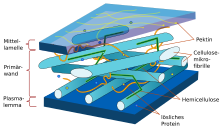
Hemicellulose
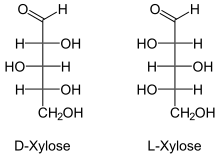
Hemicellulose is a collective term for mixtures of polysaccharides ( polysaccharides ) in variable composition that occur in plant biomass . The most common monomers ( monosaccharides = simple sugars) are pentoses , such as D- xylose and L- arabinose .
The name hemicellulose is based on the original, incorrect assumption that it is a precursor ( hemi- = Greek for half- ) of cellulose. However, this is a homopolymer made from the hexose glucose .
definition
Hemicelluloses are a component of plant cell walls , the matrix of which consists of fibrillar , partially crystalline cellulose . In the case of lignification , this matrix is also penetrated by the macromolecule lignin and thus forms lignocellulose . The hemicelluloses thus form part of the supporting and structural substance of cell walls and make up 1/4 to 1/3 of the plant mass. It is amorphous and does not form any higher structures.
The variety of carbohydrates or monosaccharides in nature is very large. In addition, they can be linked in different ways (via glycosidic bonds ) to form polymers (polysaccharides), which can also differ in the number of monomers. This great diversity is also found in hemicelluloses, so that a general definition based on the chemical structure is only vaguely possible.
physics
The hemicelluloses are soluble in an alkaline or slightly acidic environment. The physical properties of the dry substance are determined by the mixture. In terms of their mechanical and other physical properties, hemicelluloses are primarily dependent on the chain length of the sugar molecules.
Hemicelluloses are the part of the cell wall that can be dissolved by treatment with alkali or by brief extraction with dilute, hot acid . Other components such as lignin and cellulose, which is difficult to access due to its highly ordered structure, do not dissolve. These methods are e.g. B. also used in feed analysis to determine the proportions of certain fractions (cellulose, other carbohydrates).
chemistry
Monosaccharides and derivatives
The polysaccharides of hemicelluloses consist of different monosaccharides. The pentoses (sugars with 5 carbon atoms ) xylose and arabinose are often represented . Also hexoses (sugars with 6 carbon atoms), such as glucose, mannose and galactose , can be found. Compounds related to sugars such as uronic acid (certain sugar acids ), e.g. For example, from the group of hexuronic acids ( glucuronic acid , methylglucuronic acid , galacturonic acid ) and special sugars, such as deoxyhexoses (hexoses, in which an alcohol group (-OH) has been replaced by a hydrogen atom (-H)), for example. B. ( Rhamnose ) occur.
Polymers
The monosaccharides are linked to form polymers (more precisely: polysaccharides). In the case of homopolymers there is only one monosaccharide in the respective polymer, in the case of heteropolymers ( heteroglycans ) there are two or more different monosaccharides. This is partly made clear in the name of the polymer, which bears the name of the only or a common monosaccharide, with the ending ane . Examples are xylans , mannans and galactans , or the higher-level names, such as pentosans and hexosans .
The main chain is usually a homopolymer, for example xylose in the case of xylan, or a heteropolymer made up of two or more building blocks. Other sugars are branched to this and thus form an irregular macromolecule.
Occurrence
Wheat and barley mainly contain hexosans, rye and oat pentosans. The swellable slimy pentosans in the rye flour prevent pasting the formation of a gluten framework as in wheat dough. This polysaccharide is primarily arabinoxylan , the main chain of which consists of xylose and is supplemented by branches in the form of arabinose. Bran contains up to 40% hemicellulose.
Softwood mainly contains mannans, while hardwood mainly contains xylans.
| Polyoses | Softwood (content in%) |
Hardwood (content in%) |
|---|---|---|
| Mannans | 15-25 | 3-5 |
| Xylans | 5-10 | 20-30 |
| Galactans | 0.5-3 | 0.5-2 |
| Total salary | 20-30 | 25-35 |
Use and meaning
| Hemicellulose - renewable raw material for the production of chemicals |
|---|
 Furfural |
 Furfuryl alcohol |
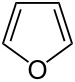 Furan |
Hemicelluloses are a component of cellulose and wood pulp in paper manufacture . They influence properties of the paper such as density, tear and tensile strength, smoothness of the surface, brightness and opacity .
With the increasing importance of renewable raw materials , the development of hemicelluloses, z. B. in biorefineries . Wood and grain could be the source of raw materials, the compounds like furfural from pentoses, e.g. B. for the production of nylon supplies. Furfuryl alcohol and furan are also derived from furfural . “Green” plastics can be produced from furfuryl alcohol. Furan can e.g. B. for the production of solvents - such as tetrahydrofuran (THF) - can be used. A number of other platform chemicals can be derived from hemicelluloses or certain monomers.
With special yeasts that can also utilize pentoses, the production of bioethanol from hemicelluloses, e.g. B. for use as a biofuel or base chemical , be economical.
In the human diet, hemicelluloses, along with the polysaccharides cellulose and pectin , represent an important physiologically harmless fiber , as they are neither digested in the stomach nor in the intestines.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Elmar Weiler, Lutz Nover: General and molecular botany . Thieme, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-13-147661-6 .
- ^ A b McGraw-Hill: Hemicellulose , Encyclopedia of Science and Technology, 5th edition, 2005, accessed at www.answers.com on March 3, 2010
- ↑ www.scientificpsychic.com: Carbohydrates - Chemical Structure , accessed March 3, 2010
- ↑ Guichun Hu et al .: Hemicellulose in pulp affects paper properties and printability , in: Appita Journal 66 (2): 139-144, April 2013; Abstract at researchgate.net.
- ↑ Hirth, T. et al .: Nature as a chemical factory - production of platform chemicals, monomers and polymers from renewable raw materials (PDF; 3.2 MB) ( Memento from December 17, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), lecture by a working group of the Fraunhofer Institute for chemical technology (ICT) at a workshop of the Society of German Chemists (GDCh) on the topic of sustainable chemistry on March 20, 2007, accessed on March 3, 2010.
- ↑ www.chemiereport.at: Swedish researchers are promoting cellulosic ethanol , report on the website of the journal Chemiereport , dated November 24, 2008, accessed on February 8, 2013.
Web links
- Ethanol from lignocellulose - overview (PDF; 2.4 MB), lecture at the New Fuels conferenceon May 6, 2008, Berlin, information on pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation.