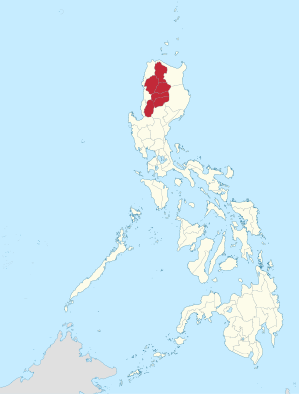
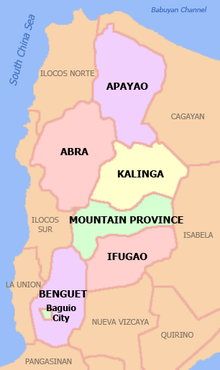
Cordillera Administrative Region
| Cordillera Administrative Region | |
|---|---|
| Regional center | Baguio |
| Residents | 1,722,006 |
| - population density | 84.6 per km² |
| surface | 19,422 km² |
| division | |
| - provinces | 6th |
| - cities | 2 |
| - Municipalities | 75 |
| - Barangays | 1,176 |
| languages | Ilokano , Kalinga , Kankanai , |
The Cordillera Administrative Region (English; Tagalog : Rehiyong Pampangasiwaan ng Cordillera ) is a region of the Philippines on the main island of Luzon and comprises six provinces.
The region is mostly located in the Philippine Cordillera (the Cordillera Central ), which here with the Pulag mountain reach a height of up to 2,922 meters. It borders the regions of Ilocos to the west and south and the Cagayan Valley to the east and north. In the region, the rivers Agno , Abra and Rio Chico have their source on the Data mountain . Other rivers are the Abulug , which drains the north, and the Amburayan , which has its source in the south-west of the region.
A total of 1,643,000 (as of 2011) people live in the 19,422 km² part of the country, resulting in a population density of 84.6 inhabitants per km². Some indigenous Filipino tribes, the Igorot , also live in the area , including the Ifugao, known for their rice terraces . The administrative center is Baguio . The main languages of the region are Ilokano , Tagalog and English .
economy
The area lives mainly from its ore deposits, such as gold, copper, silver and zinc. But sand, gravel and sulfur are also mined here. There are mineral deposits in all provinces, but mining is most common in Benguet . In the east of the administrative region in the valley of the Magat River lies the Magat reservoir , the hydropower plant of which has a capacity of 381 megawatts .
Provinces
The Cordillera Administrative Region is divided into six provinces and two cities:
Provinces:
Province, area, population (as of 2007), number of municipalities and number of barangays.
- Abra (area 4,165.25 km², 230,953 inhabitants, 27 municipalities, 303 barangays)
- Apayao (4,413.35 km², 103,633 Ew., 7 G., 133 B.)
- Benguet (2.826.59 km², 372.533 Ew., 13 G., 1 city, 269 B.)
- Ifugao (2,628.21 square kilometers, 180,711 inhabitants., 11 G, 175 B.)
- Kalinga (3,231.25 km², 182,326 Ew., 7 G., 1 city, 152 B.)
- Mountain Province (2.157.38 km², 148.661 Ew., 10 G., 144 B.)
Cities:
- Baguio (in Benguet)
- Tabuk City (in Kalinga)
Attractions
In the province of Ifugao are the world-famous rice terraces of Banaue and the petroglyphs of Bontoc , which are among the oldest cultural testimonies to humans in the Philippines. In the province of Benguet are the burial places of the Ibaloi, around the mountain Pulag , in which the Kabayan mummies were buried. Another attraction is the Sumaguing Cave in Sagada. Are located in the region a total of four national parks : The Cassamata Hill National Park , the National Park to the highest mountain in Luzon, the Mount Pulag National Park to the Bergdata nearby Mount Data National Park and the Balbalasang-Balbalan National Park .
Culture
Some special musical instruments are used in the region:
- Gangsa , flat gong made of bronze, which is usually played in ensembles of two to seven gongs during dances
- Nose flutes and other bamboo flutes
- Bangibang, tone woods of the Ifugao
- Tongatong, percussion of the Kalinga
- Diwdiw-as, a kind of pan flute
- Saggeypo, bamboo flutes
- Kolitong , bamboo zither.
Some famous festivals:
- Panagbenga or Baguio flower festival in February in Baguio with flower shows
- Ullalim festival in Kalinga in February: the founding day of the province
- Lang-ay festival in the Mountain Province in April: a week of agriculture, tourism and culture, including dances and songs by the provincial tribes
- Banaue Imbayah festival in December takes place every four years and lasts for three days: a parade shows the development of the Ifugao culture, followed by traditional games
- Tabuk Matagoan Festival in Tabuk: a marathon, cultural program and presentation of local products.
The "Bontoc Museum" in Bontoc gives an overview of the culture of the local tribes.
history
In 1908, the new American rulers established a large mountain province that occupied most of the region. In 1966 it was divided into today's Mountain Province , Benguet, Kalinga- Apayao and Ifugao.
Under the dictator Ferdinand Marcos , the largest reservoir in Asia at that time was planned at Chico. It would have destroyed the livelihoods of many tribes in the province - 100,000 people would have been relocated. The project could be prevented, but the experience with it has left many residents with great distrust of the central government. This also led to armed resistance organized by the Cordillera People's Democratic Front (CPDF), a member organization of the National Democratic Front (NDF).
Individual evidence
- ↑ 2015 Population Counts Summary. In: psa.gov.ph. Retrieved June 4, 2016 .
- ↑ http://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5018/
- ↑ http://www.kipas.nl/Instruments/Bangibang.htm
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento of the original dated May 24, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b http://www.koleksyon.com/filipinoheritage/phil-music/pre-colonial-indigenous-music.asp
Coordinates: 17 ° 10 ′ N , 121 ° 10 ′ E