Firefox OS
| Firefox OS | |
|---|---|

|
|
 Firefox OS 2.2 start screen with additional apps |
|
| developer | Mozilla Corporation |
| License (s) | MPL , Apache License ( Open Source ) |
| Current version | 2.2 (April 29, 2015) |
| Kernel | Monolithic ( Linux ) |
| ancestry |
Linux ↳ Firefox OS |
| Architecture (s) | POOR |
| Languages) | HTML5 , CSS , JavaScript , C ++ |
| www.mozilla.org/firefox/os | |
Firefox OS ( FFOS or FxOS for short , internal code name Boot2Gecko or B2G for Boot to Gecko ) was an open-source , Linux -based operating system for smartphones and tablet computers that was developed by Mozilla Corporation . The aim was to implement the entire user interface and apps using web technologies ( HTML , CSS and JavaScript ) and thus to offer users and programmers the greatest possible openness and compatibility. In 2016, the further development with version 2.6 was discontinued. KaiOS is the successor .
history
On July 25, 2011, Andreas Gal , head of the research department at Mozilla Corporation , announced a development project for a fully independent operating system for the open Internet on a mailing list . The main goal should be to give developers the opportunity to use web-based techniques to develop new apps that are in no way inferior to ordinary applications . However, the operating system was initially seen primarily as a replacement for Google's Chrome OS . But the approach was a bit more comprehensive: With Firefox OS, Mozilla wanted to create an equivalent alternative to the manufacturer's own operating systems iOS , Android and Windows Phone , which is based on completely free software . At the beginning of March 2012, the market entry of the first smartphones with Firefox OS was announced in summer 2012.
In the middle of 2012, Mozilla had won over the first partners, Telefónica and Qualcomm , five other network operators and the manufacturers ZTE and TCL ( Alcatel One Touch brand ) as allies. In July 2012, the first binary packages (so-called nightly builds ) with emulators of the hardware for installation under the most common operating systems on ordinary personal computers were published.
In September 2012, Mozilla released a first video of the Firefox OS in action. Two months later, a Firefox OS simulator was released as an extension of the Firefox browser for ordinary personal computers. This extension was released on December 3, 2012 and the system development was updated. It contains the upper layers of the Firefox OS and should enable software developers to develop apps for the operating system faster and without having to own the associated hardware .
In February 2013, several manufacturers also showed smartphones with Firefox OS at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona . Their largely very simple hardware confirmed that the market entry was to be expected especially in emerging markets such as South America .
On April 23, 2013, the public sale of smartphones with Firefox OS for developers by the Spanish manufacturer Geeksphone began. Geeksphone as a mobile small company of three young founders in Madrid was contacted by Telefónica for this purpose at the Mobile World Congress in 2012. In addition to the basic Keon model , there was also the Peak with a 1.2 GHz dual-core processor, which ensured a unique selling point under Firefox OS.
The sale of smartphones with Firefox OS for end customers began with the ZTE Open on July 2, 2013 in Spain by Telefónica. A few days later the sale of started Alcatel One Touch Fire in Poland by the German Telekom . Your subsidiary Congstar offered this smartphone in Germany from mid-October 2013. At the end of October 2013, the first Firefox smartphone from a large, well-known manufacturer, the LG Fireweb from LG Electronics, came onto the market in Brazil with slightly more sophisticated features .
Subsequently, Mozilla and the manufacturers established several devices in emerging markets such as India . On September 16, 2014, the first device with version 1.4 was presented in Bangladesh .
At the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2015, Panasonic announced that it would use Firefox OS as the operating system on Panasonic TVs in the future.
At the end of 2015, Ari Jaaksi announced that it would focus primarily on the Internet of Things in the future . Firefox OS as the operating system for smartphones should continue to exist, but should no longer be actively marketed.
In 2016, the end of development for mobile devices was announced, and in 2017 work on the operating system was completely finished. In retrospect, Firefox OS had a temporary success in some emerging markets and their low-end devices.
Fork
After Mozilla stopped further development, Firefox OS did not go away because it is open source . The following are the best-known independent follow-up projects ( forks ) that are based on the source code of Firefox OS.
KaiOS
KaiOS can be considered the successor to Firefox OS because it is based on Firefox OS. KaiOS focuses on the product category "Smart Feature Phones". The announcement in June 2018 that Google would invest 22 million dollars in KaiOS so that Google Maps , YouTube and other Google applications would become available caused a stir .
Panasonic
The manufacturer Panasonic continues to use Firefox OS as the operating system for its Smart TV televisions, among other things to operate the home screen and associated apps. Panasonic is developing it further.
H5OS
Acadine Technologies is continuing Firefox OS as its own development under the name H5OS .
Components
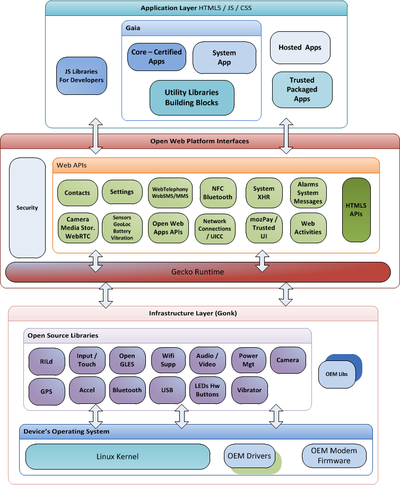
Firefox OS contains the basic components Gonk, Gecko, and Gaia. Gaia is the user interface of Firefox OS and is written entirely in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and JavaScript . Gaia is processed in Gecko , and Gecko works on the basis of Gonk when deployed in Firefox OS.
Gonk
Gonk consists of the Linux - kernel and libraries . The libraries are partly widely used open source software for Linux and partly come from Android like some minor changes to the kernel .
Gecko
Gecko is the Application Programming Interface (API) of Firefox OS, its interpreter for JavaScript, and is responsible for processing all inputs and outputs.
Application programs for Firefox OS are web applications in HTML5 and JavaScript that can also use various non-standardized web APIs to control almost all device functions. For example, the WebTelephony API provides functions for generating and accepting telephone calls. Mozilla aims to standardize its web APIs. Only HTML-based applications are used on Firefox OS, which in principle could also work offline and regardless of manufacturer in any browser; provided that all web APIs used are available on the target platform. This distinguishes the Firefox OS from iOS and Android, which mainly rely on proprietary application programs that can only run on this system. For software developers, there is the Firefox OS Simulator , which can be run as an extension in the Firefox browser and allows the most important functions to be checked. Among other things, it contains a debugger for JavaScript .
Gaia
Gaia, the user interface of Firefox OS, has a similar structure to comparable operating systems for mobile devices such as Apple iOS , Android or Microsoft Windows Phone . In addition to conventional applications such as telephone , messages , contacts and the in-house browser Firefox , information about the battery level , time and GPS is also displayed. In addition, various app groups such as games , music , films , weather , television , news , sports and shopping can also be accessed via the integrated everything.me website .
Unlike Android, every app can be found on the home screen. The user can change the arrangement of the apps on this screen.
A short glimpse of Firefox OS in operation on a demonstration device (850 MHz processor and 256 MB RAM) is given by a video that was filmed at the Consumer Electronics Show 2013 in Las Vegas.
Versions
Version designations with two dots indicate security updates, and what follows a possible third dot is up to each OEM .
At the development stage functionally complete , English functional complete or feature complete , the supplier of the chipset takes over .
| version | functionally complete | Code freeze | Published on | release | Code name | API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | December 22, 2012 | January 2013 | February 21, 2013 | TEF | Gecko 18 | |
| 1.0.1 | January 15, 2013 | May 2013 | September 6, 2013 | 2nd of July 2013 | Shira | Gecko 18 |
| 1.1 | March 29, 2013 | July 2013 | October 9, 2013 | 21st October 2013 | Leo | Gecko 18+ |
| 1.2 | 15th September 2013 | December 9, 2013 | December 10, 2013 | December 9, 2013 | Koi | Gecko 26 |
| 1.3 | December 9, 2013 | May 8, 2014 | 17th March 2014 | Gecko 28 | ||
| 1.4 | April 25, 2014 | August 8, 2014 | Gecko 30 | |||
| 2.0 | July 21, 2014 | 2014 | Gecko 32 | |||
| 2.1 | October 13, 2014 | Gecko 34 | ||||
| 2.2 | April 6, 2015 | April 29, 2015 | Gecko 37 | |||
| 2.5 | not completed | Gecko 43 | ||||
| 2.6 | not completed |
Web links
- Firefox OS home page on Mozilla Foundation
- Project page in MozillaWiki
- Source code on GitHub
- Overview of the different Firefox OS versions of congstar
Individual evidence
- ↑ mozilla.org
- ↑ github.com
- ↑ Mozilla Is Making an Android-Based Mobile OS. In: Gizmodo . July 26, 2011, accessed September 11, 2012 .
- ↑ a b c Official website with all Firefox OS versions Firefox OS versions at a glance, accessed on June 8, 2016.
- ^ B2G / Architecture - Mozilla Wiki.
- ^ B2G OS Mozilla Foundation in developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- ↑ Falk Hedemann: Boot to Gecko: Mozilla's answer to Chrome OS. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine . July 26, 2011, archived from the original on September 14, 2012 ; Retrieved September 11, 2012 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Jens Ihlenfeld: Mozilla announces Firefox OS. In: golem.de . July 2, 2012, accessed September 11, 2012 .
- ↑ Mozilla's smartphone operating system Boot to Gecko in detail. In: golem.de. March 2, 2012, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ^ Mozilla's browser OS gets partners and a name: Firefox OS. In: CNET . July 2, 2012, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ Download nightlies of Firefox OS, get your own hands-on. In: engadget. AOL , July 19, 2012, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ Lars Budde: Firefox OS: New video of the upcoming mobile OS alternative. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine. September 11, 2012, archived from the original on September 13, 2012 ; Retrieved September 11, 2012 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Addon shows Firefox OS. golem.de, November 16, 2012, accessed on January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ Version history of Firefox OS Simulator ( Memento of the original from January 23, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. - Mozilla addons page ; As of July 22, 2013
- ↑ Firefox OS Simulator. In: Mozilla Developer Network. December 27, 2013, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ Firefox OS: Mozilla developer shows the new OS and first devices in hands-on [MWC 2013]. (No longer available online.) T3n, February 28, 2013, archived from the original on March 4, 2013 ; Retrieved March 17, 2013 (original website no longer available).
- ↑ Firefox OS dev units coming to Geeksphone next week: Keon and Peak priced from € 91. In: engadget. AOL, April 18, 2013, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ UPDATED - Developers Race To Buy First Firefox OS Phones. In: forbes.com . April 23, 2013, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ The fox begins the hunt. In: Technology Review . Heise Zeitschriften Verlag , August 28, 2013, accessed on January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ ZTE Open, the first Firefox OS phone for consumers, launches tomorrow for $ 90. In: engadget. AOL, July 1, 2013, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ European start for Firefox OS smartphone at Deutsche Telekom. Deutsche Telekom AG, July 11, 2013, accessed on July 11, 2013 .
- ↑ Premiere for Firefox OS. Die Welt , October 15, 2013, accessed on January 14, 2014 .
- ↑ LG launches its first Firefox OS phone. In: ZDNet . October 24, 2013, accessed January 14, 2014 .
- ^ Ari Jaaksi: Firefox OS Pivot to Connected Devices. Posted on December 9, 2015 on Mozilla blog, accessed December 11, 2015.
