Throat cancer
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| C32 | Malignant neoplasm of the larynx |
| C32.0 | glottis
|
| C32.1 | Supraglottis (above the vocal apparatus)
The larynx does not include:
|
| C32.2 | Subglottis (below the vocal apparatus) |
| C32.3 | Laryngeal cartilage |
| C32.8 | Larynx, overlapping several parts |
| C32.9 | Larynx, unspecified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Larynx cancer ( synonyms laryngeal cancer , laryngeal tumor , larynx tumor ) is a cancer of the larynx . It is one of the most common malignant (malignant) tumors in the neck area. Mostly it is a squamous cell carcinoma .
frequency
Larynx cancer predominantly affects men between the ages of 50 and 70. Men are 5 times more likely to be affected than women. Statistically speaking, around 3,600 men and 500 women fall ill in the Federal Republic of Germany every year. The proportion of women smokers has now risen sharply. It is the third most common type of cancer in the head and neck area. More than half of the tumors in the head and neck area are already locally advanced at the time of the initial diagnosis and, according to the DGHNO-KHC, require complex interdisciplinary therapy procedures. Overall, larynx cancer is one of the rarer forms of cancer in terms of mortality : 1.5% of male cancer deaths and less than 1% of female cancer deaths had larynx cancer.
Forms and symptoms
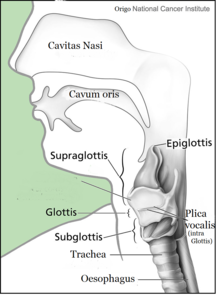
Cavitas nasi: nasal cavity
Cavis orum: oral cavity
Glottis: larynx
Plica vocalis: vocal
fold Trachea: trachea
Esophagus: esophagus
90% of the larynx carcinomas are so-called squamous cell carcinomas . Depending on the localization, a distinction is made between different forms:
- Glottic carcinoma (vocal cord cancer)
- Tumor in the area of the vocal folds and the back wall of the larynx. The most common symptom is persistent hoarseness and possible shortness of breath (medical dyspnea ).
- Supraglottic laryngeal cancer
- Tumor in the area of the epiglottis (medical epiglottis ) and the pocket near the vocal cords (medical Morgagni ventricle ); Symptoms also include hoarseness, a rough voice, and a feeling of pressure in the throat. Possible spread of cancer cells (medical metastasis ) into the surrounding lymph nodes . The medical prognosis is worse than with glottic cancer due to early metastasis and later symptoms.
- Subglottic laryngeal cancer
- Tumor below the vocal folds. Very rare form.
- Transglottic laryngeal cancer
- Tumor that spreads over the entire larynx.
As glottis ( Latin origin. Glottis vocalis ) refers to the entire human vocal tract consisting of vocal cords and glottis . 2/3 are glottic carcinomas, 1/3 are supraglottic carcinomas, rarely sub- and transglottic carcinomas.
Causes and Risk Factors
Larynx cancer usually develops due to previous damage to the larynx, a so-called precancerous condition . Dysplasia , leukoplakia and carcinoma in situ are considered to be precancerous .
Tobacco smoking and alcohol abuse are given as the most frequent causes .
Other causes can be viruses and environmental toxins such as asbestos .
It is assumed that infections with HPV viruses caused by oral sex can also be a trigger for precancerous diseases. Hereditary predisposition can favor the disease.
treatment
diagnosis
- Diagnostic procedures
The diagnosis is made by palpation, a laryngoscopy , a tissue examination ( biopsy ), otherwise by computer tomography , magnetic resonance tomography and ultrasound examinations . The result is classified according to the TNM classification and discussed at the tumor conference in order to find the appropriate therapy taking into account the anamnesis and the current physical and psychological condition of the patient .
- Synchronous tumors
Synchronous tumors occur in about 10 percent of patients.
