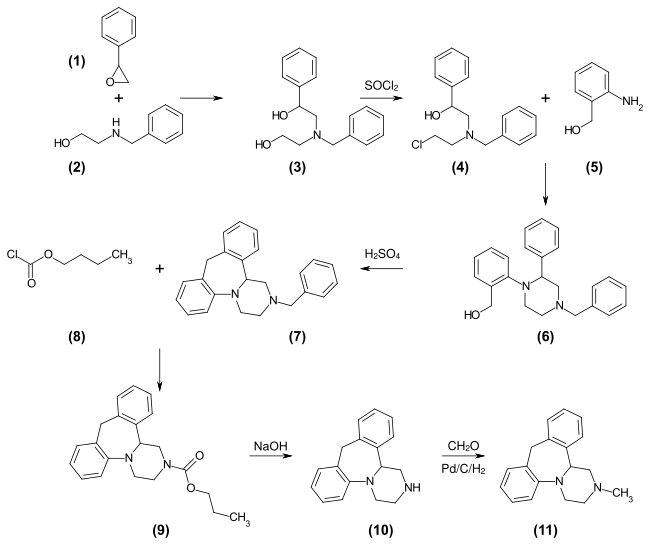
Mianserin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) -isomer (top) and ( S ) -isomer (bottom) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Mianserin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
( RS ) -2-methyl-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydrodibenzo [ c, f ] pyrazino [1,2- a ] azepine |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 20 N 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 264.36 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
282–284 ° C (mianserin hydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Mianserin is - like the analogue mirtazapine - a drug from the group of tetracyclic antidepressants .
history
While the older tetracyclic substances - apart from mianserin itself v. a. nor the maprotiline - compared to the tricyclics, did not represent any notable progress in tolerability and efficiency, the newer mianserin variant mirtazapine was described as a representative of its own type of action ( NaSSA ). The very similar looking Mianserin now also belongs to this group. Mianserin was patented by Organon in 1967 and was approved as Tolvin in Germany in 1975 and as Tolvon in Switzerland and Austria . There are numerous generic drugs .
effect
The effect of mianserin is initially mostly depressant. The indications largely correspond to those of the tricyclic antidepressants of the imipramine type. The mean daily dose is 30–90 mg. Because of the possible harmful effects, the blood count should be checked regularly while taking it. The half-life of mianserin is 17 hours. In the event of flu-like symptoms (see agranulocytosis ), the drug should be discontinued immediately .
In an experiment in which a large number of substances were tested for life-prolonging effects on roundworms, mianserin was noticed.
Contraindications and warnings
In contrast to other antidepressants, mianserin is not suitable for treating neuropathic pain. The vegetative side effects are somewhat less pronounced than with most tricyclics, but mianserin has a risk of life-threatening disorders ( blood formation disorders , including agranulocytosis ; further bone marrow damage), which means that it is usually not one of the first-line drugs for depression .
chemistry
Stereoisomerism
Mianserin is used as a racemate [1: 1 mixture of the ( S ) form and the ( R ) form], although the ( S ) form is the more pharmacologically active one. A racemate resolution using (+) - or (-) - p -ditoluoyltartaric acid is described.
synthesis
An overview of the synthesis of mianserin is described in a reference work. Several synthesis options were also proposed when the Organon company first registered. Two strategies for the construction of the tricyclic dibenzoazepine have established themselves and are used:
Structure of the 7-ring from 2-benzylaniline
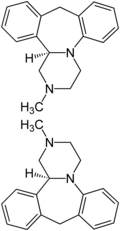
The route via 2-benzylaniline (1) was followed by the inventor and is also cited in the older literature. The dibenzoazepine is built up via an imide chloride (4) from the corresponding chloroacetanilide (3) with phosphorus oxychloride . The piperazine ring of the tetracyclic ring system of mianserin is closed from the 1,2- diamine (5) formed by reaction with methylamine by means of diethyl oxalate (6) and subsequent reduction of the piperazinedione intermediate (7) with diborane to give the target molecule (8). This complex but selective piperazine synthesis is still used.
As an alternative, the piperazine ring can be built up using highly canerogenic 1,2-dibromoethane . 2-Benzylaniline is also the starting material for the chiral synthesis of mianserin, which was published in 2015. Instead of methylamine, phthalimide is used and the dibenzazepine obtained is chirally hydrogenated .
Structure of the 7-ring by introducing the methylene group
This possibility of building up the 7-ring using 2-aminobenzyl alcohol is described in the more recent patent literature. As early as 1975, Akzo , who was Organon's parent company until 2007 , registered a process in which the 7-ring was built up using 2-aminobenzyl alcohol (5). In just four stages, mianserin is converted into intermediate stage (4) by reaction of styrene oxide (1) with N -methylaminoethanol (2), after subsequent chlorination, reaction with 2-aminobenzyl alcohol (5) to form diphenylpiperazine intermediate stage (6) and ring closure with polyphosphoric acid to form Mianserin (7) synthesized.
