Wieprza
|
Wieprza Wipper |
||
|
The Wieprza in Darłowo |
||
| Data | ||
| location | Pomeranian and West Pomeranian Voivodeship , Poland | |
| River system | Wieprza | |
| River basin district | Or | |
| Source lake |
Jezioro Białe (Biallensee) 54 ° 2 '31 " N , 17 ° 13' 8" O |
|
| Source height | 154 m | |
| muzzle | at Darłówko in the Baltic Sea coordinates: 54 ° 26 ′ 25 ″ N , 16 ° 22 ′ 38 ″ E 54 ° 26 ′ 25 ″ N , 16 ° 22 ′ 38 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 154 m | |
| Bottom slope | 1.4 ‰ | |
| length | 112 km | |
| Catchment area | 2150 km² | |
| Left tributaries | Studnica ( Stüdnitz ), Grabowa ( Grabow ) | |
| Right tributaries | Pokrzywna ( Krummbach ) | |
| Small towns | Kępice , Sławno , Darłowo | |
The Wieprza ( ˈvʲɛpʃa ; German Wipper ) is a 112 kilometer long coastal river in Pomerania in the Polish Pomeranian Voivodeship . It rises on the Pomeranian ridge at 154 meters above sea level in Lake Biallen ( Jezioro Białe ) near the village of Głodowo ( Gloddow ) near Miastko ( Rummelsburg ) and flows into the Baltic Sea at Darłowo ( Rügenwalde ) .
River name Wipper
In the German language, Wipper is the name for several, geographically widely separated rivers. A count that also took into account similar-sounding names like Wipfer resulted in the number fifteen.
It has been suggested that the origin of the name can be found in the Middle Low German , Dutch or Middle English word for rocker. Others assumed an even older origin, looked for the origin of the name in Indo-European and translate the river name as the hopping .
course
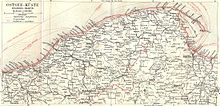
First the Pomeranian Wipper flows in a north-westerly direction, then north at Schlawe ( Sławno ) and turns west at the village Wilhelmine ( Wilkowice ). The Wipper flows into the Baltic Sea near Rügenwaldermünde ( Darłówko ).
The catchment area of the Wipper covers 2150 km². The abundant rainfall creates an even flow of water. The Wipper was straightened in 1928. In 1909 its length was given as 150 km, 128 km of which were floatable. Numerous water mills and even smaller power plants could be operated - for example at Ciecholub ( Techlipp ), municipality Kępice ( hammer mill ), and Biesowice (Beßwitz) in Powiat Słupski (Powiat Stolp) . Today only the section from Darłowo to the mouth of the Baltic Sea can be used by smaller ships.
Tributaries
Several smaller tributaries flow into the Wipper:
- Left tributaries:
- the Taukarre , which flows into the Wipper north of Sławsko ( Alt Schlawe ), municipality of Sławno ( Schlawe );
- the Motze or Schlawer Motze , which rises at Malechowo ( Malchow ), flows south of Słowino ( Schlawin ) at a distance of one kilometer from the town center in a north-easterly direction and flows into the Wipper at Schlawe;
- the Stüdnitz (formerly also Stiednitz , Polish Studnica ), which rises south of Miastko ( Rummelsburg ) and flows northwest of the village Broczyna ( Brotzen ), municipality Trzebielino ( Treblin ), into the Wipper;
- the Grabow ( Polish Grabowa ), which flows into the Wipper behind Rügenwalde.
- Right tributaries:
- the Krummbach , which rises south of the village Łubno ( Lubben ), municipality Kołczygłowy ( Alt Kolziglow ), flows north past the village Trzebielino ( Treblin ) and flows into the Wipper before the village Broczyna ( Brotzen );
- the Stibnitz, which flows into the Wipper about seven kilometers from Darłowo ( Rügenwalde );
- the Motz or Stolper Motze , which arises at Bruskowo Wielkie ( Groß Brüskow ) and flows into the Wipper at Pieszcz ( Peest ).
literature
- Leopold von Zedlitz-Neukirch : New hydrographic lexicon for the German states . Halle 1833, p. 437.
- Ludwig Wilhelm Brüggemann : Detailed description of the current state of the Königl. Prussian Duchy of Vor and Hinter Pomerania . Part II, Volume 1, Stettin 1784, pp. X-XII .
Web links
Footnotes
- ↑ Obszary dorzeczy - Ramowa Dyrektywa Woda ( Memento of the original from October 24, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed December 29, 2010
- ^ Leopold von Zedlitz-Neukirch : New hydrographic lexicon for the German states . Halle 1833, pp. 436–438.
- ↑ a b Elfriede Ulbricht: The river basin of the Thuringian Saale . 1st edition, Max Niemeyer, Halle (Saale) 1967.
- ↑ Felix Solmsen. Ed. U. edit by Ernst Fraenkel: Indo-European proper names as a mirror of cultural history . 1st edition. Carl Winter, Heidelberg 1922.
- ^ Meyers Konversationslexikon , 6th edition, 1909, 20th volume, p. 681.
- ↑ cf. z. B. Ulrich Neitzel, Fritz Schmidt and Mathias Sielaff: The mill chronicle of the Schlawe district , Genealogical writings for East Pomerania IV , East Pomerania eV, Timmendorfer Strand 2007.
- ↑ See for example Leopold von Zedlitz-Neukirch : New hydrographic lexicon for the German states . Halle 1833, p. 437.
- ^ A b Wilhelm Hoffmann: Encyclopedia of Earth, Ethnology and State Studies . Volume 2, Leipzig 1866, p. 1618 .