- Differential diagnoses
Differential diagnoses are larynx TBC , larynx syphilis , larynx paralysis, or benign tumors of the larynx.
therapy
Depending on the location and size of the tumor, surgery , radiation therapy - which requires accompanying measures such as the creation of a PEG , tracheostoma and tooth removal , chemotherapy , which requires the creation of a port , and combination therapy - are possible .
surgery
The choice of surgical method depends on the extent of the tumor and the available methods.
- Laser surgical operation
The laser surgical operation is micro-invasive. The tumor is cut out.
- Conventional surgical operation
An operation on the larynx, which may involve surgically removing parts of the larynx or the entire larynx, is another method. However, the removal of the entire larynx ( laryngectomy ) has significant consequences for the patient: In addition to the loss of the voice, the separation of the air and food ducts results in encrustations of the nasal mucosa, which leads to odor disorders. There are some voting replacement procedures. An esophageal replacement language can be learned through training with the help of a speech therapist and there are electronic speech aids ( voice prostheses ). The neck dissection , in advanced disease an extended operation included clearing out the lymph nodes and the surrounding soft tissue is usually the method of choice, because often metastases occur in the lymph nodes of the neck region. A PET / CT examination , which can detect hidden cancer foci in the body, partially spares patients neck dissection.
- Artificial larynx
The implantation of an artificial larynx is in the experimental stage. There were attempts to do this as early as 1869 ( Czermak ). Research is being carried out into replacing the vocal cords with tissue engineering .
radiotherapy
X- rays are used in radiation therapy, the use of heavy ion therapy is being studied.
Radiation therapy for cancer of the larynx requires the creation of a tracheostoma and a PEG as well as dental restoration as preparation. and a mouthguard . An individual mask is made for the irradiation, which is used to fix the area to be irradiated during the irradiation. The irradiation takes place according to the results of a planning CT. With radiation therapy, the risk of secondary tumors should be considered.
Combination therapy
If radiation therapy is combined with chemotherapy, a port is also required.
Combination therapy for larynx cancer is usually carried out gradually. It is first checked whether the tumor is responding to chemotherapy. Thereafter, in-patient chemotherapy and radiation therapy for one week, four-week radiation therapy and finally again in-patient chemotherapy and radiation therapy for one week are carried out.
chemotherapy
A chemotherapy is selected for distant metastases.
Antibody therapy is a special type of chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy and for relapses .
Palliative treatment
Chemotherapy is usually used as palliative treatment .
Alternative medicine and complementary medicine
40 to 50 percent of all cancer patients in Germany use complementary or alternative therapy options.
- Complementary medicine
The complementary medicine as a naturopathic adjuvant treatment of cancer is also found in the field of scientific medicine ,
- Alternative medicine
The alternative medicine is strictly distinguished from complementary medicine and rejected because for most popular method verifiable data is missing or insufficient data to be able to really judge a therapy.
Accompanying tasks
Since the disease can cause trauma , psycho-oncological support for the patient and their relatives is necessary. This support can take place on an inpatient or outpatient basis.
forecast
The Saarland Cancer Register gives a five-year survival rate of 65.4% for men (i.e. after five years 34.6% of the patients have died). In women, the five-year survival rate is 75.8%. The prognosis depends on the location and stage of the larynx cancer as well as the causation. Different numbers are given for combination therapy ,
aftermath
The after-effects depend on the type of therapy used and the respective patient.
- Operative therapy
Speech therapy is often required , especially after laryngectomy .
- chemotherapy
The after-effects of chemotherapy depend on the choice of chemotherapeutic agent and its side effects .
- radiotherapy
The after-effects of radiation therapy are late reactions such as scarring in the connective tissue, discoloration of the skin, hardening in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, dry mouth, loss of taste, bone and tooth damage.
- psyche
In patients after partial resection of the larynx - in addition to the immediate consequences - a fear of a relapse and a fear of progression is found.
In particular after a larynxectomy, the impairment of the possibilities for social communication creates stress.
Aftercare
As with all tumor diseases , follow-up care is required. The patient is examined every one to three months in the first two years, every six months in the third and fourth year, and then annually thereafter, and the accompanying measures are terminated, whereby side effects of the radiation, such as wound healing disorders , must be observed.
Self-help groups have been set up for people who have had their larynx removed in whole or in part, or who have been treated for a throat or larynx cancer disease. They also look after relatives .
Remarks
- ↑ CT also increases the risk of tumors (see following reference).
See also
literature
- Adel K. El-Naggar, John KC Chan, Jennifer R. Grandis (Eds.): WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours (World Health Organization Classification of Tumors) . 4th edition. WHO, 2017, ISBN 978-92-832-2438-9 (English).
- Working group of the scientific medical societies (ed.): S3-guideline diagnostics, therapy and aftercare of laryngeal cancer . January 2019 ( awmf.org [PDF; accessed on August 4, 2019]).
Web links
Videos
- Doctor's Message is Still Heard Despite Losing Vocal Cords To Throat Cancer on YouTube in English
- Radiation Treatment - Head and Throat Cancer on YouTube in English
- Michael Douglas Speaks About His Battle With Cancer at the 2014 AHNS and IFHNOS Meeting on YouTube in English
Other web links
- Throat and larynx cancer brochure. (PDF) German Cancer Aid Foundation , accessed on March 8, 2019 .
- Fedor Singer: Health guide on the topic of throat cancer: What is throat cancer? GFMK , accessed March 8, 2019 .
- Malignant diseases of the head and neck area. Heidelberg University Hospital , accessed on March 8, 2019 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Blaue_Ratgeber (PDF) German Cancer Aid.
- ↑ What is throat cancer and what causes it? Techniker Krankenkasse , accessed on March 8, 2019 .
- ↑ Larynx cancer ( Memento of the original from May 22, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , University Hospital Marburg.
- ↑ Jana-Teresa Stratmann: Investigation of the expression of cellular markers in metastatic head and neck cancer in the primary tumor and in the metastases . Ed .: University of Würzburg. Würzburg February 28, 2013 ( uni-wuerzburg.de [PDF]).
- ↑ C. Wittekindt, S. Wagner, S. Mayer, JP Klußmann: Fundamentals of Tumor Development and the Significance of Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) in Head and Neck Cancer . In: Laryngo-Rhino-Otology . Thieme, 2012, p. 1–26 , doi : 10.1055 / s-0031-1297241 ( thieme-connect.de [PDF]).
- ↑ Springer (Ed.): Die Onkologie . Berlin, Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-540-79724-1 , Tumors in the head and neck area, p. 1300-1334 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-540-79725-8_64 .
- ↑ Madiha Mahfoudhi, Khaled Khamassi, Sami Turki, Adel Kheder: Difficulté diagnostique d'une tuberculose laryngée isolée chez une femme diabétique ., June 9, 2015, PMC 4546710 (free full text), doi: 10.11604 / pamj.2015.21.106.6361 (French )
- ^ VE Negus: Differential Diagnosis of intrinsic Carcinoma of the Larynx . doi : 10.1001 / archotol.1939.00650050243002 (English, jamanetwork.com ).
- ↑ Larynx cancer - causes, symptoms and diagnosis of larynx cancer or malignant larynx tumor. WakeUp Media, accessed April 19, 2019 .
- ↑ Malignancies in the head and neck area. University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, accessed April 9, 2019 .
- ↑ Radiation and chemotherapy are safe alternatives to surgery in throat cancer. Image of Science , August 13, 2002, accessed March 8, 2019 .
- ↑ New approaches to the therapy of throat cancer in Leipzig. Retrieved April 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Petra Busch: First have a look: In head and neck tumors, neck dissection can often be avoided with PET / CT. June 2, 2016, accessed March 30, 2019 .
- ↑ First implantation of an artificial larynx. Retrieved April 16, 2019 .
