Thierstein Castle
| Thierstein Castle | ||
|---|---|---|
|
View of the Thierstein castle ruins |
||
| Creation time : | First mentioned in 1340 | |
| Castle type : | Höhenburg, spur location | |
| Conservation status: | Keep and masonry of the residential buildings | |
| Standing position : | Ministerialenburg, later Princely Amtsburg | |
| Construction: | Keep made of layered granite rubble stones; Remaining building remains made of basalt quarry stone masonry | |
| Place: | Thierstein | |
| Geographical location | 50 ° 6 '28.6 " N , 12 ° 6' 11.4" E | |
| Height: | 615 m above sea level NN | |
|
|
||
Thierstein Castle is the ruin of a spur castle which is 615 m above sea level. NN high mountain spur rises above the village of Thierstein in the district of Wunsiedel in Bavaria .
history
In 1310 , Albrecht VI , who came from Wildstein Castle . In an emergency , King Heinrich VII made it imperial forester in the Egerland . Albrecht XI. followed his father in this office and built Thierstein Castle, first mentioned in 1340, as the administrative seat in the middle of the imperial forests entrusted to him. In 1340, the city of Eger was entrusted with the forester's office in Egerland by King John of Bohemia , competing with the emergency . This was followed by protracted feuds between the Thierstein lords of the castle and the city of Eger, for whose financing the Notthracht were forced to sell their Thierstein property piece by piece. At the end of the 14th century they finally sold Thierstein Castle with the neighboring Thiersheim market .
The buyer was Margrave Wilhelm I of Meissen . From his heirs, the castle and its territory came to the Burgraves of Nuremberg from the Hohenzollern family in 1415 . They occupied the castle with officials . In 1462, during the Bavarian War , in which the Bohemian King Georg von Podiebrad also fought against Margrave Albrecht Achilles , the bailiff Friedrich von Dobenck set fire to the village of Thierstein himself, at the foot of the castle, in order to deny the enemy the opportunity to entrench themselves. In 1497 the keep of the castle became part of a system of waiting areas for national defense and Thierstein was designated as a meeting place for the citizens' militias of the Sechsämterland in the event of an enemy invasion. In 1553, during the Federal War , Thierstein was occupied by Bohemian troops. After Margrave Georg Friedrich took office , he decided, probably because of the poor structural condition of the old castle, to leave the Thierstein office vacant for the time being. In 1562 Beringer von Kotzau was able to move into Thierstein as bailiff. After his death in 1575 Thierstein was co-administered by Wunsiedel; the old castle remained uninhabited. In 1603 Margrave Georg Friedrich von Brandenburg ordered the abandonment of the castle and the construction of a new office building outside the town of Thierstein. Nevertheless, the most necessary repairs were still carried out on Thierstein Castle in order to preserve it as a place of refuge and fortified grain depot for the population during the Thirty Years' War . It was once again brought into a makeshift state of defense in the War of the Spanish Succession in 1703. Thierstein Castle came to an end in 1725, when it fell victim to a fire disaster that struck the entire Thierstein market.
description
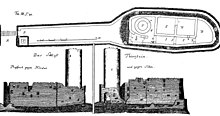
The spur castle was built on a narrow basalt spur facing northeast , which is separated from the inland terrain in the southwest by a neck ditch . A second neck ditch, which separated the elongated outer bailey from the core bailey, was filled in in the 19th century. Only sparse remains of the walling of the outer bailey, which also surrounded the inner bailey as a kennel wall , have survived. The well-preserved cylindrical keep covered the main attack side at the gate to the main castle, which had also disappeared . The area to the east of the keep was occupied by the residential buildings of the core castle, some of the surrounding walls of which still protrude three stories high into the sky.
The oldest view of Thierstein Castle comes from the Selber chronicle of Magister Paul Reinel from 1612. The cartographer Johann Christoph Stierlein (1759–1827) made a carefully drawn topographical view . Another historical view was created almost at the same time by the Hofer grammar school director Johann Theodor Benjamin Helfrecht in 1795. The various representations document, among other things, the gradual decline of the complex, but they also allow conclusions to be drawn about the earlier appearance of the castle.
Todays use
The castle ruins, visible from afar, are a popular tourist destination; From the viewing platform of the preserved 24 meter high keep you can enjoy an all-round view of the entire interior of the Fichtelgebirge up to the Egerland. A key is required to visit the castle and is handed over against a deposit.
literature
- Bernhard Hermann Röttger : District of Wunsiedel and urban district of Marktredwitz . The Art Monuments of Bavaria , VIII. Administrative Region Upper Franconia, Volume 1 . Munich 1954. ISBN 3-486-41941-2 . Pp. 323-341.
- Harald Stark : Castle and Office Thierstein, Selber Hefte Vol . 12 . Selb 1993, ISBN 3-927313-07-6 .
- Harald Stark: The Notthracht family - looking for traces in Egerland, Bavaria and Swabia . Weißenstadt 2006, ISBN 3-926621-46-X .
- Hans Vollet, Kathrin Heckel: The ruins drawings of the Plassenburg cartographer Johann Christoph Stierlein . 1987.
Web links
- Thierstein Castle at www.notthracht.de
- Thierstein castle ruins on the House of Bavarian History site
- Thierstein Castle ruins on the Burgenwelt.de site
Individual evidence
- ^ Burgruine Thierstein, tourist information on the website House of Bavarian History