- ↑ Sören Hentzschel: Firefox OS: Focus on IoT and Connected Devices, no longer on smartphones. Published December 8, 2015, accessed December 11, 2015.
- ↑ computerbild.de
- ↑ chip.de
- ↑ a b Jo Bager: Final end for Firefox OS. In: heise online. February 3, 2017, accessed June 8, 2019 .
- ↑ Tobias Költzsch: For the next billion users: Google is investing in the KaiOS mobile phone operating system. In: t3n News. June 28, 2018, accessed July 3, 2018 .
- ↑ Yang Wang: The Birth of the Smart Feature Phone Revolution. In: kaiostech.com. March 20, 2019, accessed June 8, 2019 .
- ↑ Daniel Herbig: Google is investing 22 million dollars in the mobile operating system KaiOS. In: heise online. June 28, 2018, accessed June 8, 2019 .
- ↑ T3 Smackdown: Sony KD-65ZD9 vs LD OLED65E6 vs Panasonic TX58DX802B. Retrieved May 13, 2020 .
- ↑ Stephen Shankland: Startup picks up the torch for troubled Firefox OS. December 10, 2015, accessed December 12, 2015 .
- ↑ Josh Horwitz: Ex-Mozilla employees are teaming up with the Chinese government to kill Android. July 16, 2015, accessed December 12, 2015 .
- ^ The Firefox OS platform. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on December 24, 2013 ; Retrieved December 23, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Gaia. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on February 10, 2014 ; Retrieved December 23, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Gonk. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on December 24, 2013 ; Retrieved December 23, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b B2G / Architecture. (No longer available online.) In: MozillaWiki. Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on June 4, 2014 ; accessed on February 21, 2014 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ wiki.mozilla.org
- ↑ Firefox OS application development. Mozilla Foundation, accessed December 23, 2013 .
- ↑ w3.org
- ↑ Ragni Zlotos: Mozilla: Boot2Gecko becomes Firefox OS. In: heise online . July 2, 2012, accessed on December 23, 2012 : "Mozilla wants to submit to the W3C for standardization"
- ↑ Kim Rixecker: Web Apps for Firefox OS - This is what you can expect. (No longer available online.) In: t3n magazine. July 11, 2013, archived from the original on July 15, 2013 ; Retrieved July 13, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Firefox OS at CES 2013 (video)
- ↑ a b Firefox OS 1.1 Notes. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on January 20, 2014 ; accessed on January 10, 2014 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Versions and Scheduling. In: Release Management / B2G Landing. MozillaWiki, December 16, 2013, accessed January 10, 2014 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Feature Complete (FC) dates. In: B2G / Roadmap. MozillaWiki, December 20, 2013, accessed January 10, 2014 .
- ↑ Index of /pub/mozilla.org/b2g/manifests/nightly. (No longer available online.) Mozilla FTP server, archived from the original on September 27, 2013 ; Retrieved September 10, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Firefox OS 1.0.1 Notes. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on December 4, 2014 ; accessed on March 16, 2015 : "First offered to partners for release on July 2, 2013" Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Firefox 26 for developers. Retrieved March 7, 2018 (American English).
- ↑ Firefox OS 1.2 Notes. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on January 11, 2014 ; accessed on January 10, 2014 : "First offered to partners for release on December 9, 2013" Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ blog.mozilla.org
- ↑ Firefox OS 1.3 Notes. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on March 4, 2015 ; accessed on March 16, 2015 : "First offered to partners for release on March 17, 2014" Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Firefox OS 1.4 Notes. (No longer available online.) Mozilla Foundation, archived from the original on December 4, 2014 ; accessed on March 16, 2015 : "First offered to partners for release on August 8, 2014" Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Fire E: Alcatel One Touch distributes Firefox OS 2.0 and Firefox Hello. Sören Hentzschel, December 25, 2014, accessed on March 16, 2015 .