Roller (construction machine)
A roller (commonly known as a road roller ) is a construction machine and belongs to the group of compaction equipment . With their help, a large area can cohesive and non-cohesive soils , supporting and frost protection layers and asphalt are compressed. Sufficient compression is necessary in order to be able to guarantee the load-bearing capacity and durability of the building materials mentioned above .
In the case of rollers, a distinction must be made between a dynamic (compaction by movement) and a static (compaction by weight) mode of action during compaction. They are used on construction sites in earthworks and in road and path construction . Different types of rollers have developed over time, depending on the place of use and the ground to be compacted.
history
Rollers have been used in road construction and earthworks since around 1830 and, in the early days, were mainly horse- drawn devices. At first they were made of stone and later exclusively made of cast iron . They were also weighted down with stones and water ballast .
Steam rollers were developed and used successfully in the early 1860s. The steam rollers are in principle self-propelled locomobiles in which the wheels are replaced by rollers.
The steam rollers were replaced at the beginning of the 20th century by rollers with diesel engines , whereby the basic configuration with a continuous roller at the front and two roller wheels at the rear was initially retained. The first roller with a diesel engine was brought onto the market by the Hamm company in 1911 .
The first tandem roller , i.e. a roller with two driven roller drums , was developed in 1932. This roller did not yet have a vibration function . The tandem vibratory roller did not follow until 1958 . From then on, this technology enabled more effective and faster compaction work. Before the introduction of single drum rollers in 1976, the single vibratory roller was mainly pulled as a trailer by bulldozers or tractors .
Classification
Single drum roller
The compactor is equipped with both a roller drum and pneumatic tires. Both parts can be connected either rigidly or by means of an articulated joint. The driver's cab is in the middle of the machine, behind the engine compartment . From there, the construction machine operator has a good view of the machine. To prevent loamy soils from sticking to the drum , they are removed by the scraper , which is located directly on the drum . There is additional weight at the rear end of the compactor to increase compaction performance.
The drive is usually accomplished with a diesel engine via a hydrostatic drive . The devices are equipped with a vibration unit and have a driver's cab with roll-over protection (ROPS) . The operating weight is between 3.3 and 32.5 t, depending on the design, the output is between 22 and 190 kW .
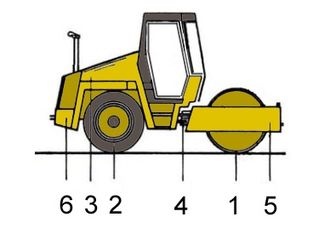
|
Components of a single drum roller
|
Pneumatic tire roller
The rubber-tyred roller causes a "static" compaction of the ground through its weight, i.e. without vibration. Due to the special Walk - and kneading the smooth tire is a pore sealer on the surface of the asphalt surface achieved. Rubber tires stress hard fixtures (stone paving, iron manhole, water slide) more gently than steel rollers. The (identical) air pressure in all wheels can be varied centrally during operation and is set according to the ballast .
Rubber-tyred rollers are mostly used in asphalt compaction , but are also suitable for earthworks. The use of rubber-tyred rollers should be avoided if asphalt layers with loose grains (i.e. open-pored) are built in ( stone mastic asphalt ) or non-cohesive soils are to be compacted.
The machine typically has 4 wheels each at the front and rear, with side gaps slightly less than the width of the tires, the rear ones are typically offset by about half the grid dimension to the left, so that when driving straight ahead, the alternating gap between the wheels causes the driving surface to be completely rolled becomes. The frame therefore has a certain asymmetry, as does the structure, so that the operator can see all 4 wheels at the edge.
Rubber rollers are typically ballasted with iron or magnetite. or concrete slabs, either a forklift pushes a slab into position or the machine can pull a slab up from the floor by itself.
Rubber-tyred rollers can either be equipped with a rigid frame and paired steering of the front wheels or with articulated steering . They have a dead weight of up to 14 t, which can be doubled to up to 28 t by ballasting. The single wheel load then reaches 3.5 t and the tire pressure 8 bar.
Tandem vibratory roller
Tandem vibration rollers (also known as double vibration rollers) have two roller bodies with a smooth jacket and are used to compact rolled asphalt . Smaller hand-held devices are also suitable for compaction tasks in earthworks. As with the single drum compactor , the driver's cab is arranged in the middle ; the frame can be equipped with either articulated or pivot steering. Water tanks are attached above the roller body or below the driver's cab , which serve to weigh down the tandem vibration roller and enable the drums to be sprinkled with water . The sprinkling is necessary to prevent fresh asphalt mix from sticking .
The roller bodies have a vibration or oscillation unit inside , which enables better compaction results. In addition to its surface pressure , the roller can also introduce dynamic energy into the asphalt layer. To reduce the shear forces when compacting in curves , tandem rollers can be equipped with split vibration drums, depending on the weight class . For technical reasons, oscillation drums are always undivided. The travel and vibration drives are hydrostatic .
At the rear of a tandem vibratory rollers can gritting bucket be appropriate. A distinction is made between plate spreaders , vibration spreaders and bar spreaders . With its help, the surface of the fresh asphalt pavement can be sprinkled with sand or chippings and in this way the initial grip can be improved. Furthermore, the roller has a side edge cutting or pressing wheel on the roller body , with the help of which the asphalt edge can be cut and pressed on. The inclination of the pressure roller is either 1: 1 (45 °) or 2: 1 (60 °). The pressure device is controlled hydraulically from the driver's cab.