- ^ Prosthetic voice rehabilitation after total larynx removal - a historical treatise since Billroth (1873). Retrieved April 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Mike Orcutt: The vocal cord grafts are coming. Heise online , December 30, 2015, accessed June 16, 2019 .
- ↑ UW Researchers bioengineer vocal cord tissue that transmits soound. University of Wisconsin – Madison , accessed June 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Deutsche Krebshilfe (Ed.): Pharynx and larynx cancer . S. 21 ( dkfz.de [PDF]).
- ↑ Proton therapy and heavy ion therapy - high-precision treatment against cancer. Retrieved May 9, 2019 .
- ↑ Venkatesh S. Anehosur, first Pallavi Karadiguddi, Vajendra K Joshi, Basavraj C. Lakkundi, R. Ghosh, Gopalkrishnan Krishnan: [ PMC 5483806 (free full text) Elective tracheostomy in Head and Neck Surgery: Our Experience .] In: Clinical Diagnostic Research . May 11, 2017. doi : 10.7860 / JCDR / 2017 / 24117.9854 .
- ↑ Consultation version of the S3 guideline for diagnosis, therapy and follow-up care of laryngeal cancer long version 0.1 (consultation version). (PDF) June 2018, accessed April 13, 2019 .
- ^ Radiation Treatment - Head and Throat Cancer. Retrieved April 13, 2019 .
- ^ Bradley A. Schiff: Larynx Cancer. Retrieved April 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Cancer risk in 680,000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: data linkage study of 11 million Australians . PMC 3660619 (free full text) (English)
- ↑ Larynx Tumors - Alternatives to Surgery. Retrieved April 16, 2018 .
- ↑ Larynx cancer. Retrieved April 16, 2019 .
- ↑ Federal Association of Larynx Surgeons (ed.): Larynx cancer . 5th edition. 2013, p. 29 ( larynx-surgery-bv.de [PDF]).
- ↑ a b Complementary Medicine in Cancer - Possibilities and Limits. Retrieved May 10, 2019 .
- ↑ cancers. Immanuel Hospital Berlin , accessed on May 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Alternative and Complementary Methods in Cancer Therapy: An Overview. Cancer Information Service, German Cancer Research Center, 2019, accessed on May 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Cancer and the psyche: Courage to survive. Association for Independent Health Advice , accessed on May 29, 2019 .
- ^ Diagnosis of cancer - psychological help for patients and relatives. test (magazine), March 4, 2016, accessed May 10, 2019 .
- ↑ Cancer of the throat and larynx . In: Deutsche Krebshilfe (ed.): Blue advice . ( krebshilfe.de [PDF]): "The prognosis with HPV involvement is often better than without HPV"
- ↑ Radiation and chemotherapy are safe alternatives to surgery in throat cancer. Wissenschaft.de, accessed on March 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Susanne Heinzl: Larynx carcinoma: With whom can the voice be preserved? New score improves personalized therapy. Medscape, February 14, 2017, accessed March 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Peter Dicks, Ulla Manter: Laryngectomy. Retrieved May 11, 2019 .
- ↑ Side effects of chemotherapy. German Cancer Society , May 10, 2019, accessed on May 11, 2019 .
- ↑ Risks and side effects. Lüneburg Municipal Hospital , accessed on May 11, 2019 .
- ^ Maurus Johannes Asen: fear of progression after partial resection of the larynx. University of Leipzig, August 15, 2017, accessed on March 29, 2019 .
- ↑ Life after Total Laryngectomy. (PDF) Atos medical, accessed on May 11, 2019 .
- ^ Laryngeal cancer guideline. 2019, accessed March 30, 2019 .
- ↑ Norbert Schwenzer (Ed.): Special surgery . Thieme, 2002, ISBN 978-3-13-593503-4 , p. 118 .
- ^ Federal Association of Larynx Surgeons. Retrieved March 30, 2019 .