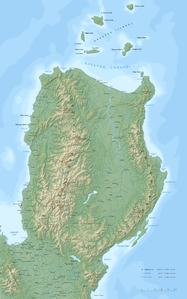
Cordillera Central (Philippines)
| Cordillera Central | |
|---|---|
|
Topographic map showing the |
|
| Highest peak | Pulag ( 2928 m ) |
| location | Luzon , Philippines |
| part of | Luzon island |
| Coordinates | 17 ° 0 ′ N , 121 ° 0 ′ E |
The Cordillera Central is a mountain range on the Philippine island of Luzon .
geography
The Cordillera Central is the most extensive mountainous area on the island of Luzon and covers a sixth of the island's area, which corresponds to 18,300 km². It is considered to be the central part of the Philippine Cordilleras . The mountains rise from the great plains of Luzon and reach the north coast. The width of the Cordillera varies between 60 and 90 kilometers. Several, chain-like, almost parallel mountain ranges run in a north-south direction. Three main chains can be distinguished: the western coastal cordillera ( Malaya chain ), the central cordillera (Cordillera Central) and the poliskette .
In the Malaya chain running in the west, the greatest heights are around 1800 m compared to the main axis of the mountainous region, the Central Cordillera, which has heights of over 2700 m. The further east running polis chain with the highest elevations in Luzon, the Pulag (2922 m). Around the Pulag, the Mount Pulag National Park was established in 1987 on an area of 11,550 hectares. All mountain ranges experience a slope to the north up to 1000 m in the coastal area, the highest elevations are in the southern part.
In the west a narrow foreland accompanies the Cordilleras, in the east a broadly developed zone of gently sloping hill country with height differences between 300 and 500 m. The Cordilleras are densely forested and extend to the Cagayan.
Numerous rivers originate from the Cordillera Central, such as the Agno , the Abra and the Rio Chico, which have their sources on the mountain Data . Other major rivers are the Abulug , the Amburayan and the Laoag . In the valley of the Magat River lies the Magat reservoir , it is the largest reservoir in the Cordillera Central and its hydropower plant has a capacity of 381 megawatts.
Between the Cordillera Central and the Sierra Madre lie the Caraballo Mountains , these are the central junction of the Philippine Cordillera.
The climate of the Cagayan Valley is characterized by a short dry season from March to May and a less intense rainy season from June to February. In the cool dry season, the temperatures in the highlands near Baguio (1500 m altitude) drop to 6 degrees Celsius and at even higher altitudes, ground frosts can occur.
geology
The Central Cordillera is made up of granites , effluent rocks , sandstones , shale and limestone . The basement emerges in a central strip, but there is no clarity about the actual extent. In the west and east there are extensive volcanic deposits, especially andesite .
In the Poliskette, the andesites are overlaid by sandstones in the east . Young tertiary limestones are deposited on them in numerous places , especially on the heights, and are remnants of a much more widespread cover.
The Malaya chain, on the other hand, is predominantly porphyry; to the west sandstones and shale are deposited. The result is a characteristic world of shapes depending on the rock material:
- Cast rocks : generally irregular shapes predominate. The horizon lines are irregular and jagged.
- Sedimentary cover : long and calm lines are characteristic here
- Limestone areas: near Sagada , early tertiary limestones predominate; Flat, plateau-like forms can be found on the heights of the mountains; the construction took place in the early morphological period of the area. In the rainy season these lead to swamp formation .
The central cordillera at the height of the mountain Data and around Baguio carries the largest flat form remnant. Signs that the Cordilleras are relatively young are features such as steep slopes and the receding of the remains of terraces in the valleys.
Culture
In the area of the Cordillera Central, which largely coincides with the Cordillera region , a large number of indigenous tribes live, such as the Igorot , Ifugao and the Ibaloi .
Until they were Christianized, the Ibaloi had a unique technique of mummifying important members of society ( Kabayan mummies ).
In the central mountain range of the Cordeliera Central you can find some of the oldest human cultural evidence in the Philippines: the Bontoc petroglyphs have been classified as the national cultural heritage of the Philippines.
In the Cagayan Valley east of the Cordillera Central are important archaeological excavation sites, which are collectively referred to as archaeological excavation sites in the Cagayan Valley and made it possible to reassess the settlement history of the island archipelago.
The most famous cities of the Cordillera Central are Banaue and Baguio . Famous are the rice terraces near Banaue , which are a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The Spaniards could not enforce their rule in the difficult to access area during the colonial period. After independence, the lack of understanding between the central government and the Igorot continued. This led to the formation of the Cordillera People's Democratic Front (CPDF) resistance movement and violent incidents.
Individual evidence
- ^ Petroglyphs and Petrographs of the Philippines. Information on the UNESCO website (accessed December 17, 2016).