , from Toitenwinkel to Gehlsdorf , from the Südring to Thierfelderstraße, from Lichtenhagen to Warnemünde and to the center of Reutershagen. A connection with the tram to Groß Klein and Schmarl is also being discussed.
vehicles
The Rostock tram started operating as a horse-drawn tram in 1881 . In 1903 the introduction of electrical operation by the Elektrizitäts-AG Frankfurt a. M. On May 21, 1904, the first electric tram railcar drove through Rostock. By June 18, all lines were covered with the "Electrische". First series railcars were (modernized) in service until 1961.
At the time of the GDR the Rostock tram car received the type LOWA and Gotha , including four-axle setup -Gelenkwagen that are usually used with a two-axle trailer car. Gothawagen were in use until 1996. Tatra cars did not come to Rostock until 1989/1990 . The modernized railcars last only ran on weekdays with low-floor sidecars, preferably on line 1.
Low-floor articulated trolleys have also been in use since 1994. All vehicles in regular service are directional vehicles which are final stops with turning loops equipped.
Tatra T6A2m
In the spring of 2013, 17 of these high-floor one-way railcars were still in regular service. In 1989 and 1990, Rostock received 24 four-axle T6A2 open-plan cars with 6 matching sidecars from the Czechoslovakian manufacturer ČKD Tatra . They had car numbers 601 to 624 and 801 to 806. They were 14.5 meters long and had a top speed of 55 km / h. In the years 1995 to 2001 the railcars were modernized to T6A2m and got new car numbers (701–712 and 801–812). They received outward swinging doors, new destination displays, angular headlights and a modernized interior with a new heating system. From 1996 all six B6A2D sidecars were parked and from 2005 some of them were sold to Szeged . Since April 25, 2015, no more Tatra railcars are used in scheduled service. One vehicle (704) has been preserved as a historic vehicle, again given a cream-colored paint job and converted into a saloon car. It can be rented.
4NBWE
2001/2002 22 were low-floor - sidecar manufacturer Bombardier procured whose car bodies were made in Poland. They were ordered together with the car for the Leipziger Verkehrsbetriebe (LVB). Five of the Rostock cars were handed over to the Leipzig tram in 2013 . Another came to the Kassel tram on a trial basis in November 2013 , where another 14 followed. Since April 25, 2015, they are no longer used in planning service.
6N GTW DE "6N1"
These low-floor articulated multiple units have been running on the Rostock tram since July 1994. 40 cars of this type were procured, they have the car numbers 651 to 690. They are six-axle one-way vehicles with a step-free passenger compartment with a low-floor share of around 90%. Only the two single-leaf doors at the front and rear have a step; in addition to the four seats in the rear by the auxiliary drive switch, another step has to be overcome. The vehicles were manufactured mechanically / mechanically by DUEWAG or Waggonbau Bautzen and electrically equipped by ABB Daimler-Benz Transportation (converters and traction motors) and Siemens (control and other electrical equipment). The middle sections run on two single-wheel single-axle bogies (EEF), and the end sections attached to them also run on a motorized bogie with two water-cooled three-phase motors with an output of 95 each kW. One car is 30.4 m long, 2.3 m wide and 3.38 m high (above sheet metal) and has three double-leaf and two single-leaf pivoting sliding doors, the latter at the ends of the car.
Tramlink "6N2"
Main article: Vossloh Tramlink
13 new “Tramlink 6N2” railcars from the manufacturer Vossloh Kiepe gradually replaced the Tatra railcars and the low-floor sidecars by December 2014. The five-part multi-articulated multiple units are 32 m long and completely low-floor. They have 71 seats, and 139 standing places are provided. The interior is divided into two multifunctional areas and three seating areas. On July 30, 2014, the two cars 601 and 602 began to be used on Line 1. All cars were delivered by December 2014; they are used throughout the route network.
These vehicles have two special features:
- The 32 m long and 2.65 m wide vehicles are in the area of the entry height at 2.3 m drafted. This means that the existing infrastructure (e.g. B. the platform edges) can be used without modifications.
- High-performance capacitors , so-called super - capacitors , are integrated in the vehicle roof . They store the electrical energy gained during braking, which can then be used again for acceleration and for heating and air conditioning. It is hoped that this will result in a significantly lower overall energy requirement.
Technical data of the vehicle:
- Vehicle length: 32.0 m
- Total vehicle width: 2.65 m
- Vehicle height: 3.51 m
- Entry height: 290 mm
- Track gauge: 1435 mm
- Empty weight: 43.9 t
- Number of doors: 6
- Seats: 71
- Standing: 139
- Contact wire tension: 750 V
- Drive power: 4 × 100 kW
- Top speed: 70 km / h (electrically slowed to 60 km / h)
- Special features: energy storage device (supercap) to reduce start-up currents, water-cooled drive, modern passenger information system
See also
literature
- Rüdiger Grabowski, Norbert Enenkel: Trams and buses in Rostock. Kenning Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-933613-81-7 .
- Rostocker Straßenbahn AG: People • Technology • Episodes. ISBN 3-934116-11-6 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ RSAG Statistics ( Memento from August 10, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Jan-Peter Schulze: Richard Siegmann:… but we were Germans. Max-Samuel-Haus / Foundation meeting place for Jewish history and culture in Rostock (ed.), Redieck & Schade, Rostock 2011, ISBN 978-3-942673-08-2 , p. 35.
- ^ Rüdiger Grabowski, Norbert Enenkel: Trams and buses in Rostock. Kenning Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-933613-81-7 , p. 161.
- ^ Rüdiger Grabowski, Norbert Enenkel: Trams and buses in Rostock. Kenning Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-933613-81-7 , p. 174.
- ^ Rüdiger Grabowski, Norbert Enenkel: Trams and buses in Rostock. Kenning Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-933613-81-7 , p. 180.
- ↑ Pictures of the tunnel-like underpass
- ↑ Article from the Ostsee-Zeitung of November 30, 2015: New tram lines: City harbor instead of green meadow?
- ↑ Page 78 in the draft plan of the mobility plan
- ↑ Article from the Ostsee-Zeitung from August 1, 2018: New tram lines: Six new lines? Rostock wants to expand the tram
- ↑ Trailer for trams: KVG Kassel In: kvg.de , November 18, 2013, accessed on November 21, 2018.
- ^ New trams in Rostock. ( Memento from December 3, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Vossloh report , accessed on June 26, 2015