Picric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Picric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 3 N 3 O 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
bright yellow leaf or prismatic crystals that taste extremely bitter and fizzle out when heated quickly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 229.11 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.76 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
0.29 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in ethanol (80 g l −1 at 20 ° C), benzene, |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.1 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Picric acid (Greek πικρος, pikros = bitter) is the common name for 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP). The acid consists of a benzene ring to which a hydroxyl group (-OH) and three nitro groups (-NO 2 ) are attached as substituents . It comes within the substance group of trinitrophenols . Their salts are called picrates .
history

By treating indigo with nitric acid , Peter Woulfe was the first to be able to produce picric acid in 1771. In addition to the yellow coloration of silk , it was initially of no greater importance.
The substance was the first detonating, explosive projectile -Füllmittel and was as Lyddit , Ekrasit , Schimose or Melinit from 1886 used so after the Frenchman Eugène Turpin had discovered the explosive properties of the long previously known acid.
In 1864 the German doctor Wilhelm Erb wrote a paper on the physiological and therapeutic effects of picric acid . In 1865 he completed his habilitation with a thesis on this subject.
In the catastrophic Halifax explosion in 1917, 2300 tons of picric acid detonated.
The use of picric acid to color baked goods in the late 19th century was widespread and known as Weltersches Bitter , but this was stopped after an accumulation of poisoning cases.
Presentation and extraction
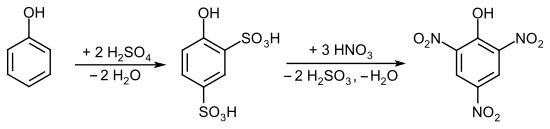
The picric acid is the sulfonation of phenol to phenol-2,4-disulfonic acid followed by treatment with nitric acid produced.
Alternatively, it can be prepared from chlorobenzene via 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene , 2,4-dinitrophenol and its renewed nitration. The substance can be produced directly by oxynitration of benzene with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of mercury (II) nitrate . In the past, picric acid was also made from acaroid resin .
properties
Picric acid forms bright yellow, strongly bitter-tasting crystals . It is only sparingly soluble in cold water, more soluble in boiling water and easily soluble in ethanol and benzene . Due to the accumulation of electron-withdrawing nitro (-NO 2 ) reacts the phenolic hydroxy group of picric acid strongly acidic (pK s = 0.29).
Picric acid burns in the air with a lot of smoke; if heated very quickly or ignited, detonation occurs . Picric acid is sensitive to thermal (heat, fire) and mechanical ( impact , friction ) loads and is considered an explosive substance in the sense of the Explosives Act . For shipping for use as a laboratory chemical (see below), the crystallized acid is stabilized (" phlegmatized ") by adding about 30–50% water .
Table with important explosion-relevant properties: Educational energy −865.9 kJ kg −1 Enthalpy of formation −936.2 kJ kg −1 Oxygen balance −45.4% Nitrogen content 18.34% Normal gas volume 881 l kg −1 Explosion heat 3546 kJ kg −1 (H 2 O (l))
3465 kJ kg −1 (H 2 O (g))Specific energy 1033 kJ kg −1 (105.3 mt / kg) Lead block bulge 31.5 cm 3 g −1 Detonation velocity 7350 m · s −1 Steel sleeve test Limit diameter 4 mm Sensitivity to impact 7.4 Nm Rubbing sensitivity no reaction up to 353 N.
Picric acid forms salts with numerous inorganic and organic bases, which are known as picrates . As a strong acid, it also attacks base metals in aqueous solution, forming picrates. Some of the salts e.g. B. Lead picrate are extremely sensitive to shock , friction and sparks. They therefore behave like initial explosives . Ammonium picrate was used as an explosive .
Also called picrates are the charge transfer complexes that picric acid forms with aromatics . These solids are often sparingly soluble and colored. Because of its characteristic and sharp melting points (e.g. benzene picrate 84 ° C, toluene picrate 88 ° C, anthracene picrate 138 ° C), picric acid was primarily used as a detection reagent for the identification of aromatics.
