Ili (river)
|
Ili Іле (İle), Или, 伊犁河 (Yili He), ئىلى دەرياسى (Ili Dəryasi), Chüngges |
||
|
Course of the Ili |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
Xinjiang ( PR China ), Almaty ( Kazakhstan ) |
|
| River system | Ili | |
| Confluence of |
Künes and Tekes 43 ° 34 ′ 45 " N , 82 ° 32 ′ 51" E |
|
| muzzle |
Lake Balkhash coordinates: 45 ° 24 ′ 0 ″ N , 74 ° 8 ′ 0 ″ E 45 ° 24 ′ 0 ″ N , 74 ° 8 ′ 0 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height |
340 m
|
|
| length | 1001 km (with source river Tekes 1439 km) | |
| Catchment area | 140,000 km² | |
| Outflow location: 270 km above the mouth |
MQ |
479 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Qaskeleng , Talghar , Schilik , Scharyn , Kürti | |
| Right tributaries | Kax , Qorghas , Össek | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Qapshaghai Reservoir | |
| Big cities | Gulja | |
| Medium-sized cities | Qapshaghai | |
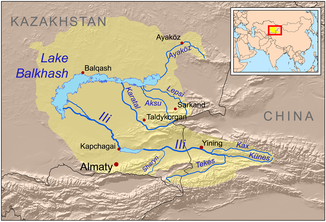
The Ili ( Kazakh Іле (İle), Chinese 伊犁河 , Pinyin Yīlí Hé , Uighur ئىلى دەرياسى Ili Dəryasi , Russian Или ; also Chüngges ) is a 1001 km long river in China and Kazakhstan ( Central Asia ). With the left source river Tekes ( Tekes He ) it is 1439 km long.
course
The Ili arises on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains in the Uyghur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang in the northwest of the People's Republic of China at the confluence of its two source rivers, the Tekes from the left and the Künes from the right. The source of the Künes lies between the Narat ( Khaliq tau ) and Irenchabirga ( Ereen Chabarg ) mountain ranges , which rise up to 5500 m . From there, the water-rich Künes flows in a westerly direction through an ever-widening high mountain valley, passing the Ili Mountains rising to the south , another part of the Tianshan. Then the Künes unites with the 438 km long Tekes coming from the south to the Ili.
Then the Kax meets the Ili from the north. A little later, its water reaches the Chinese city of Gulja , the capital of the Kazakh Autonomous District Ili (in China). Further to the west, the Ili crosses the border with Kazakhstan. Shortly after the border, it forms the southern border of the Altyn-Emel National Park in sections . To the north of the former Kazakh capital Almaty , which the Ili passes in this direction about 70 km away, it flows through the Qapschaghai reservoir (area 1847 km²; content 28.10 km³), which withdraws plenty of water for irrigation purposes and for drinking water supply.
Regardless of this, the Ili still flows with a relatively large amount of water through the Siebenstromland in a north-westerly direction through a desert steppe , but then still loses plenty of water through evaporation and flows into the outflowless Lake Balkhash via an extensive, species-rich delta . Its size has decreased (and continues to decrease) for several years due to the increasing water abstraction in China and Kazakhstan.
River length
The Ili, as mentioned above, initially called Künges , is 1,001 km long from the confluence of the 438 km long Tekes to its confluence with Lake Balkhash. From the source of the Tekes, one of its left tributaries, the water travels 1,439 km. Within Kazakhstan, the flow distance of the Ili is according to various sources of 815 and 768 km.
Ili Delta
The Ili flows into Lake Balkhash in the southwest, where it forms an approximately 8000 square kilometers (km²) delta. A possible settlement of the tiger is currently being examined in the delta of the Ili , which occurred there until at least 1948 in the form of the Caspian tiger . Since this subspecies has been completely eradicated, the introduction of the closely related Siberian tiger is being considered . In the area of the Ili Delta there are large populations of wild boars and gazelles , as well as some deer. A smaller population of saiga antelope also lives in the area of the Saryesik-Atyrau desert east of the delta . In contrast, the Bukhara deer and the Asiatic half- ass have been exterminated as further potential prey. These species would also be reintroduced. The vegetation of the delta consists of river forests, which are mainly formed by olive willows , willows and poplars , as well as high grass and reed areas, which are interrupted by dunes, steppes and bush areas. Semi-desert areas dominate around the delta.
The delta is sparsely populated and is mainly used for animal breeding and fishing. The only major settlement in the delta is Kuigan .
An area of 9766 km² in the area of the delta was declared a Ramsar area . This is home to 427 plant and 345 animal species, including important populations of rare species such as the Dalmatian pelican , goiter gazelle , marbled polecat , white-headed duck , red-breasted goose and bastard sturgeon . The Kazakh government plans to create a national park from three reserves, the Balkash, the Karoy and the Kukan reserves, which are located in the delta.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Article Ili in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ^ Richard Stone: For China and Kazakhstan, No Meeting of the Minds on Water. In: Science . Volume 337, No. 6093, 2012, pp. 405-407, doi: 10.1126 / science.337.6093.405
- ↑ Hartmut Jungius (2010). Feasibility Study on the Possible Restoration of the Caspian Tiger in Central Asia ( Memento of the original from November 17, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. . WWF
- ↑ Masha Vinokurova (Press officer), Olga Pereladova (Head of the WWF Central Asia Program): Kazakhstan names large inland delta , WWF Information February, 2012