Glacier Bay National Park
| Glacier Bay National Park | ||
|---|---|---|
| Margerie Glacier and Mount Fairweather | ||
|
|
||
| Location: | Alaska , United States | |
| Next city: | Juneau | |
| Surface: | 13,287 km² | |
| Founding: | 2nd December 1980 | |
| Visitors: | 597,915 (2018) | |
The Glacier Bay National Park ( English Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve ) is a national park in the USA in southern Alaska , near Juneau , in the so-called Alaska Panhandle . The park has more than 50 named glaciers , 7 of which extend into the by the tidal influenced water of the fjords as the Tarr Inlet traversed, Glacier Bay called Bay ( "Glacier Bay"). There, ice chunks over 50 meters high often break off and fall explosively into the water ( calving ).
The region around Glacier Bay was first placed under protection as a national monument on February 25, 1925 . The national park that resulted from the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act in 1980 was expanded by 2,100 km² and extends over an area of 13,287 km². A large part of it (10,784 km²) is designated as wilderness area . The park is an IUCN Category V ( Protected Landscape / Protected Marine Area ) protected area . The park is classified by UNESCO as part of an international biosphere reserve and a world natural heritage . In 1979 the Canadian Kluane National Park , together with the US Wrangell-St.-Elias National Park , was declared a cross-border world natural heritage. This world natural heritage was then supplemented in 1992 by the Glacier Bay National Park and in 1994 by the Canadian Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park to form a joint and contiguous world natural heritage. A small expansion area in the far west of the national park is designated with the lower protection status of a National Preserve . Hunting was common here even before it was placed under protection; it is still allowed.
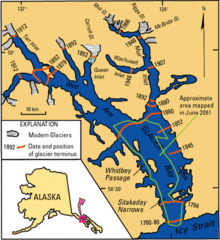
The glaciers of the national park are of scientific importance because they mark the retreat of a smaller ice age 4000 years ago . When Captain George Vancouver explored the region in 1794, the bay was almost completely filled with ice from the glaciers. The ice was several kilometers wide and over 1,000 meters high. In 1879, less than 100 years later, the naturalist John Muir discovered that the glaciers had regressed significantly. The ice mass known today as the Muir Glacier has shortened by 77 kilometers in these 85 years. Today that glacier retreat has slowed. Three glaciers are retreating while eight are getting longer. Scientists are researching the influence of glacier movement on the global climate and the flora in the areas cleared by the glaciers.
The approximately 380,000 visitors annually arrive mainly by cruise ships , or in some cases by ferries operated by the National Park Service . The only road leads from the small airport via the village of Gustavus , both outside the park limits in the southeast, to the visitor center, the campsite and the Glacier Bay Lodge , the only hotel in the park.
There are over 100 glaciers in the four mountain ranges. The highest point in the park is on the flank of the 4663-meter-high Mount Fairweather , whose summit is on the Canadian side outside the park's boundaries. Wolves , brown bears , black bears and mountain goats are characteristic large animal species of the national park. Numerous marine mammals such as killer whales , humpback whales , gray whales , sea otters , seals and Steller's sea lions can also be found in the coastal waters . The area is also one of the few places where the endangered short-billed lalk can still be found.
Other mammals in the area are snowshoe hares , ice gray marmots , beavers , porcupines and red squirrels . The Sitka black-tailed deer has its northernmost occurrence in this region. Since the 1960s, moose have also been found in the area that were not previously found here. The coyote is also a recent immigrant. Pumas could also advance further and colonize the park in the near future. Other predators such as wolverine , North American river otter , mink, and red fox also live in the park. Canadian jacks , on the other hand, are rare.
Web links
- National Park Service: Glacier Bay National Park (official site; English)
- History & Culture of Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve (English)
Single receipts
- ^ Paul Carlson and Peter Barnes: Spring Multibeam Cruise in Glacier Bay Provides Spectacular Images , USGS, 2001 http://soundwaves.usgs.gov/2001/07/fieldwork2.html
- ↑ World Database on Protected Areas - Glacier Bay (English)
- ↑ Kluane / Wrangell-St. Elias / Glacier Bay / Tatshenshini-Alsek. World Heritage Committee , accessed August 3, 2015 .
- ^ Anthony J. Gaston and Ian L. Jones: The Auks . Oxford University Press, Oxford 1998, ISBN 0-19-854032-9 , p. 201