Picric acid is poisonous. It can cause severe allergic reactions on the skin. The contamination with dusts and vapors should be avoided.
use
Picric acid is primarily used by the dye industry to produce 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol (picric acid ). It was previously used with gum arabic and distilled water to make yellow ink. Another area of application is organic analysis for the detection of amines , alkaloids and creatinine . These basic substances form yellow salts, which were characterized by their melting point (derivative formation).
In histology , picric acid is used in the fixation mixture according to Bouin (Bouin's solution).
The use of picric acid as a filling material for grenades (as in the First and in part also Second World War) was discontinued because of the uncontrolled formation of very shock-sensitive heavy metal picrates. The picric acid has been replaced by TNT here . In microscopy , picric acid is used as a component of fixative liquids (to preserve cellular structures) and to stain specimens. Another area of application for picric acid is metallography . Here the substance is used to etch metallic surfaces, e.g. B. in the preparation of magnesium alloys or in segregation studies on steels. The steels are etched using Igeweskys reagent , a five percent solution of picric acid in anhydrous alcohol. Picric acid is also used to measure creatinine concentration: Creatinine forms a Meisenheimer complex (Jaffé reaction) in alkaline solution with picric acid , the red color of which is measured photometrically .
Amines form salts with picric acid, which have a sharp, characteristic melting point. In the past (and still today in chemistry training) amines were identified in this way.
Legal
According to the German Explosives Act, picric acid is classified as an explosive substance in substance group A (dry) or C (moistened with 25% water) in accordance with Section 1 (3) of the Explosives Act. For private individuals, dry picric acid is therefore subject to approval according to Section 27 SprengG. When dry, picric acid is classified in storage group 1.1 or I or as a dangerous good in class 1.1 (substances that are capable of mass explosion), moistened with 30% water in storage group 1.4.
As a commercially available product, picric acid is moistened with> 30% water and thus phlegmatized . When moistened (> 30% water), picric acid behaves like a flammable solid and is labeled for transport as a flammable solid of dangerous goods class 4.1 according to ADR .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Weltersches Bitter . In: Brockhaus' Kleines Konversations-Lexikon. 5th edition. Volume 2, Leipzig 1911, p. 970.
- ↑ D`Ans, Ellen Lax, Handbook for chemists and physicists, Volume II, Springer-Verlag 1964th
- ↑ A. Bernthsen: Short textbook of organic chemistry. Friedr. Vieweg & Son, Braunschweig 1914.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on picric acid, dry or moistened with less than 30% water in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification . 3. Edition. 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ a b c A. Koffler; M. Brandstätter: On the isomorphic justifiability of H, OH, Cl: s-trinitrobenzene, picric acid, picryl chloride. In : months booklet Chem. 78, 1948, pp. 65-70. doi: 10.1007 / BF00942489 .
- ↑ Entry on Picric acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Picric acid data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 20, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limits - Current MAK and BAT values (search for 88-89-1 or picric acid ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on picric acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 14, 2014.
- ↑ W. Erb: The physiological and therapeutic effects of picric acid. In: Archives Pharm. . 181, 1867, pp. 123-124. doi: 10.1002 / ardp.18671810180
- ↑ Jay White: Exploding Myths: The Halifax Explosion in Historical Context. In: Alan Ruffman, Colin D. Howell (Eds.): Ground Zero: A Reassessment of the 1917 explosion in Halifax. Nimbus Publishing, 1994, ISBN 1-55109-095-3 , p. 266.
- ^ Hans Beyer , Wolfgang Walter : Organic chemistry. 22nd edition. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1984, ISBN 3-7776-0485-2 , pp. 504-505.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k J. Köhler, R. Meyer, A. Homburg: Explosivstoffe. 10th, completely revised edition. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, ISBN 978-3-527-32009-7 , p. 234.
- ↑ Working aid for the investigation of blasting sites, PDF file at www.lfu.bayern.de
- ↑ List of existing substances in the Federal Gazette No. 233a of December 16, 1986 with correction of BAnz. No. 51, p. 2635 of March 14, 1987.
- ↑ Federal Institute for Materials Testing, Storage Group Assignment of Other Explosive Substances, Berlin.
- ^ Hommel: Handbook of dangerous goods. Springer publishing house.
literature
- Louis F. Fieser , Mary Fieser: Textbook of Organic Chemistry. translated and edited by Hans R. Hensel. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1954, pp. 663-665.