In addition, larger tandem rollers have the option of moving their drums towards one another . The process, known as crab steering , distributes the roller weight over a larger area and thus enables material that is sensitive to sliding . The smoothing of the asphalt layer, known as "ironing" in construction site jargon, can also be carried out with a roller on large areas.
Combination roller
Combination rollers combine the compaction effect of a pneumatic tire roller and a tandem vibration roller in one device. The structure corresponds to that of a tandem vibration roller with the difference that the rear drum has been replaced by rubber wheels . These types are used depending on the weight class with push-sensitive asphalts in the parking lot - and road construction , as well as walking and biking trails . For the sprinkling of cold rubber wheels one is emulsion tank is available with a water release agent - mixture can be refueled.
Tricycle roller
The three-wheel roller lies between the steam roller and the vibrating roller. Their construction is accordingly kept simple, compression with the aid of vibration is not possible. The driver's cabs are simple driver's cabs that are open on all sides and are located at the end of the roller. The three-wheel roller works solely through its static weight and has no articulated steering. All three bikes are equipped with a smooth jacket . It is driven by a diesel engine.
These machines are still produced in a slightly modified form and even some of the older models are still in use on construction sites. The reason for this is their simple operation and robust construction.
Trench roller
Trench rollers are small vibratory rollers that are either directly hand-controlled or steered by remote control . The remote control is used so that the machine operator does not have to go down into the trench to operate the machine. This has the advantage that the machine operator stays outside the danger area in the event of a ditch intrusion.
Due to their size and their maneuverability, they are mainly used to compact trenches in sewer and pipeline construction. As a rule, they have four independently controlled sheep's foot drums for compacting cohesive soil material. However, they are not suitable for compacting rocky soils.
Technology and equipment
bandage
The jacket of the roller body is called a bandage. Depending on the application and compaction task, different drums are used:
- Smooth coat bandage
- Stamp or sheep's foot bandage
- Belt wheel bandage
- Cage wheel drum
- Disc wheel bandage
- Polygonal bandage
Smooth coat drums are used to compact asphalt or non-cohesive soil . The stamped or sheep foot bandages as well as the polygonal bandages are intended for use on cohesive soils. The Gürtelrad - grating wheel - or Scheibenradbandagen are particularly effective in the compression of rocky ground, because they can shatter the rock constituents.
Vibration and oscillation unit
Modern rollers have the ability to introduce additional energy into the ground in addition to their own weight . The introduction of compression energy results in grain rearrangements in the soil or in the asphalt and thus a reduction in the pore content . During compaction with vibration, an imbalance acts in the roller body , which creates a beating movement. The advantage of the circular vibrator is an effective and high compaction performance, but this type of compaction causes vibrations in different frequency ranges . In order to counteract this disadvantage, certain types of vibratory rollers were equipped with directional vibration systems in order to achieve a regulated and continuous adjustment of the compaction energy . So are the roller driver different directions of oscillation provided by vertical to horizontal , which automatically as well as manually can be regulated. The technology of oscillation compression reduces these undesirable vibrations by installing two unbalances in the roller body. The direction of action of the compression energy is then no longer vertical, but horizontal. Directional vibrator and oscillation compaction can mostly be found in rollers from 7 t.
Compaction control
The so-called comprehensive dynamic compaction control ( FDVK for short ) is a test method for checking the compaction performance of rollers that has been used since 1988. For this purpose, the roller is equipped with an appropriate measuring device, which takes measurements while driving over the ground. Basically, the changed rebound acceleration of the floor on the vibrating roller body is evaluated. The measurement results are graphically output to the roller operator on a display in the driver's cab and can be printed out if required.
The roller is calibrated beforehand to assess the load-bearing capacity of the subsurface . The density and E V2 values are determined using field tests ( e.g. plate pressure test ) and compared with the measurement recordings of the roller.
safety
Since rollers are used in earthworks and road construction in areas with an increased risk of falling or tipping , such as embankment edges , ditch edges or carriageway ledges , drive with appropriate caution. In addition, the machines are equipped with ROPS protection devices, which reduce deformation of the driver's cab in the event of a rollover and secure the survival space inside the driver's cab.
The statutory accident prevention regulations stipulate that only persons who have been instructed , are physically and mentally suitable and are at least 18 years old may operate a roller . The machine operator's exposure to noise and vibrations is increased on this machine and can be reduced by wearing hearing protection and special driver's seats .
Manufacturer
Steam rollers were among the first motorized construction machines and were produced by a large number of manufacturers in their early days. Well-known brands were, for example, Henschel , Kaelble , B. Ruthemeyer or Zettelmeyer . Companies that still produce rollers today are Ammann , BOMAG , Volvo Construction Equipment , Hamm , JCB , Wacker Neuson , Dynapac and Caterpillar .
See also
- List of construction machinery and construction equipment
- List of construction machinery manufacturers
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Manfred Hoffmann: Number tables for the construction company . Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden 2006, ISBN 3-519-65220-X , p. 637 .
- ↑ a b c d Felix Kernze: Fascination Road Construction . Motorbuch Verlag, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-613-02499-3 , p. 13 ff .
- ↑ Horst König: Machines in construction . Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden 2005, ISBN 3-519-00495-X , p. 195 .
- ↑ Leaflet on comprehensive dynamic methods for testing compaction in earthworks (M FDVK E) 2014 edition, drawn up by the Research Association for Roads and Transport (FGSV), working group “Earthworks and Foundation Engineering”, in Road Construction A – Z , Road Research Association - and transport e. V. Cologne (editor), Erich Schmidt Verlag , ISBN 978-3-503-00344-0