Synthesis of mianserin from styrene oxide (without protecting groups)
In 1994 this route was used again with small changes, the complex reaction mixture making it necessary to work up the final stage by chromatography . Because of this fact, a process with protective group technology was registered in 1993 , which starts analogously to the previous route, but with benzylaminoethanol (2) and provides for the purification of the intermediate stages via salt formation. The debenzylation of the intermediate of the formula (7) succeeds with chloroformic acid n-butyl ester (8) to give the carbamate of the formula (9), which is saponified to the nor-mianserin (10). In the last step, a reductive methylation takes place, whereby a purer product (11) than with the direct route is obtained. Despite the larger number of intermediate stages, this route with a Leuckart-Wallach reaction to the final stage Mianserin is apparently still chosen in the Far East.
Synthesis of mianserin from styrene oxide (with protecting groups)
In 1990, another process was registered in which the carcinogenic starting material styrene oxide is replaced by 2-chloro-2-phenylacetyl chloride, which, after an analogous reaction with an N -methylamine, delivers the corresponding amide , but which then only becomes the equivalent building block after subsequent reduction Phenylaminoethanol results.
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index : An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals . 14th edition. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station NJ 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , p. 1064.
- ↑ a b Mianserin hydrochloride data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 10, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on Mianserin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Patent DE 1 695 556 (1967) ; Willem Jacob van der Burg; Jaques Delobelle (ORGANON); Process for the preparation of piperazine derivatives.
- ^ Volkhard Kurowski: Intoxications. In: Jörg Braun, Roland Preuss (Ed.): Clinic Guide Intensive Care Medicine. 9th edition. Elsevier, Munich 2016, ISBN 978-3-437-23763-8 , pp. 673-706, here: p. 684 ( tetracyclic antidepressants ).
- ↑ M. Petrascheck et al .: An antidepressant that extends lifespan in adult Caenorhabditis elegans. In: Nature , Volume 450, 2007, pp. 553-556, PMID 18033297 , doi: 10.1038 / nature05991 .
- ↑ RMPinder, AML Van Delft: The Potential Therapeutic Role of the Enantiomers And Metabolites Of Mianserin . In: Br.J.clin.Pharmac. , 15, 269S (1983), PMC 1427891 (free full text)
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for p-ditoluoyltartaric acid : CAS number: 32634-66-5, EC number: 251-131-7, ECHA InfoCard: 100.046.468 , PubChem : 3037000 , ChemSpider : 87601 , Wikidata : Q72469493 .
- ↑ Patent WO 99 16 769 ; Jackson Roy William, Subasinghe Kamani Rupika (Monash University, Australia; Polychip Pharmaceuticals Pty. Ltd.); Resolution of optically active compounds.
- ^ Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher, Dietmar Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances . 4th edition. 2 volumes. Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for 2-benzylaniline : CAS number: 28059-64-5, EC number: 248-806-3, ECHA InfoCard: 100.044.355 , PubChem : 119805 , ChemSpider : 106974 , Wikidata : Q72440687 .
- ^ WJ Van der Burg, IL Bonta, J Delobelle, C Ramon, B Vargaftig: Novel type of substituted piperazine with high antiserotonin potency . In: J.Med.Chem. , 13, 1970, 35, doi : 10.1021 / jm00295a010
- ↑ Hulinska Hana, Polivka Zdenek, Jilek Jiri et al .: Experimental antiulcer agents: N-substituted 2- (4-methyl-1-piperazinyl) acetamides as pirenzepine models and some related compounds . In: Collect.Czech.Chem.Commun. , 53, 1988, 1820. cccc.uochb.cas.cz Chem. Abstr. 1989: 439 321
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,217,452 (1980) ; Olivie Jacques (Akzono); Synthesis for the preparation of tetracyclic compounds.
- ↑ Piotr Roszkowski, Jan. K. Maurin, Zbigniew Czarnocki: The enantioselective synthesis of (S) - (+) - mianserin and (S) - (+) - epinastine . In: Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry , 11, 2015, 1509, beilstein-journals.org
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for 2-aminobenzyl alcohol: CAS number: 5344-90-1, EC number: 226-293-7, ECHA InfoCard: 100.023.903 , PubChem : 21439 , ChemSpider : 20149 , DrugBank : DB03058 , Wikidata : Q27094019 .
- ↑ Patent DE 2,505,239 (1975) ; Olivie Jaques (AKZO NV Neth); Process for making tetracyclic compounds.
- ↑ Patent PL 175 287 (1998) ; Lypacewicz Maria K, Poslinska-bucewka Halina, Smolinska Jadwiga et al. (Instytut Farmaceutyczny, Warszawa); Preparation of 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methyldibenzo [c, f] pyrazino [1,2-a] azepine .; Chem. Abstr. 130, 296 698 (1999).
- ↑ Patent DE 4 305 659 (1993) ; Kisielowski-Ruppert, Lothar; Mörsdorf, Johann Peter; Grafe, Ingomar; Ahrens, Kurt-Henning (HEUMANN Pharma GmbH & Co); Process for the preparation of 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methyl-dibenzo [c, f] -pyrazino [1,2-a] azepine and its salts.
- ↑ Patent CN 101 544 644 (2009) ; Zhao, Zhenqiao. (Shandong Renhetang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Peop. Rep. China); Process for preparation of mianserin hydrochloride .; Chem. Abstr. 2009: 1,216,535.
- ↑ Patent CH 678 623 (1990) ; Haider Akhtar, Bollinger Heinrich, Fischer Alan (SA SOCHINAZ, Switz.); Procédé de Preparation d'un composé tetracyclique.