Electoral Palatinate Bavaria
|
Territory in the Holy Roman Empire |
|
|---|---|
| Electoral Palatinate Bavaria | |
| coat of arms | |

|
|
| map | |
|
|
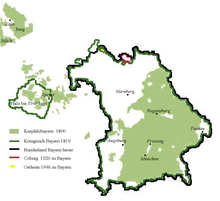
| Electoral Palatinate Bavaria (green) within the boundaries of 1800 (with today's Bavaria bordered in black) | |
| Alternative names | Churpfalz-Baiern or Pfalz-Baiern |
| Arose from | Spa Bavaria , Electoral Palatinate , Duchy of Jülich , Duchy of Berg |
| Form of rule | County, Electorate |
| Ruler / government | Elector |
| Today's region / s | DE-BY , DE-NW , DE-RP , DE-BW , DE-HE |
| Parliament | Kurfürstenbank, Electoral Council |
| Reichskreis | Kurrheinisch , Niederrhein-Westfälisch , Bavarian |
| Capitals / residences | Mannheim , Munich |
| Dynasties | Wittelsbacher |
| Denomination / Religions | Roman Catholic , Lutheran , Reformed tolerated: Jews and Mennonites |
| Language / n |
German
|
| Incorporated into | 1806 Kingdom of Bavaria , already in 1801/03 major changes of territory, losses to France , Baden , Nassau-Usingen , Principality of Leiningen , Duchy of Jülich a . a.
|
Electoral Palatinate Bavaria , also contemporary Churpfalz-Baiern or Pfalz-Baiern (as well as Palatinate and Baierland ) was created in 1777 when Elector Karl Theodor von der Kurpfalz took over the legacy of the male line of his house ( Electorate of Bavaria ), which had died out in the male line . The early modern state went up in 1806 after various territorial losses in the Kingdom of Bavaria .
history
The amalgamation of the states took place through inheritance contracts at the end of December 1777 after the death of Elector Maximilian III. Joseph . In 1778 the War of the Bavarian Succession broke out shortly afterwards . Emperor Joseph II had asserted Austria's claims on Lower Bavaria and the Upper Palatinate and reached an agreement with Karl Theodor. The emperor's war with Prussia was largely bloodless and ended in the Peace of Teschen in 1779 with the cession of the Innviertel to Austria.
In 1785, Karl Theodor tried to hand Bavaria over to the Habsburgs in exchange with the Austrian Netherlands , but this again failed due to the resistance of Prussia and the princes' league. If the attempt to exchange had been successful, Bavaria would have lost its statehood to the Habsburg Empire, and a kingdom of Burgundy on the left bank of the Rhine with Brussels as its residence would have emerged. Frederick II of Prussia therefore enjoyed a great reputation in old Bavaria .
After that there was a certain standardization of the administration in Electoral Palatinate Bavaria. The residence was moved from Mannheim to Munich as early as 1778 . Furthermore, the troops from the Electorate of the Palatinate and Bavaria were combined and given uniform master numbers. Benjamin Thompson , Count of Rumford, a native American, reformed the army system and initiated social reforms (thermal insulation, Rumford soup , Rumford stove, founding schools for soldiers' children, poor houses and factories). The English Garden in Munich, which was opened in 1792, also goes back to him .
The territory of the Electoral Palatinate of Bavaria underwent extensive changes and expansions from 1793 during the French Revolution and the subsequent Napoleonic era. Initially, Palatinate Bavaria lost all areas on the left bank of the Rhine through the First Coalition War , as France was able to enforce the Rhine as the eastern border. Bavaria had hardly participated in this dispute and left the coalition in 1796, but had to cope with the largest losses after Austria ( Duchy of Jülich and the western Electoral Palatinate ).
In 1799 Karl Theodor died without a legitimate descendant. The Palatinate-Zweibrücken family with Elector Maximilian IV. Joseph came into play , so that all of the Wittelsbach principalities were reunited, although the Duchy of Pfalz-Zweibrücken itself was under French occupation. In the Peace of Lunéville in 1801 , the empire formally recognized the cessions to France, however, Emperor Franz II had already given up the Rhineland in the Peace of Campo Formio in 1797, the imperial estates and thus also the Electoral Palatinate-Bavaria were on a losing position.
As a compensation, Bavaria was able to considerably expand its national territory through the mediatization and secularization decreed in the 1803 Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (Bamberg, Würzburg, Kempten, Ulm, Nördlingen, Augsburg). Since the remaining Palatinate area on the right bank of the Rhine had to be ceded to Baden (Heidelberg, Mannheim), the history of Palatinate Bavaria ended. In 1805/1806 Maximilian I Joseph sold the Duchy of Berg and Düsseldorf in exchange for Brandenburg-Ansbach .
The recovery of Bavaria was secured by the secret Bogenhausen Treaty , an alliance treaty concluded in 1805 between the Electorate of Bavaria and France. It led to the creation of the Kingdom of Bavaria (proclamation in January 1806).
Parts of the state of Electoral Palatinate Bavaria
-
 Electorate of Bavaria
Electorate of Bavaria
-
 Electoral Palatinate (until 1797 or de jure until 1801 on the left of the Rhine; until 1803 on the right of the Rhine)
Electoral Palatinate (until 1797 or de jure until 1801 on the left of the Rhine; until 1803 on the right of the Rhine) -
 Duchy of Jülich (until 1797, de jure until 1801)
Duchy of Jülich (until 1797, de jure until 1801) -
 Duchy of Berg (until 1806)
Duchy of Berg (until 1806) - Duchy of Palatinate-Neuburg
- Pfalzgrafschaft Pfalz-Sulzbach
- Margraviate of Bergen op Zoom (until 1797)
- Duchy of Palatinate-Zweibrücken (from 1799, but not enforceable as French occupied)
- Rappoltstein rule (de jure from 1799 to 1801, but de facto already expropriated by France in 1789/1793)
literature
- Gerhard Köbler : Historical lexicon of the German countries. The German territories from the Middle Ages to the present. 7th, completely revised edition. CH Beck, Munich 2007, ISBN 978-3-406-54986-1 , p. 518 ff.
Web links
- German translation of the French text of the treaty - including secret articles - pdf Peace of Campo Formio between Austria and France with the cession of the left bank of the Rhine in the secret additional articles
Individual evidence
- ↑ Anna Maus: The history of the city of Frankenthal and its suburbs. Frankenthal, 1970, pp. 71-80, here: p. 76.
- ↑ See list of the Electoral Palatinate Bavarian regiments of the early modern period